SSC CGL - Detailed Guide 2025
Self-Paced Course

Union Government
Reference: Lucent GK, NCERT Class 6–12
President of India
Constitutional Head of the Union (Nominal Executive) Part V, Articles 52–62
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Election | Indirectly elected by an electoral college: MPs (LS + RS) + MLAs (States + UTs with Legislature) |
| Voting System | Proportional Representation + Single Transferable Vote (STV) |
| Tenure | 5 years; eligible for re-election |
| Qualifications | Indian citizen, ≥35 years, eligible for LS, not hold any office of profit |
| Oath | Administered by Chief Justice of India |
Powers of the President:
| Type | Key Functions |
|---|---|
| Executive | Appoints PM, Governors, CJI, Judges, AGI, CAG, etc. |
| Legislative | Summons & dissolves Parliament; gives assent to bills; Ordinance power (Art. 123) |
| Financial | Prior recommendation needed for Money Bills; causes Budget to be laid |
| Judicial | Pardoning powers under Article 72 |
| Emergency | Can declare National, State, or Financial Emergency |
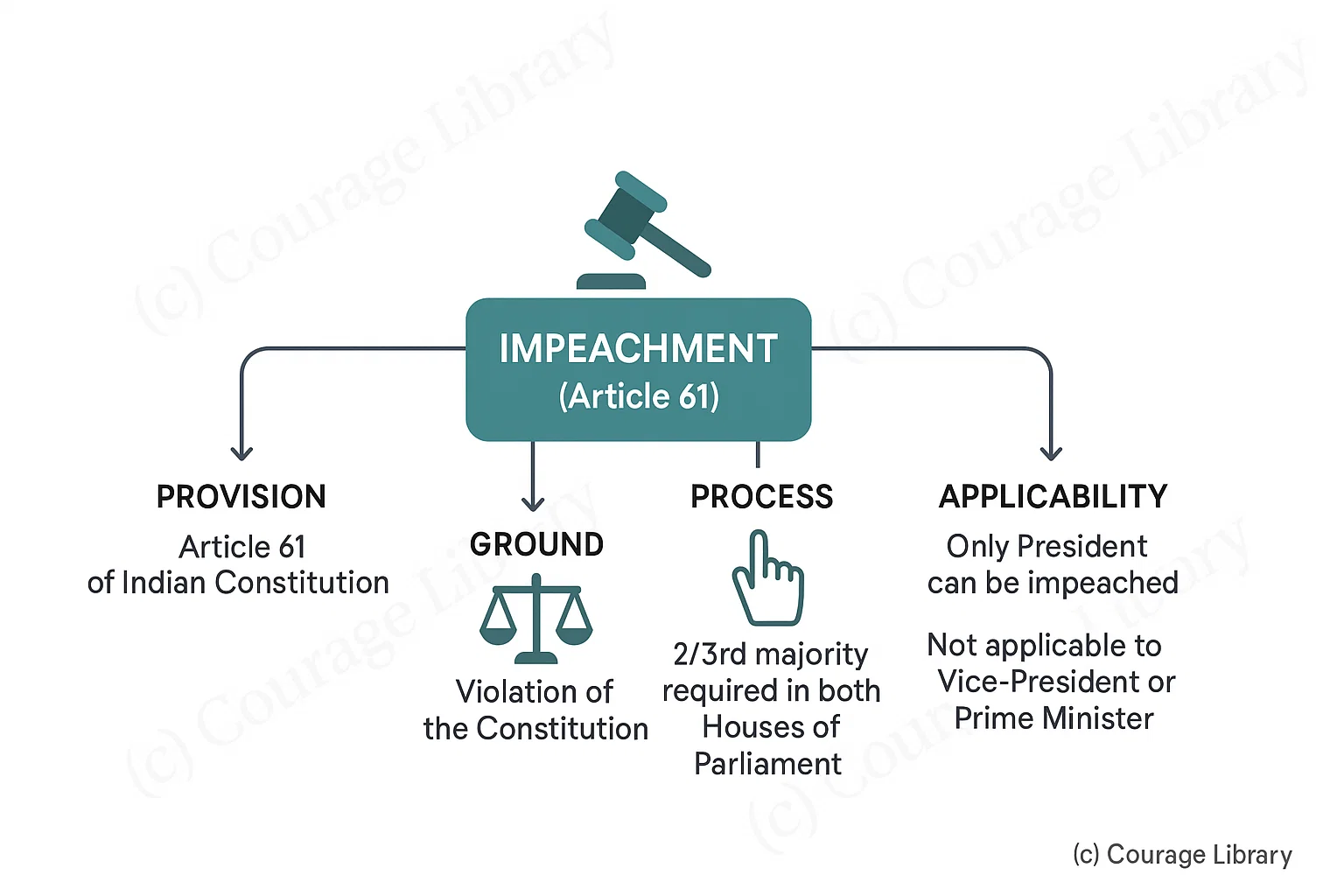
Impeachment:
- Article 61: For "violation of the Constitution"
- Requires 2/3rd majority in both Houses of Parliament
- Only President can be impeached (not Vice-President or PM)
Vice President of India
- Article 63–70
- Second highest constitutional office in India
