SSC CGL - Detailed Guide 2025
Self-Paced Course

Industry and Infrastructure
Reference: Lucent GK, NCERT Class 6–12
Major Industries:
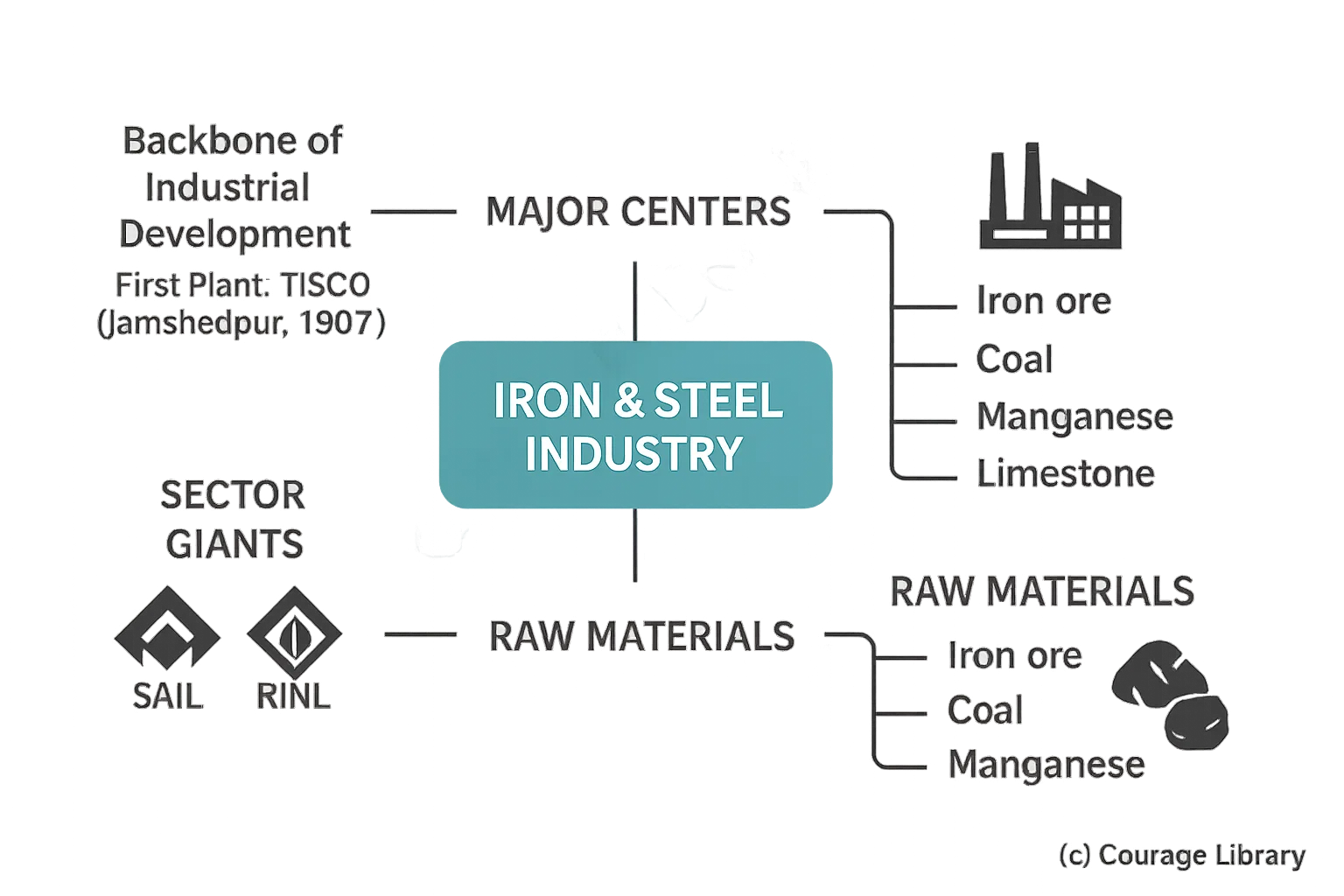
Iron & Steel Industry
- Backbone of industrial development
- First plant: TISCO (Jamshedpur, 1907).
- Major centers: Bhilai, Bokaro, Durgapur, Rourkela, Salem.
- Sector Giants: SAIL (Steel Authority of India Ltd.), RINL
- Raw materials: Iron ore, coal, manganese, limestone.
