SSC CGL - Detailed Guide 2025
Self-Paced Course

Foreign Trade and International Organisations
Reference: Lucent GK, NCERT Class 6–12
1. India's Foreign Trade – Imports/Exports Composition
Key Points:
- India follows a mixed economy model with liberalized trade policies post-1991.
- Trade is managed by the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- India's foreign trade accounts for ~40% of GDP (2023 estimate).
Export Composition (Major Items):
| Category | Products |
|---|---|
| Petroleum Products | Refined petrol, diesel |
| Engineering Goods | Machines, tools, auto components |
| Gems and Jewellery | Diamonds, gold jewellery |
| Textiles and Apparel | Cotton, readymade garments |
| Chemicals & Pharmaceuticals | Generic drugs, fertilizers |
| Agricultural Products | Basmati rice, tea, spices, marine items |
Import Composition (Major Items):
| Category | Products |
|---|---|
| Crude Oil & Petroleum | Largest import |
| Gold and Precious Stones | For consumption and re-export (jewellery) |
| Electronics | Mobiles, semiconductors |
| Machinery | Industrial equipment |
| Chemicals & Fertilizers | Raw materials for industries |
| Coal and Natural Gas | For power and industrial use |
Major Trade Partners:
Exports:
- USA
- UAE
- Netherlands
- Bangladesh
Imports:
- China
- USA
- UAE
- Saudi Arabia
2. Balance of Payments (BoP) and Trade Deficit
Balance of Payments (BoP):
- A statement that records all economic transactions between India and the rest of the world.
| BoP Account | Components |
|---|---|
| Current Account | Trade of goods/services, transfers, income |
