SSC CGL - Detailed Guide 2025
Self-Paced Course

Money and Banking
Reference: Lucent GK, NCERT Class 6–12
Functions of Money
Money = Any commodity that is universally accepted in exchange of goods and services.
Primary Functions:
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Medium of Exchange | Eliminates the need for barter system |
| Measure of Value | Common standard to measure value of goods |
Secondary Functions:
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Store of Value | Can be saved and used in future |
| Standard of Deferred Payment | Used for future payments, credit transactions |
Contingent Functions:
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Basis of Credit | Supports credit system via banks and lending |
| Liquidity Provision | Facilitates easy and quick transactions |
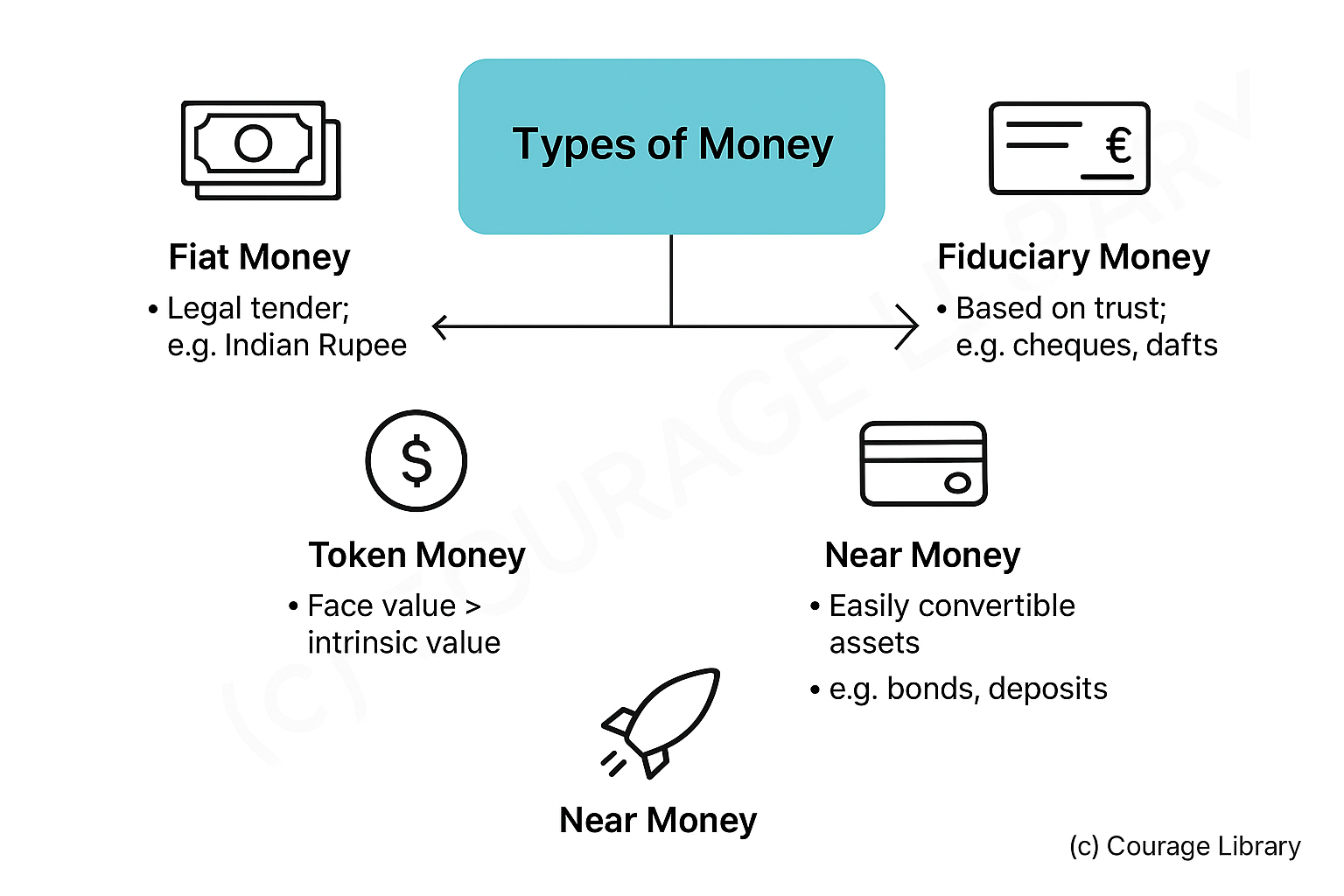
Types of Money:
- Fiat Money (legal tender): e.g. Indian Rupee
- Fiduciary Money: cheques, drafts
- Token Money: face value > intrinsic value
- Near Money: assets easily convertible to cash (bonds, deposits)
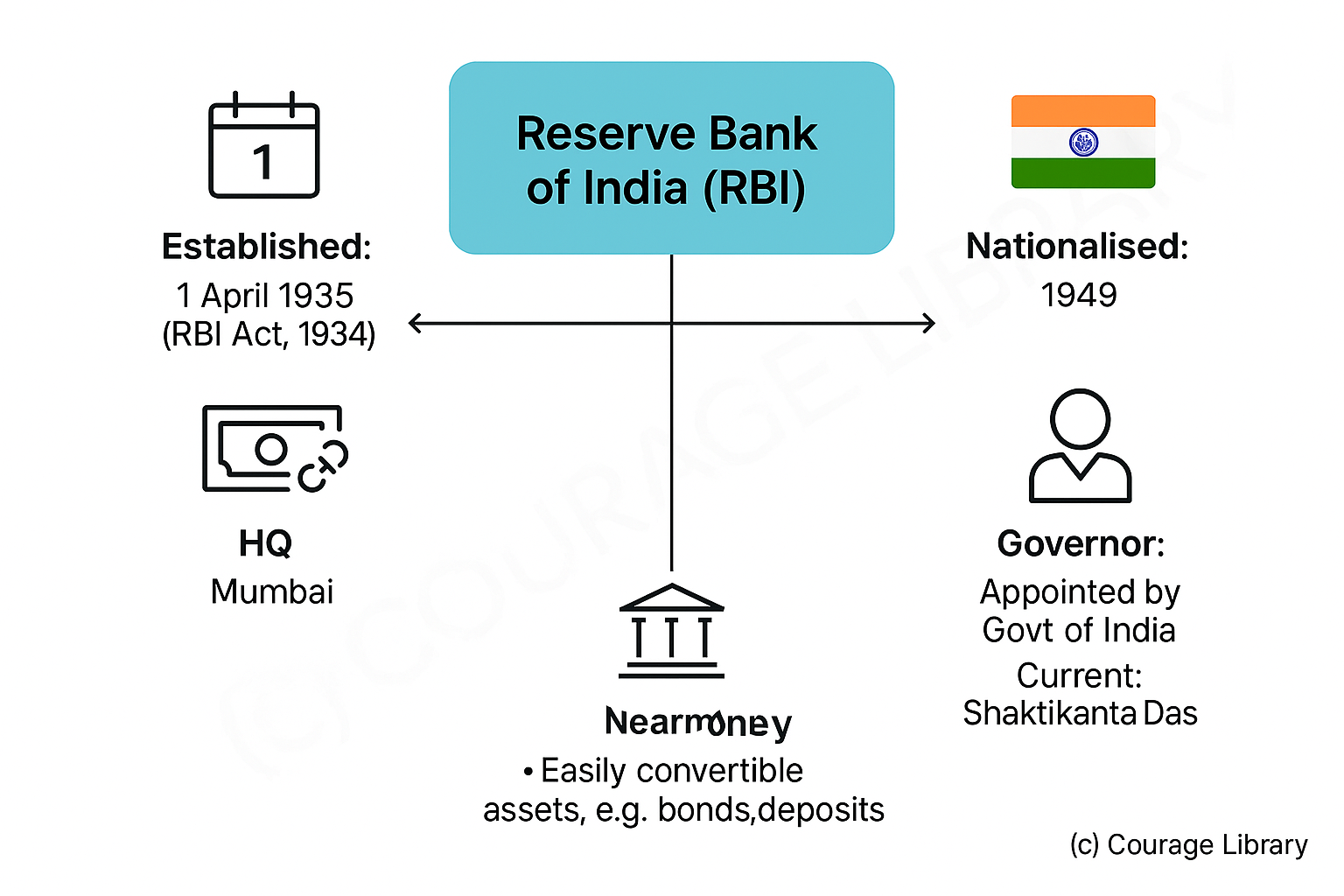
Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
- Established: 1 April 1935 under RBI Act, 1934
- Nationalised: 1949
- HQ: Mumbai
- Governor: Appointed by Government of India (Currently: Shaktikanta Das)
Key Functions of RBI:
| Function Category | Roles |
|---|---|
| Currency Issuer | Sole authority to issue currency in India (except ₹1 note/coin) |
| Banker to Government | Manages govt’s accounts, public debt & auctions |
| Banker’s Bank | Regulates and lends to commercial banks |
| Monetary Authority | Controls inflation, credit, and liquidity |
| Foreign Exchange Manager | Manages Forex reserves, exchange rate (via FEMA, 1999) |