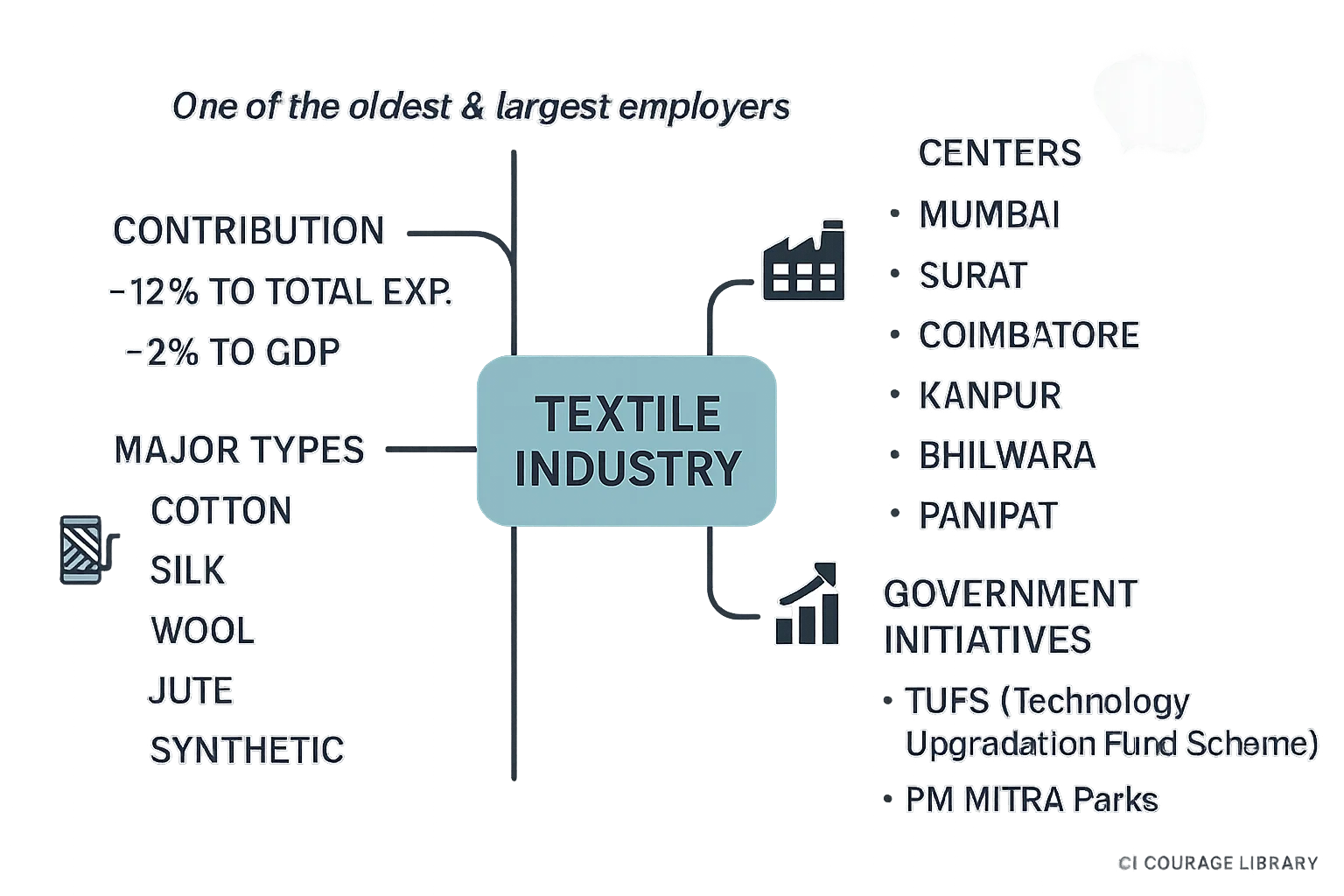
Textile Industry
- One of the oldest & largest employers.
- Contributes ~12% to total exports & ~2% to GDP.
- Major types: Cotton, Silk, Wool, Jute, Synthetic
- Centers: Mumbai, Surat, Coimbatore, Kanpur, Bhilwara, Panipat.
- Government Initiatives: TUFS (Technology Upgradation Fund Scheme), PM MITRA Parks.