| Capital Account | FDI, FII, ECBs, loans, NRI deposits |
Managed by RBI.
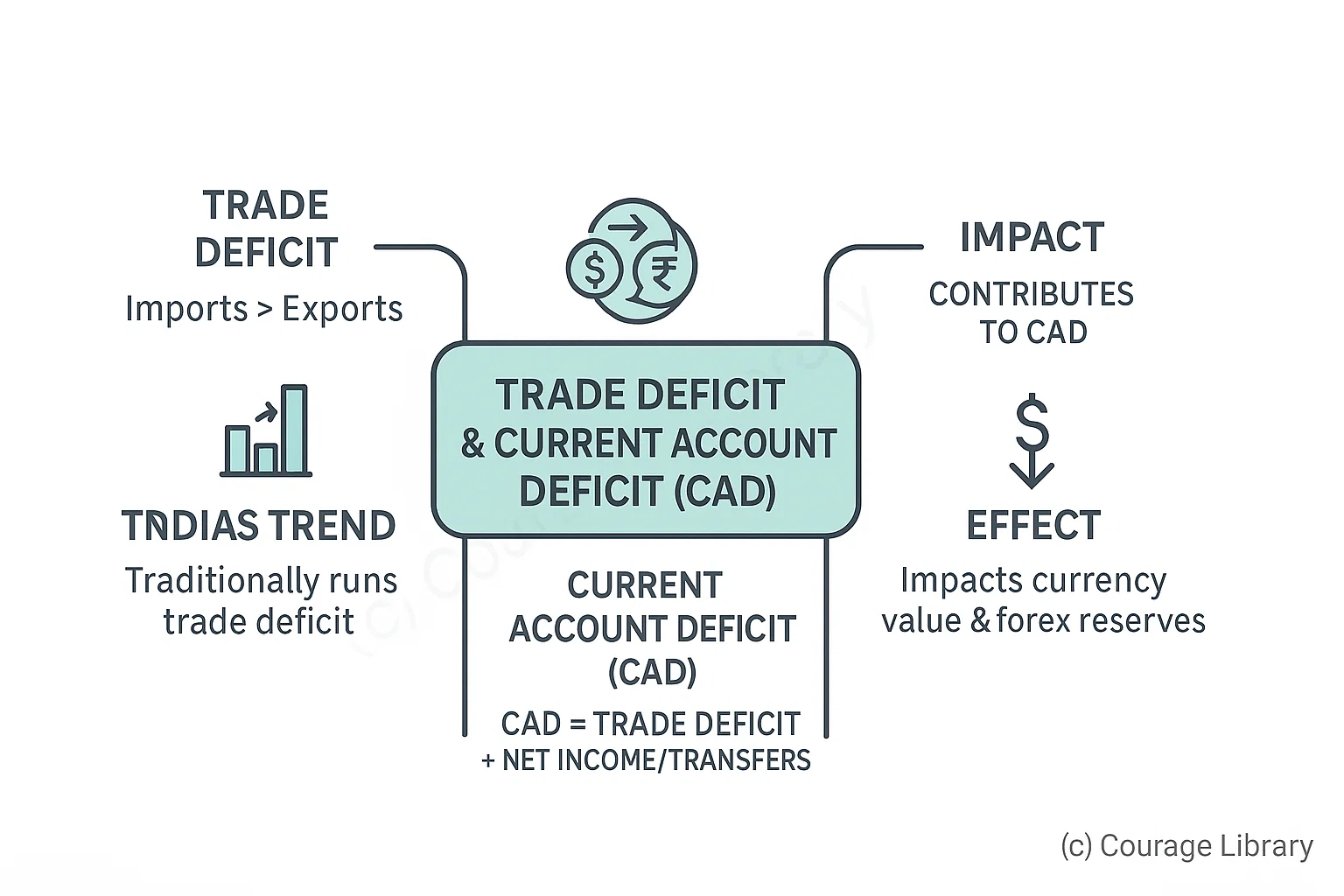
Trade Deficit:
- Occurs when imports > exports.
- India traditionally runs a trade deficit.
- Trade deficit contributes to current account deficit.
Current Account Deficit (CAD):
- CAD = Trade Deficit + Net income/transfers.
- High CAD can affect currency value and forex reserves.
3. Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
Definition:
Investment made by a foreign entity into the capital/assets of Indian companies.
Types:
| Type | Example |
|---|---|
| Automatic Route | No prior govt. approval (most sectors) |
| Government Route | Requires prior approval (defense, media) |
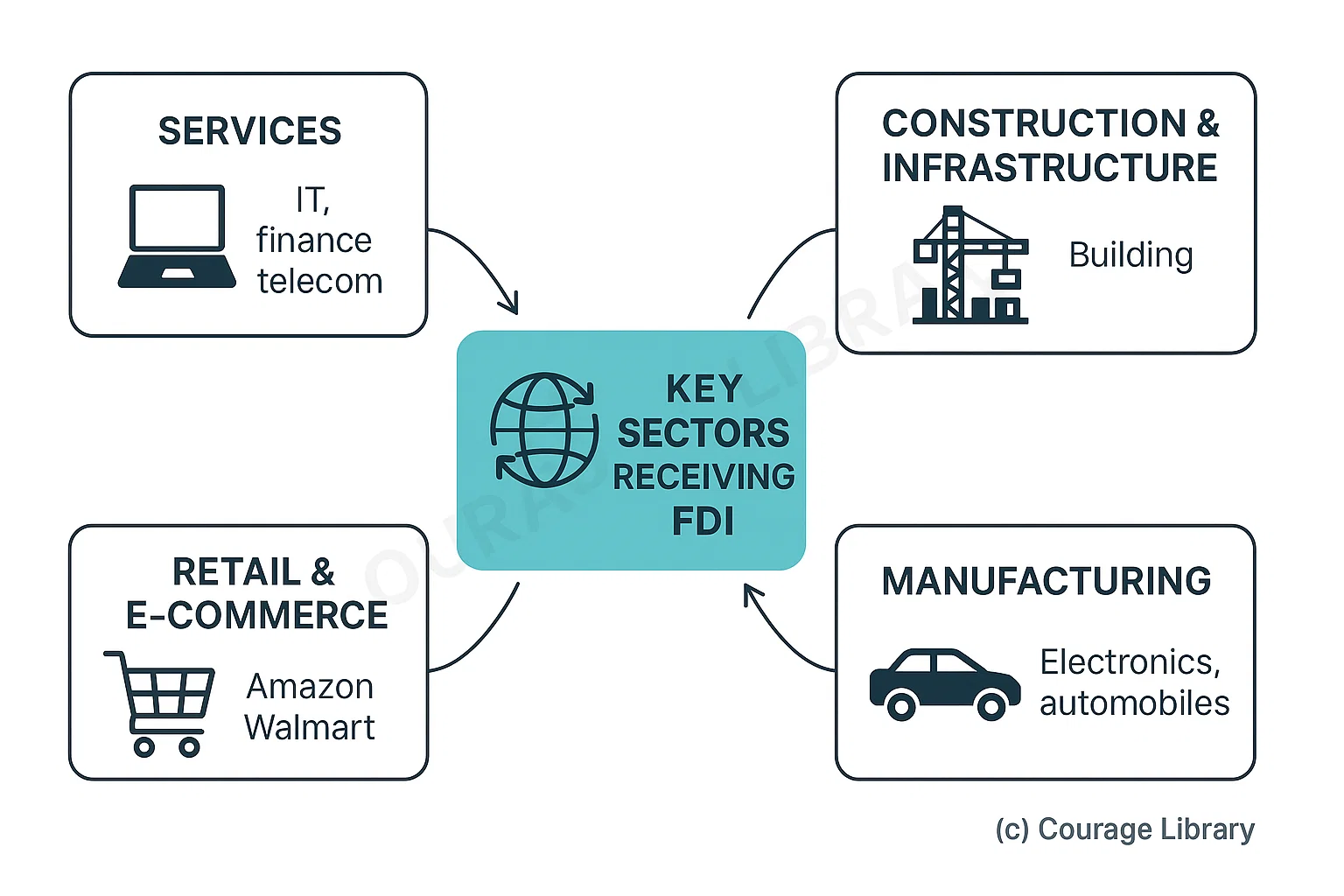
Key Sectors Receiving FDI:
- Services (IT, finance, telecom)
- Construction & infrastructure
- Retail and e-commerce (Amazon, Walmart)
- Manufacturing (especially electronics, automobiles)
FDI Benefits:
Capital inflow
Technology transfer
Employment generation
Boost to Make in India
FDI Regulator: Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT)
4. WTO, IMF, World Bank, BRICS, ADB
WTO (World Trade Organization):
- Established: 1995
- HQ: Geneva, Switzerland
- Aim: Promote free and fair global trade
- Functions: Trade negotiations, dispute resolution, trade monitoring
- India's Interests: TRIPS (IPR), agricultural subsidies
IMF (International Monetary Fund):
- Established: 1944 (Bretton Woods)
- HQ: Washington, D.C.
- Aim: Ensure global monetary stability
- Key Roles:
- Lending to countries in crisis
- Surveillance and economic guidance
