SSC CGL - Detailed Guide 2025
Self-Paced Course

Centre–State Relations
Reference: Lucent GK, NCERT Class 6–12
1. Legislative, Administrative & Financial Relations
Constitutional Basis: Part XI (Articles 245–263)
A. Legislative Relations — Articles 245–255
| Subject | Description |
|---|---|
| Distribution of Powers | Via Seventh Schedule – 3 Lists:
|
| Residuary Powers | Parliament has exclusive power (Art. 248) |
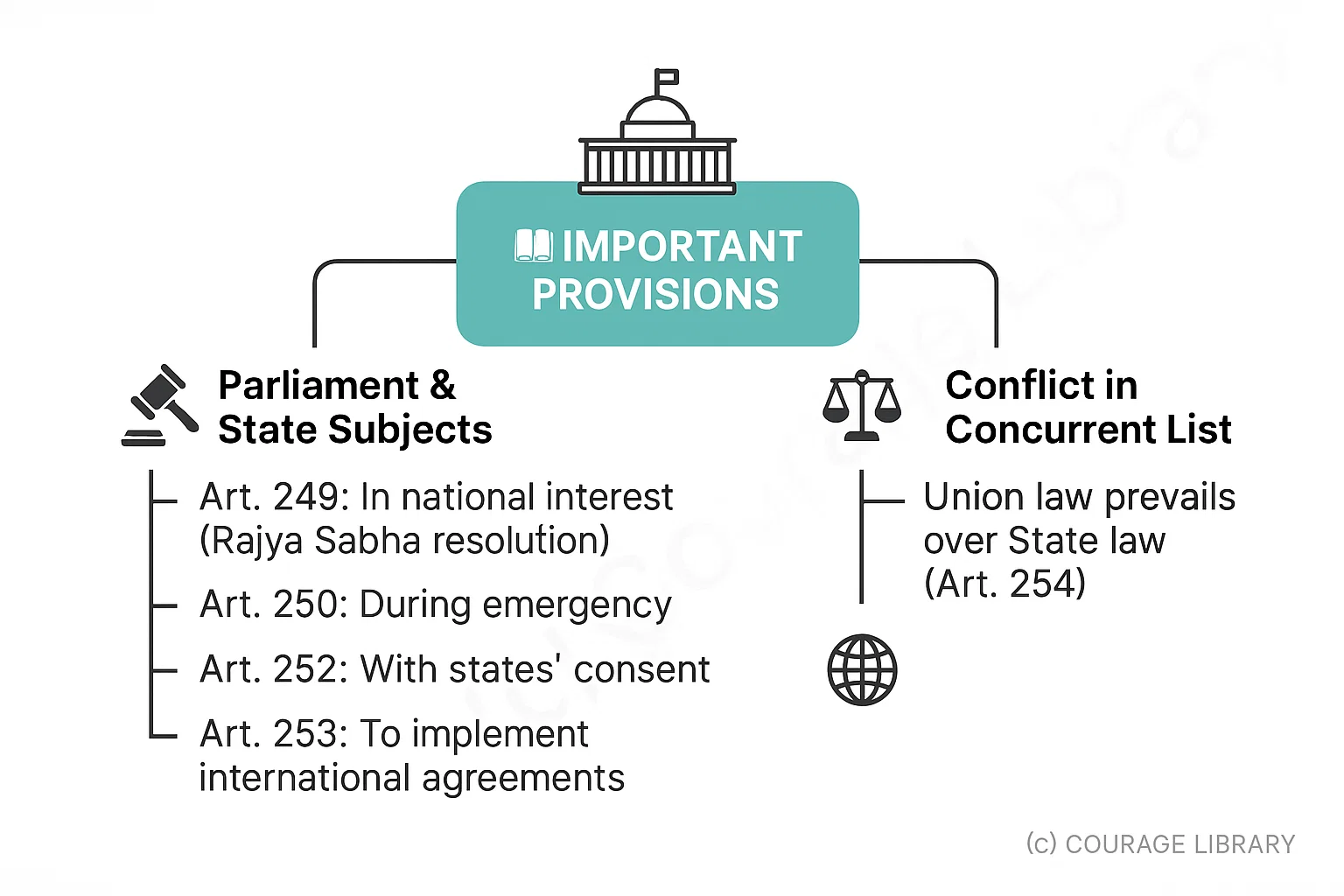
Important Provisions:
- Parliament can legislate on State subjects:
- In national interest (Art. 249 – Rajya Sabha resolution)
- During emergency (Art. 250)
- With states' consent (Art. 252)
- To implement international agreements (Art. 253)
- Conflict in Concurrent List: Union law prevails over State law (Art. 254)
B. Administrative Relations — Articles 256–263
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Executive Power | States to comply with Union laws and not impede Union executive power |
| Centre's Directions | Can direct states for construction of communication, Hindi promotion, etc. |
| Delegation of Union Functions | President may entrust functions to states with consent (Art. 258) |
| Obligation of State & Union | Mutual cooperation required |
| All-India Services | IAS, IPS, IFoS – Common to Centre and States |
| Inter-State Council | Established under Article 263 for coordination (explained below) |
C. Financial Relations — Articles 268–293
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Taxation Powers | Clearly divided between Centre and States |
| Centre levies & collects | Customs, excise (except alcohol), income tax (except on agriculture), etc. |
| States levy & collect | Sales tax, land revenue, stamp duty, etc. |
| Shared Revenue | Article 270 – Income tax & Union excise shared between Centre & States |
| Grants-in-aid | Article 275 – Grants from Union to certain states |
| Finance Commission | Article 280 – Recommends distribution of taxes between Centre & States |
| Loans to States | Article 293 – Centre may lend and regulate borrowing by States |
GST: Introduced via 101st Amendment Act, 2016 – Combined indirect taxes of Centre & States
2. Inter-State Council
Article 263 – Recommended by Sarkaria Commission
Purpose: To discuss, investigate, and advise on inter-state matters
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Established | 1990 by Presidential Order |
| Chaired by | Prime Minister of India |
| Members | Chief Ministers of all States & UTs with legislature |
| Role | Forum for dialogue between Centre and States |
| Functions | Coordination, resolving disputes, policy formulation |
Not a permanent constitutional body; can be dissolved/reconstituted by President
3. Zonal Councils
Statutory Bodies under States Reorganisation Act, 1956
Purpose: Promote cooperation among states in each zone
| Zone | Includes States/UTs |
|---|---|
| Northern | Delhi, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, J&K, Punjab, Rajasthan, Chandigarh |
| Central | Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh |
| Eastern | Bihar, Jharkhand, Odisha, West Bengal |
| Western | Goa, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Dadra & Nagar Haveli, Daman & Diu |
| Southern | Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Telangana, Puducherry |
North-Eastern: NOT under Zonal Councils → covered under separate North Eastern Council (NEC)
Key Points:
- Chaired by Union Home Minister (Standing Committee led by Home Secretary)
- Chief Ministers of states in the zone = Vice Chairperson (rotation basis)
- Discuss inter-state cooperation in transport, border disputes, language, economy, etc.
Summary Table:
| Relation Type | Articles | Key Body/ Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Legislative | 245–255 | 3 Lists in Seventh Schedule |
| Administrative | 256–263 | Inter-State Council, Directions by Centre |
| Financial | 268–293 | Finance Commission, Grants, Shared Taxes |
Start Your SSC CGL Journey Now!
Join Courage Library to experience disciplined study and expert support.
Be a Couragian!