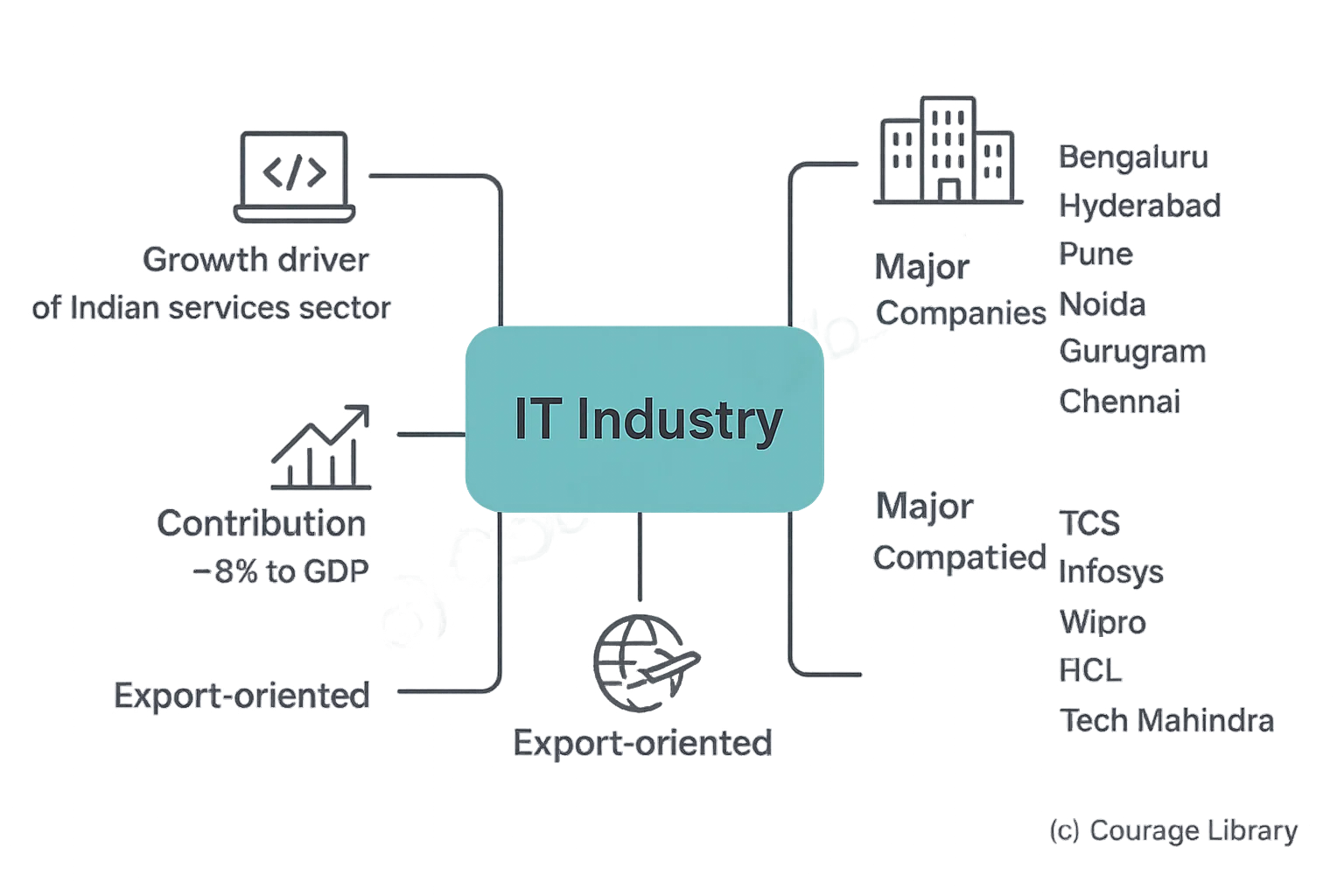
IT Industry
- Growth driver of Indian services sector.
- Major Hubs: Bengaluru, Hyderabad, Pune, Noida, Gurugram, Chennai.
- Contributes ~8% to GDP
- Export-oriented; major companies: TCS, Infosys, Wipro, HCL, Tech Mahindra.
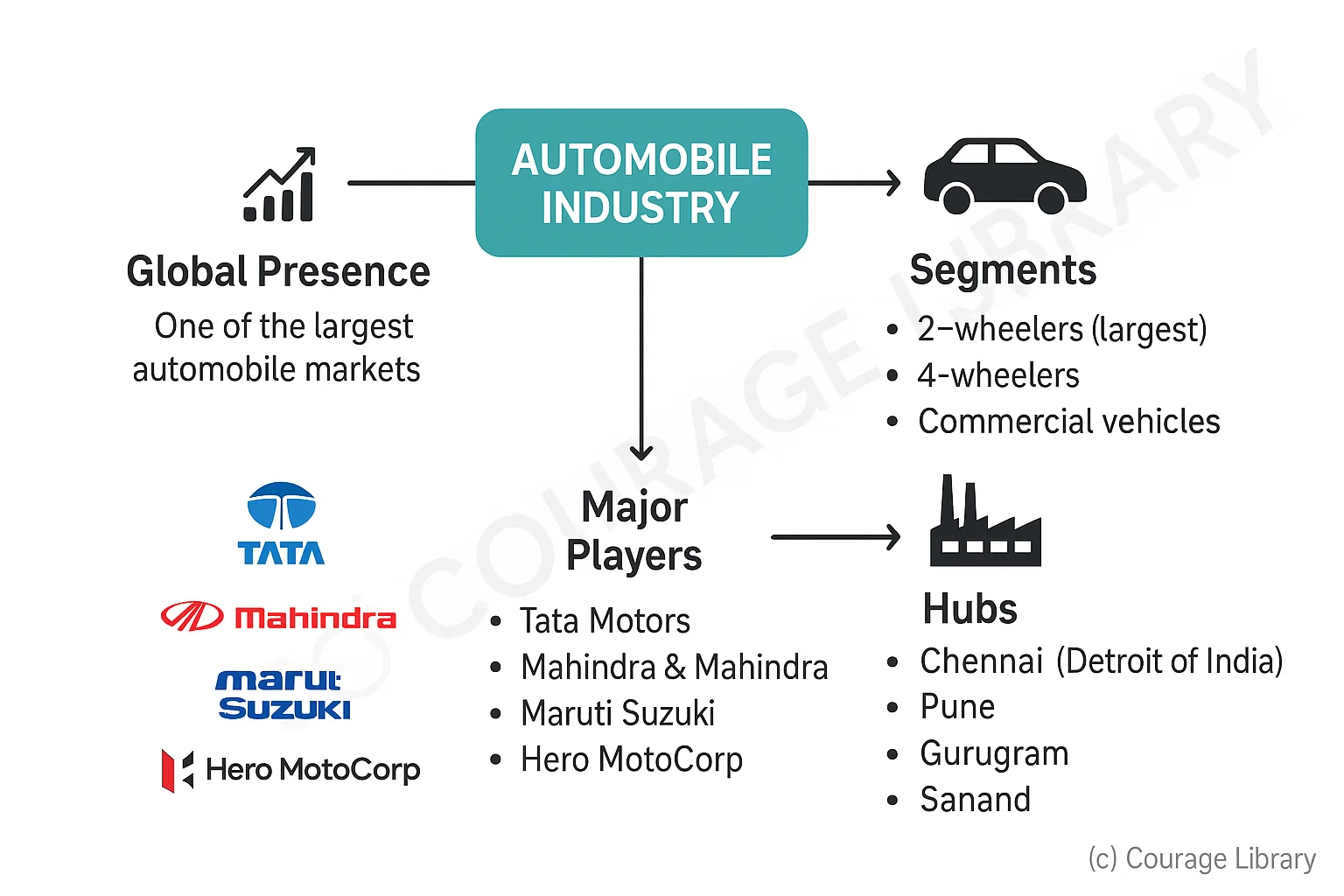
Automobile Industry
- India is one of the largest automobile markets globally.