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Election | Indirectly elected by MPs of both Houses (Electoral College) |
| Voting System | Proportional Representation + STV |
| Tenure | 5 years, re-election allowed |
| Qualification | Indian citizen, ≥35 years, eligible for RS |
| Role | Ex-officio Chairman of Rajya Sabha (Article 64) |
| Acts as President | In absence or vacancy of President (Article 65) |
Prime Minister & Council of Ministers
- Prime Minister → Real Executive Head
- Articles 74 & 75
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Appointment | By the President (Leader of majority in Lok Sabha) |
| Tenure | As long as enjoys majority support in Lok Sabha |
| Role | Head of Government, chairs Cabinet meetings, principal advisor to President |
Council of Ministers:
- Types: Cabinet Ministers, Ministers of State (independent charge), Ministers of State
- Collective Responsibility: To Lok Sabha under Article 75(3)
- Cabinet = Core group of senior ministers → decision-making body
Functions of PM:
- Policy-making
- Coordinating ministries
- Representing India nationally and internationally
- Advising President

Parliament of India
Bicameral Legislature: Rajya Sabha (Upper House) + Lok Sabha (Lower House) Articles 79–122
Lok Sabha (House of the People):
| Feature | Detail |
|---|---|
| Strength | Max 552; Currently 545 members |
| Tenure | 5 years unless dissolved earlier |
