SSC CGL - Detailed Guide 2025
Self-Paced Course

Emergency Provisions
Reference: Lucent GK, NCERT Class 6–12
- Constitutional Basis: Part XVIII (Articles 352 to 360)
- Purpose: To enable the Central Government to meet extraordinary situations threatening the security, governance, or financial stability of India.
- There are three types of emergencies:
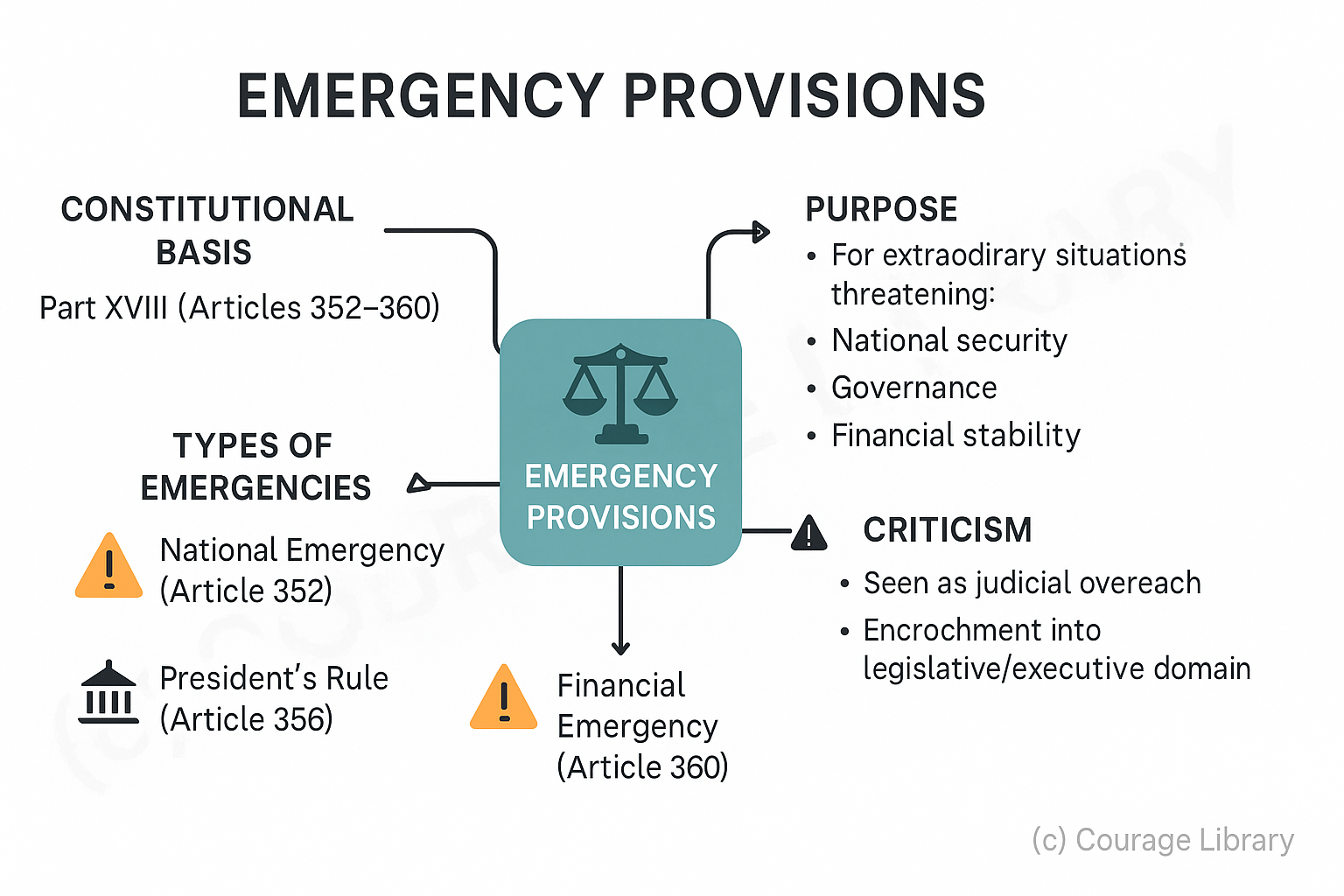
1. National Emergency (Article 352)
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Reason | War, External Aggression, or Armed Rebellion (earlier: internal disturbance) |
| Proclamation | By President on written advice of Cabinet |
| Parliamentary Approval | Must be approved within 1 month by both Houses; renewed every 6 months |