- Segments: 2-wheelers (largest), 4-wheelers, commercial vehicles.
- Major players: Tata Motors, Mahindra & Mahindra, Maruti Suzuki, Hero MotoCorp
- Hubs: Chennai (Detroit of India), Pune, Gurugram, Sanand.
Industrial Policies in India
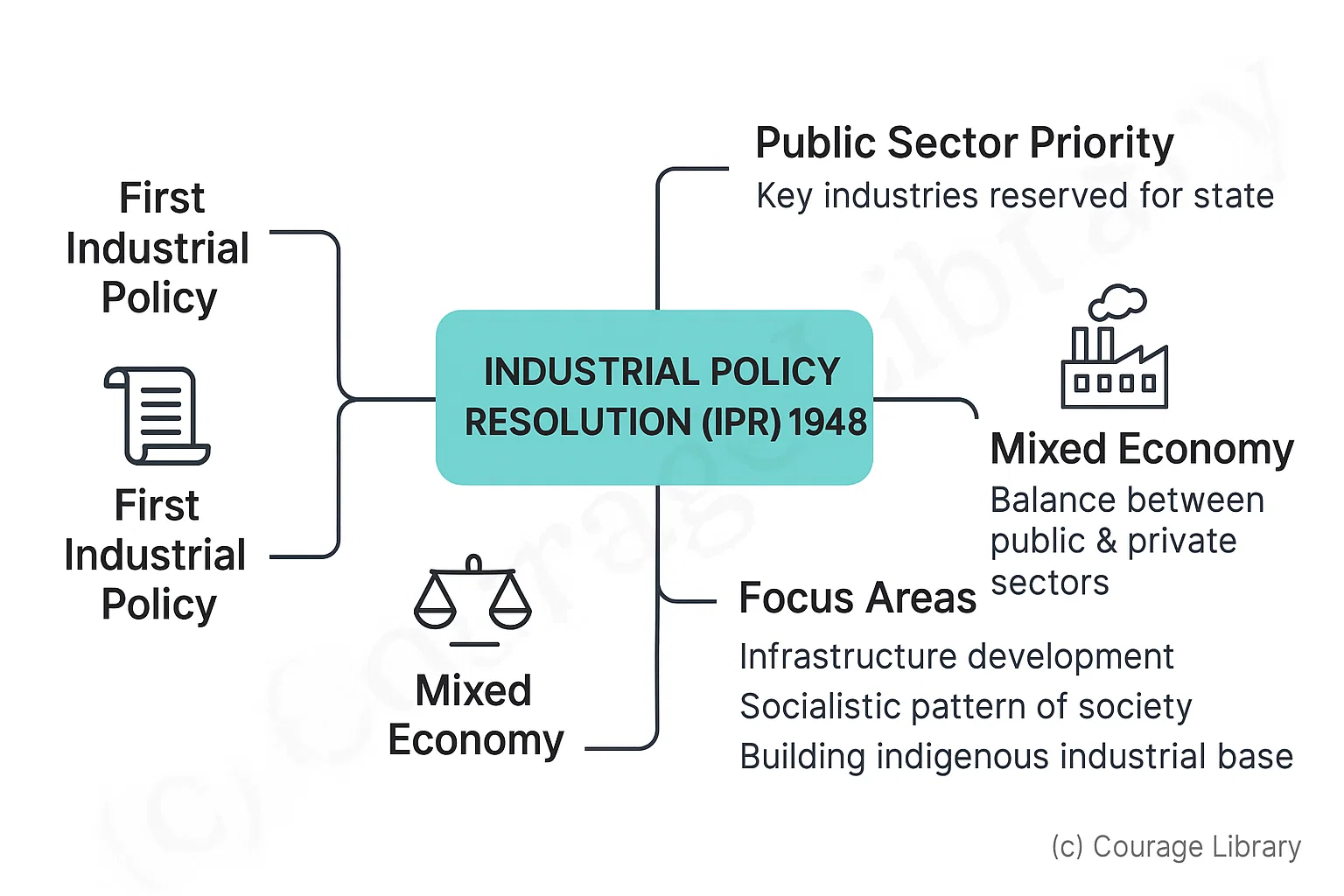
Industrial Policy Resolution (IPR) 1948
- First post-independence policy
- Public sector given importance in key industries.
