SSC CGL - Detailed Guide 2025
Self-Paced Course

Amendment of the Constitution
Reference: Lucent GK, NCERT Class 6–12
1. Procedure of Amendment -- Article 368
| Provision | Description |
|---|---|
| Amending Power | Parliament (Constituent Power -- different from ordinary law-making) |
| Authority | Article 368 -- Part XX of the Constitution |
| Initiation | Only by Parliament (No role of states in initiation) |
| Bill Type | Constitutional Amendment Bill -- No need for President's recommendation |
| Passage | Passed in each House separately by Special Majority |
| President's Role | Cannot withhold assent (must sign) |
Special Majority:
- Majority of total membership of the House (not just present & voting)
- 2/3rd majority of members present and voting
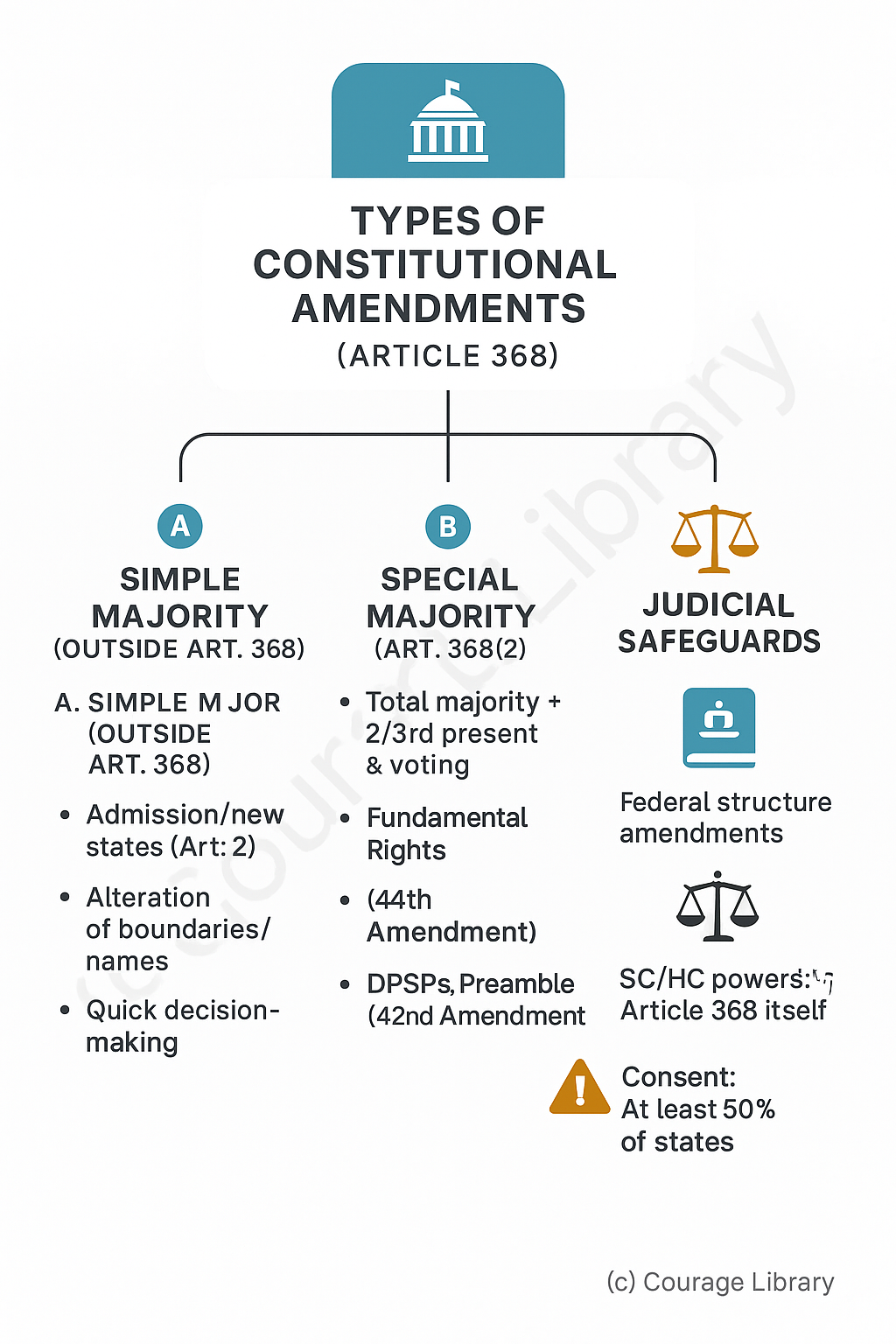
2. Types of Amendments
Based on Article 368 and other provisions, there are 3 types of amendments:
A. By Simple Majority of Parliament
(Not under Article 368)
Examples:
- Admission/Establishment of new states (Art. 2)
- Alteration of state boundaries/names (Art. 3)
- Salaries, privileges of MPs
- Use of English in Parliament
B. By Special Majority of Parliament (Art. 368(2))
- Majority of total membership + 2/3rd of members present & voting
- Used for most constitutional amendments
Examples:
- Fundamental Rights (e.g., 44th Amendment)
- DPSPs changes
- Preamble (42nd Amendment)
C. By Special Majority + Consent of Half of the
States
(Art. 368(2) Proviso)
Required when amendment affects federal structure:
Examples:
- Election of President
- Extent of executive power of Union/State
- Powers of SC/HC
- Representation of States in Parliament
- Article 368 itself
Consent = Resolution passed by at least 50% of states (not all)
3. Important Amendments (from exam perspective)
| Amendment | Year | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| 42nd | 1976 | "Mini Constitution" -- Gave primacy to DPSPs over FRs, added words: Socialist, Secular, Integrity to Preamble; curbed judiciary |
| 44th | 1978 | Reversed many provisions of 42nd Amendment; Restored Article 19 in Emergency; Guaranteed Right to Life (Art. 21) |
| 52nd | 1985 | Introduced Anti-Defection Law (Tenth Schedule) |
| 73rd | 1992 | Gave Constitutional status to Panchayati Raj Institutions (Part IX) |
| 74th | 1992 | Constitutional status to Urban Local Bodies -- Municipalities (Part IXA) |
| 86th | 2002 | Made Free & Compulsory Education a Fundamental Right (Article 21A) |
| 101st | 2016 | Introduced Goods and Services Tax (GST); created GST Council |
Quick Summary Table
| Type of Amendment | Procedure Involved | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Simple Majority | Like ordinary law | Creation of states, salaries |
| Special Majority | Article 368(2) only | FRs, DPSPs, Preamble |
| Special Majority + States | Art. 368(2) + 50% States' consent | Federal structure changes |
Note:
- No provision for referendum or direct public participation
- SC in Kesavananda Bharati Case (1973): Basic Structure of the Constitution cannot be amended
Developed By Satyam Kumar
Next
Master Indian Polity with Us!
Join Courage Library for comprehensive study materials and expert guidance.
Be a Couragian!