- Technical assistance
World Bank:
- Established: 1944
- HQ: Washington, D.C.
- Components: IBRD, IDA(part of World Bank Group)
- Focus: Long-term development aid
- Key Projects in India: Education, sanitation, water supply, rural roads
BRICS:
- Founded: 2009 (South Africa joined in 2010)
- Focus: Multilateral cooperation, reform of global institutions
- Institutions: New Development Bank (NDB)
- India's Role: Promoting multipolar global order
ADB (Asian Development Bank):
- Established: 1966
- HQ: Manila, Philippines
- Mandate: Socio-economic development of Asia-Pacific
- India: Major recipient of loans for infrastructure, health, urban reforms
5. Trade Agreements and Economic Diplomacy
Types of Trade Agreements:
| Type | Example |
|---|---|
| Bilateral Trade Agreement | India–UAE CEPA, India–Japan CEPA |
| Regional Trade Agreement | ASEAN–India FTA, SAFTA |
| Multilateral Trade Agreement | WTO agreements |
India's Major Trade Agreements:
- India–ASEAN Free Trade Agreement
- India–UAE CEPA (2022)
- India–Australia ECTA (2022)
- Ongoing negotiations: India–EU FTA, India–UK FTA
Economic Diplomacy:
- Using trade, investment, and aid to enhance foreign relations.
- Managed by Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) & Ministry of Commerce.
- Focus on:
- Energy security (e.g., Middle East, Russia)
- Supply chains diversification (e.g., Quad)
- Export promotion councils and overseas missions
Developed By Jan Mohammad
Next
Start Your SSC CGL Journey Now!
Join Courage Library to experience disciplined study and expert support.
Be a Couragian!