- Set framework for mixed economy.
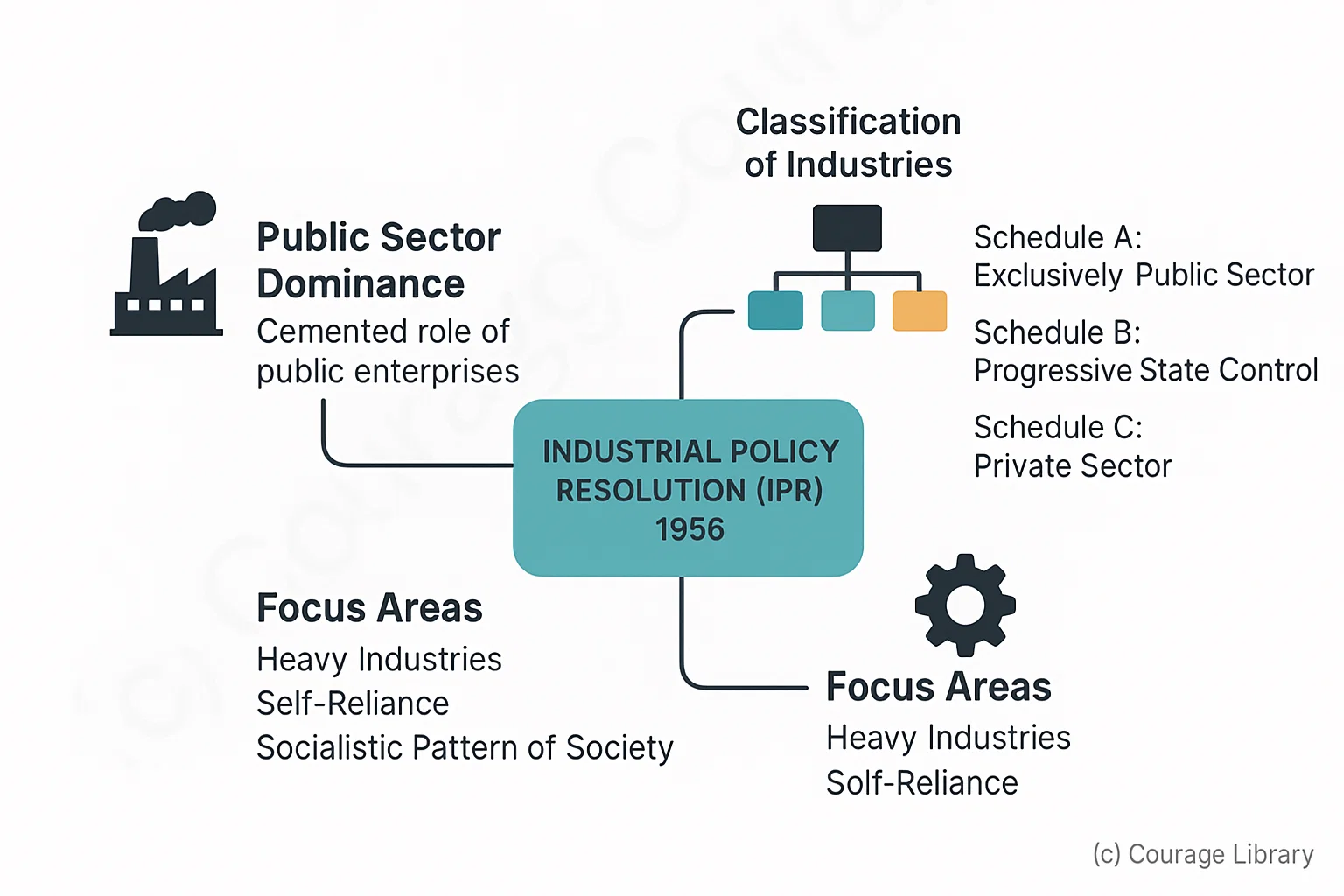
Industrial Policy Resolution (IPR) 1956
- Cemented public sector dominance.