| Supervisor & Regulator | Licenses banks, regulates NBFCs, ensures stability |
Monetary Policy Tools (to control inflation & liquidity):
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| CRR (Cash Reserve Ratio) | % of net demand & time liabilities (NDTL) banks must keep with RBI in cash |
| SLR (Statutory Liquidity Ratio) | % of NDTL banks must maintain in gold/govt securities |
| Repo Rate | Rate at which RBI lends to banks → ↑ Repo = ↓ money supply |
| Reverse Repo Rate | Rate at which RBI borrows from banks → tool to absorb excess liquidity |
| Bank Rate | Long-term lending rate by RBI (not for daily operations) |
| MSF (Marginal Standing Facility) | Emergency borrowing by banks from RBI at slightly higher rate |
| Open Market Operations (OMO) | Buying/selling govt securities to control liquidity |
RBI's monetary policy is announced bi-monthly by the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC).
Monetary Policy vs Fiscal Policy
| Aspect | Monetary Policy (by RBI) | Fiscal Policy (by Govern- ment) |
|---|---|---|
| Authority | RBI (Monetary Policy Committee) | Ministry of Finance |
| Focus | Control inflation, interest rates | Revenue generation & expenditure |
| Instruments | Repo, CRR, SLR, etc. | Taxes, public spending, subsidies |
| Type | Indirect tool | Direct tool |
| Speed of Implement- ation | Faster | Comparatively slower |
Commercial Banks – Functions, Types
Functions of Commercial Banks:
| Function Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Functions | Accept deposits (savings, current, fixed), lend money |
| Secondary Functions | Issue drafts, locker facility, bill payments, forex services |