| Presiding Officer | Speaker (Article 93) |
| Powers | More powerful than RS (controls money matters & no-confidence motion) |
Rajya Sabha (Council of States):
| Feature | Detail |
|---|---|
| Strength | Max 250; Currently 245 members |
| Tenure | Permanent body; 1/3rd retire every 2 years |
| Presiding Officer | Vice President (Chairman) |
| Powers | Can initiate bills (except money bills), reviews LS decisions |
Parliamentary Sessions (Article 85):
| Session Name | Time Period |
|---|---|
| Budget Session | Feb–May |
| Monsoon | July–Sept |
| Winter | Nov–Dec |
Devices of Parliamentary Proceedings:
| Device | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Question Hour | MPs ask questions to ministers |
| Zero Hour | Unscheduled discussion on urgent matters |
| Adjournment Motion | For discussing a serious issue causing Lok Sabha disruption |
| Calling Attention Motion | To draw attention of minister to an issue |
| No-Confidence Motion | To test majority of ruling govt. (Lok Sabha only) |
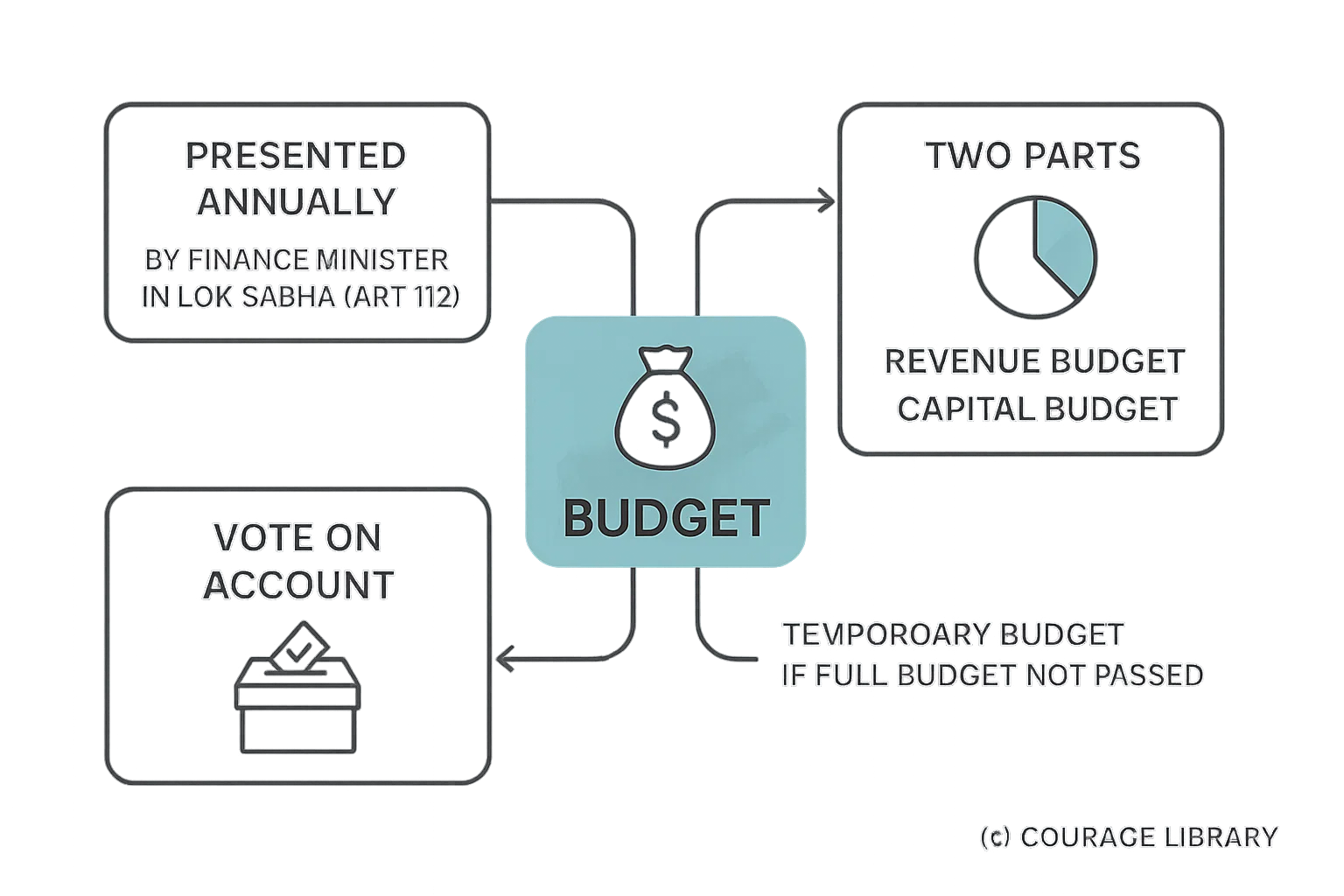
Budget:
- Presented annually (by Finance Minister in LS) – Article 112
- Consists of Revenue Budget + Capital Budget
- Vote on Account: Temporary budget if full budget not passed
Money Bill (Article 110):
| Feature | Detail |
|---|---|
| Origin | Only in Lok Sabha |
| Certification | By Speaker of Lok Sabha |
| Rajya Sabha Power | Can only make recommendations within 14 days |