-
Classified industries into 3 categories:
- Schedule A: Exclusively public sector
- Schedule B: Progressive state control
- Schedule C: Private sector
- Focus on heavy industries and self-reliance
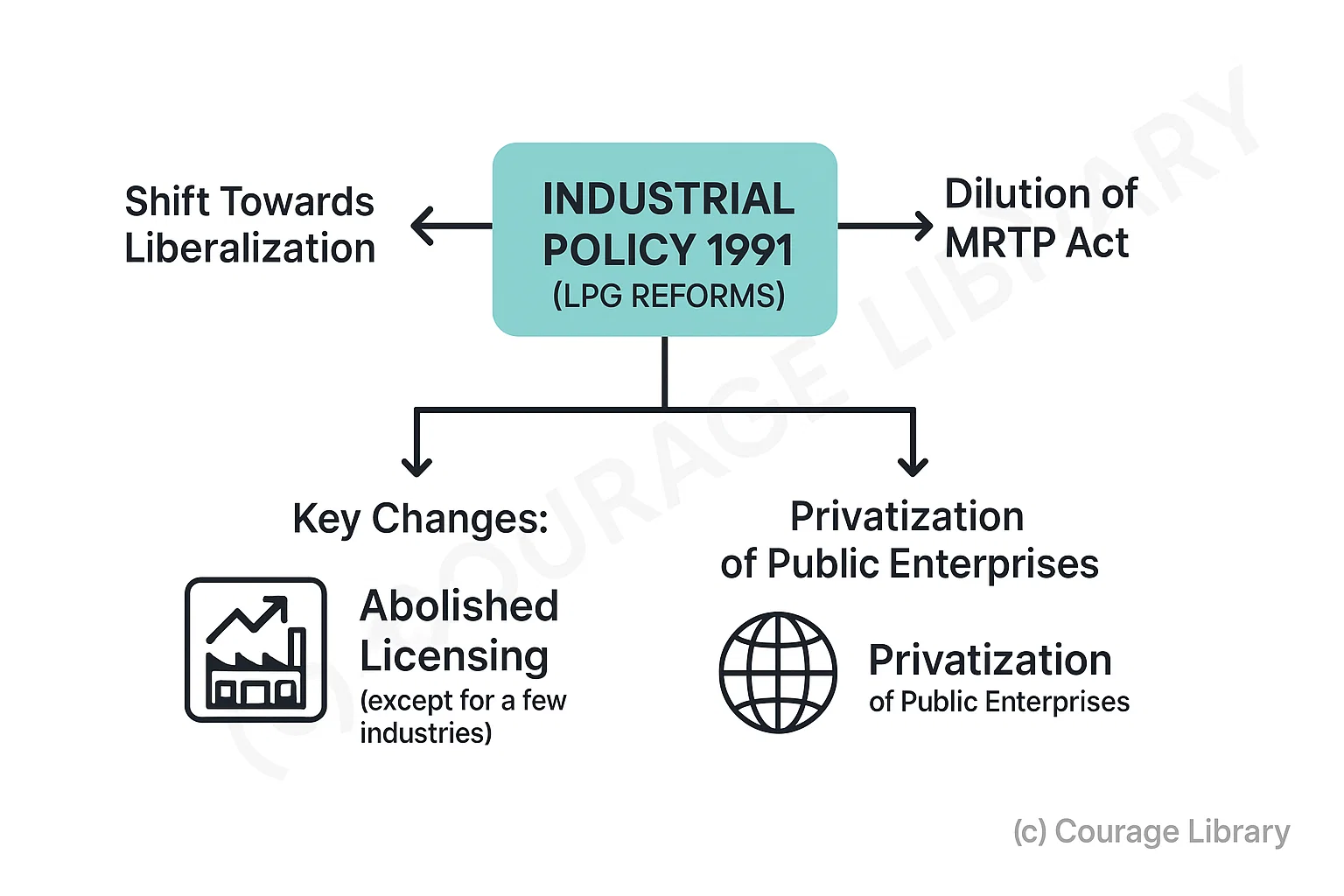
Industrial Policy 1991 (LPG Reforms)
- Marked a shift towards liberalization.
-
Key Changes:
- Abolished industrial licensing (except for a few industries)
- Dilution of MRTP Ac
- Encouraged FDI
- Privatization of public enterprises
MSME Sector & Startups
-
MSME (Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises)
- Contribute ~30% to India’s GDP.
- Major employment generator (second to agriculture).