| Duration | Indefinite, with parliamentary approval every 6 months |
| Effect on States | Centre assumes greater control; State governments continue but are under Union direction |
| Effect on FRs | Article 19 suspended (only in case of War/External Aggression) |
| Examples | 1962 (China War), 1971 (Pakistan War), 1975 (Internal Emergency by Indira Gandhi) |
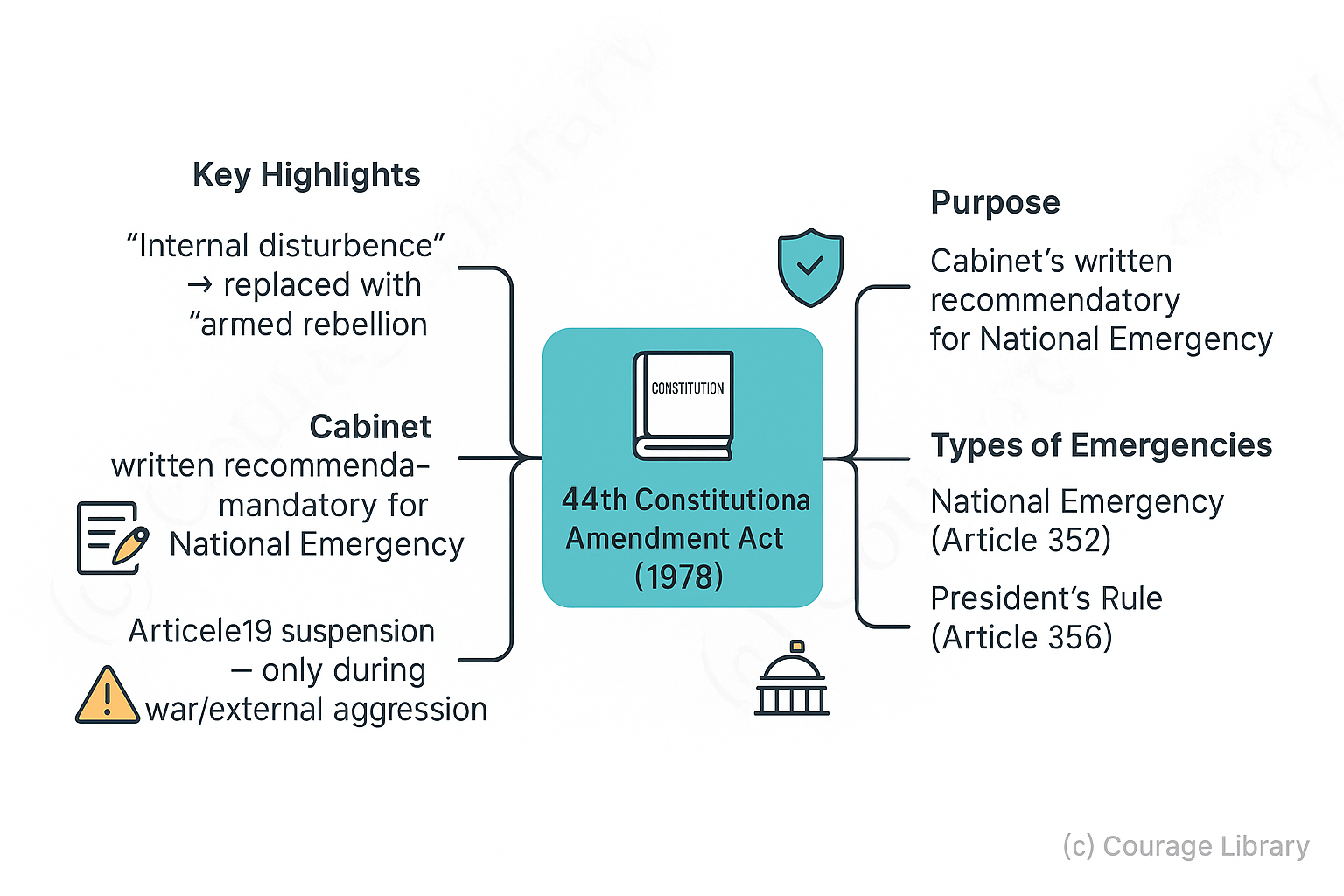
44th Constitutional Amendment Act (1978) Highlights:
- Internal disturbance replaced with "armed rebellion"
- Cabinet must give written recommendation
- Article 19 can only be suspended during war/external aggression
- Emergency approval needs special majority