| Credit Creation | Lend more than deposits through fractional reserve system |
Types of Banks:
| Type | Examples |
|---|---|
| Public Sector Banks | SBI, Bank of Baroda, PNB |
| Private Sector Banks | HDFC, ICICI, Axis |
| Foreign Banks | HSBC, Citibank, Standard Chartered |
| Regional Rural Banks | Prathama Gramin Bank |
| Cooperative Banks | District & Urban cooperative banks |
| Small Finance Banks | AU SFB, Equitas SFB |
| Payments Banks | Airtel Payments Bank, India Post Payments Bank |
Scheduled vs Non-Scheduled Banks: Scheduled banks are listed in the Second Schedule of RBI Act, 1934 and maintain CRR with RBI.
Digital Payments and UPI
UPI (Unified Payments Interface):
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Launched by | NPCI (National Payments Corporation of India) in 2016 |
| Real-time | Instant transfer 24x7 across banks |
| Linked to Mobile | Uses mobile number + UPI ID (e.g., name@upi) |
| Interoperability | Works across apps like PhonePe, GPay, BHIM, Paytm etc. |
Other Digital Payment Methods:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| NEFT | Batch-based fund transfer (no min limit) |
| RTGS | Real-time transfer for high-value (≥ ₹2 lakh) |
| IMPS | Instant transfer; 24x7 service |
| AEPS | Aadhaar Enabled Payment System |
| QR Code Payments | Scan-and-pay via UPI/Wallets |
| Mobile Wallets | Paytm, Freecharge, Mobikwik |
| Debit/Credit Cards | Card-based offline & online payments |
Key Initiatives:
- Digital India Campaign
- Jan Dhan – Aadhaar – Mobile (JAM Trinity)
- UPI Lite for small payments
- Bharat Bill Payment System (BBPS)
Developed By Jan Mohammad
Next
Start Your SSC CGL Journey Now!
Join Courage Library to experience disciplined study and expert support.
Be a Couragian!