- Classification (revised 2020):
| Category | Investment (Plant & Machinery) | Turnover |
|---|---|---|
| Micro | ≤ ₹1 crore | ≤ ₹5 crore |
| Small | ≤ ₹10 crore | ≤ ₹50 crore |
| Medium | ≤ ₹50 crore | ≤ ₹250 crore |
-
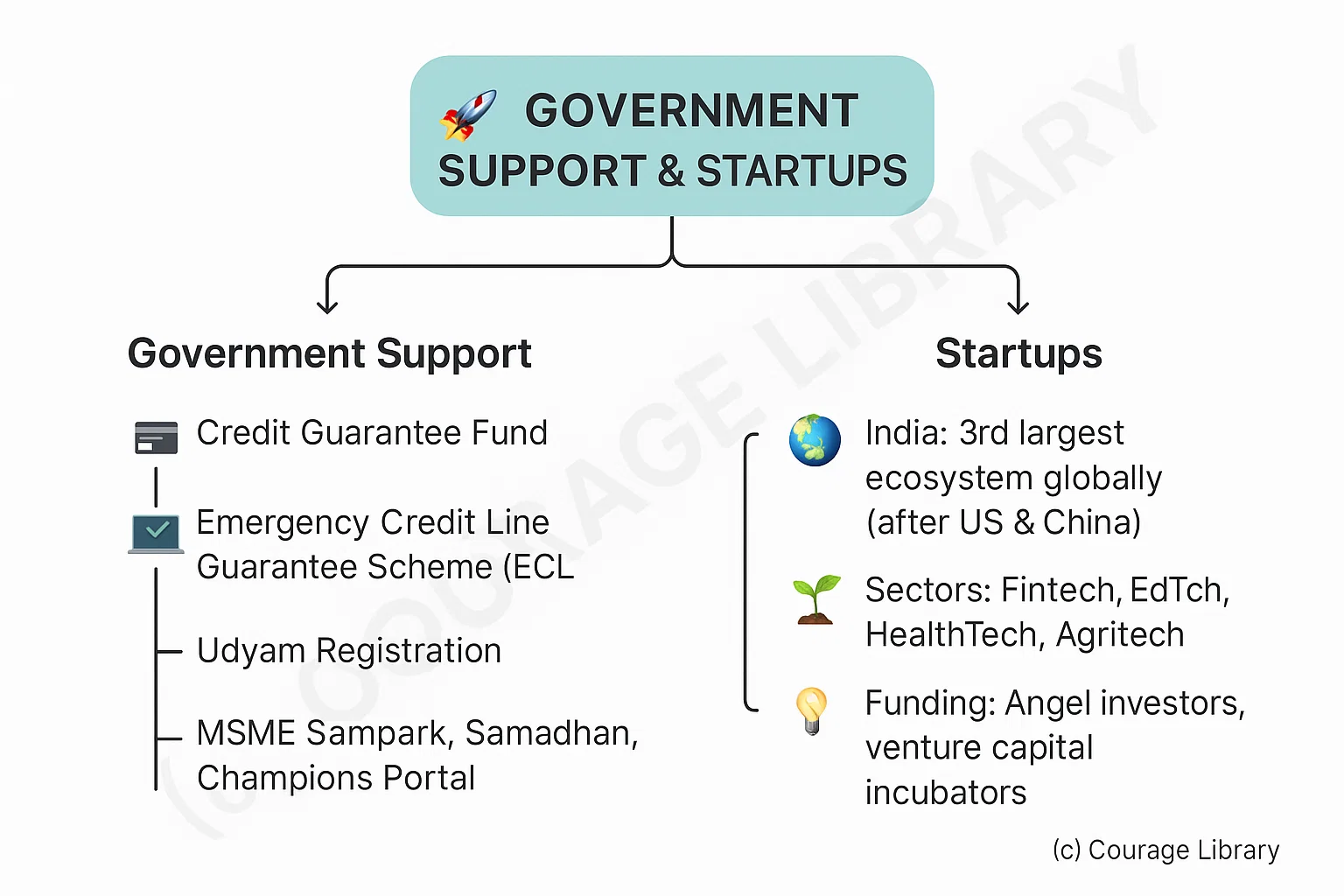
Government Support:
- Credit Guarantee Fund
- Emergency Credit Line Guarantee Scheme (ECLGS)
- Udyam Registration portal
- MSME Sampark, Samadhan, and Champions Portal
-
Startups:
- India: 3rd largest startup ecosystem globally (after US & China)
- Startups in sectors: Fintech, EdTech, HealthTech, Agritech
- Funding via angel investors, venture capital, and incubators
Make in India, Startup India
Make in India (Launched 2014)
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Objective | Boost manufacturing, create jobs |
| Target | Raise manufacturing share to 25% of GDP |
| Focus Sectors | 25 sectors incl. Auto, Pharma, Defense, Rail |
| Key Enablers | Ease of Doing Business, FDI reform, skill dev |
Startup India (Launched 2016)
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Objective | Promote innovation, entrepreneurship |
| Benefits | Tax exemption (3 years), faster patent clearance |
| DPIIT Recognition | Needed for availing benefits |
| Other Support | Startup Fund, Incubators, Seed Funding Scheme |
Infrastructure – Roads, Railways, Airports, Smart Cities
-
Roads
- India has 2nd largest road network globally (~63 lakh km).
- NH Development: Bharatmala Pariyojana.
- Expressways: Delhi-Mumbai Expressway, Purvanchal Expressway
-
Railways
- One of world’s largest railway networks (~67,000 km).
- Operated by: Indian Railways (Ministry of Railways).
- Electrification, modernization via schemes like PM Gati Shakti.
- Vande Bharat trains – semi-high-speed network expansion.
-
Airports
- Rapid airport expansion under UDAN Scheme (Ude Desh ka Aam Nagrik).
- Major airports: Delhi, Mumbai, Bengaluru, Hyderabad
- Managed by AAI & PPP model.