| Presidential Assent | Mandatory |
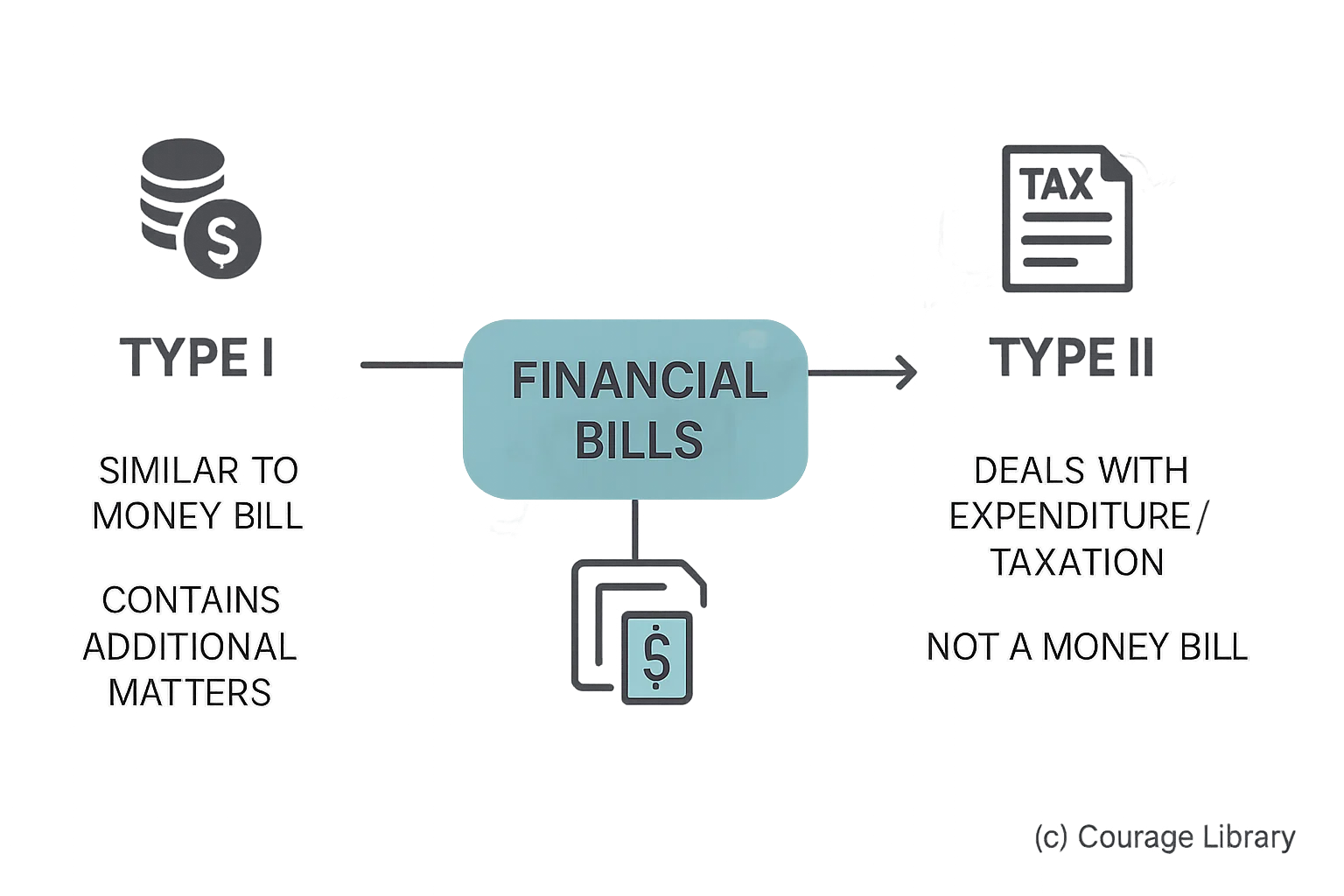
Financial Bills:
- Type I: Similar to Money Bill but contain additional matters
- Type II: Deals with expenditure/taxation but not a Money Bill
Attorney General of India (AGI)
- Article 76
- Chief legal advisor to the Government of India
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Appointed by | President |
| Eligibility | Must be qualified to be a Supreme Court judge |
| Term | No fixed term; serves at pleasure of President |
| Rights | Can take part in Parliament proceedings (no voting rights) |
| Duties | Advises government on legal matters; represents govt. in SC & HC |
Note: AGI is not a government servant; can take private practice (with restrictions)
Comptroller and Auditor General of India (CAG)
- Article 148–151
- Constitutional authority responsible for auditing government accounts
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Appointment | By President |
| Tenure | 6 years or until age 65 (whichever earlier) |
| Removal | Same as SC judge (via impeachment) |
| Reports Submitted to | President → tabled in Parliament |
| Powers | Audits expenditure of Union & State governments, PSUs, etc. |
Called "Guardian of the Public Purse”
Developed By Roopasree Challa
Next
Start Your SSC CGL Journey Now!
Join Courage Library to experience disciplined study and expert support.
Be a Couragian!