-
Smart Cities Mission (Launched 2015)
- Goal: Transform 100 cities into sustainable and citizen-friendly cities
- Focus: Smart governance, transport, sanitation, waste mgmt, ICT infra.
- Each city receives ₹500 crore from Centre + matching funds from states.
Public Sector Enterprises (PSEs)
Definition: Government-owned corporations with majority stake (>51%) by central or state governments.
Classification:
| Category | Criteria |
|---|---|
| Maharatna | Net worth ≥ ₹15,000 cr, global operations |
| Navratna | Moderate autonomy, strong performance |
| Miniratna | Profitable PSEs with limited autonomy |
Examples
| Category | Enterprises |
|---|---|
| Maharatna | ONGC, IOCL, NTPC, SAIL, BHEL, GAIL |
| Navratna | BEL, HAL, RITES, NALCO |
| Miniratna | BSNL, AAI, HLL, MOIL |
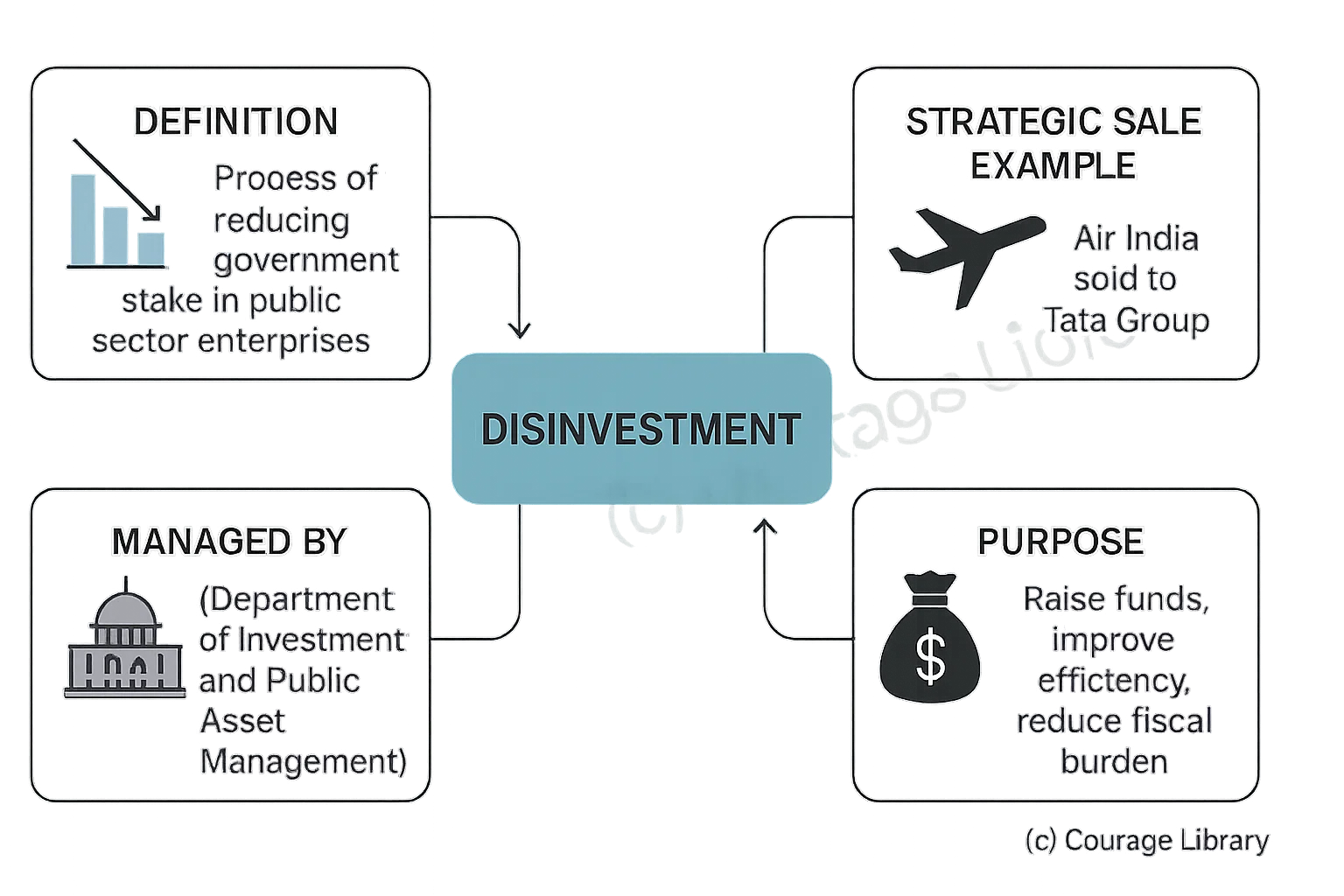
Disinvestment:
- Process of reducing government stake.
- Managed by DIPAM (Department of Investment and Public Asset Management).
- Strategic Sale Example: Air India to Tata Group.
Developed By Roopasree Challa
Next
Start Your SSC CGL Journey Now!
Join Courage Library to experience disciplined study and expert support.
Be a Couragian!