2. President’s Rule / State Emergency (Article 356)
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Reason | Failure of constitutional machinery in a state (breakdown of governance) |
| Proclamation | By President on report of Governor or otherwise |
| Parliamentary Approval | Within 2 months by both Houses; can be extended every 6 months (up to 3 years) |
| Effect on State | President takes over administration; Governor runs the state on behalf of Centre |
| Legislative Powers | Parliament makes laws for the state |
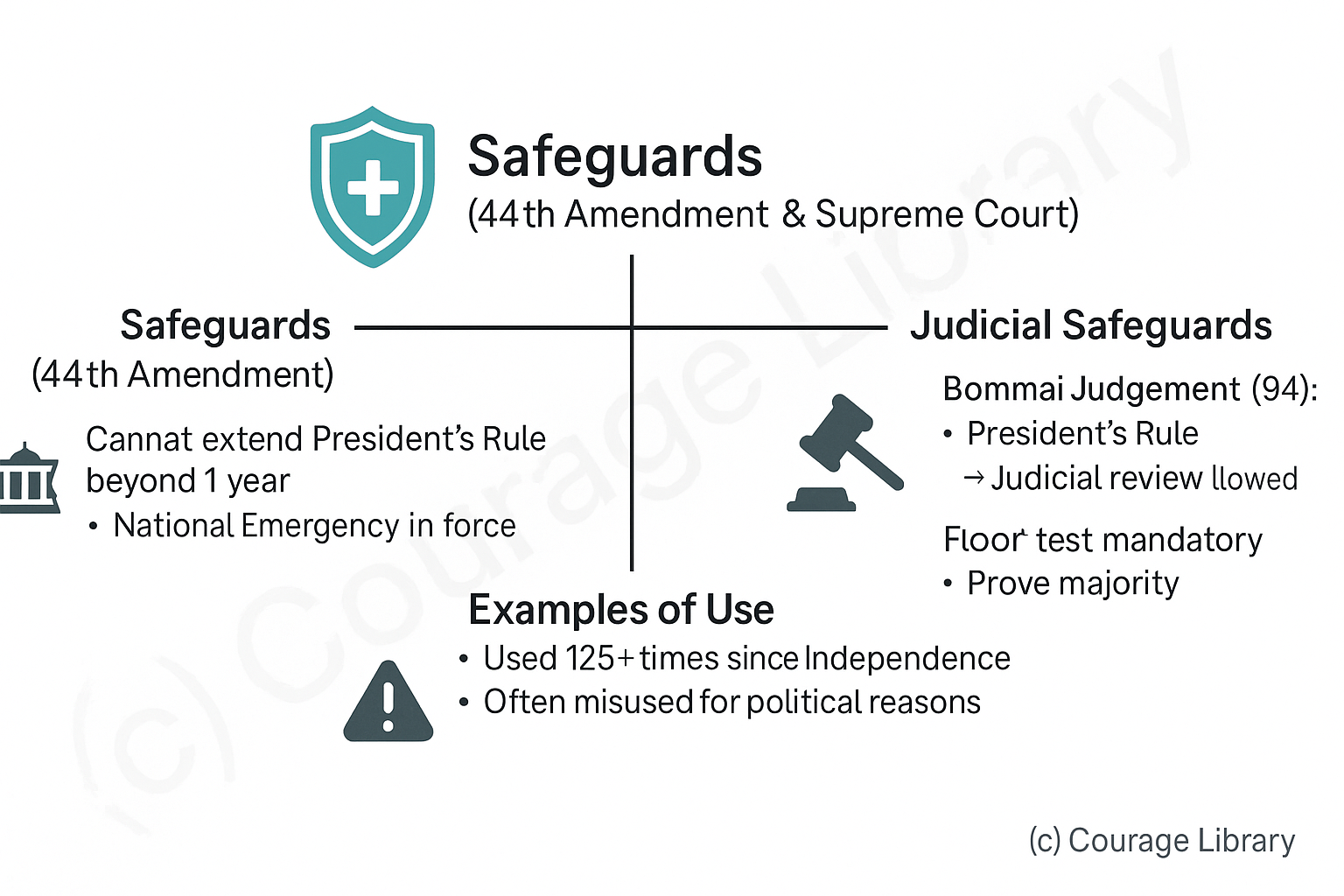
Safeguards (44th Amendment & Supreme Court):
-
Cannot be extended beyond 1 year unless:
- National Emergency is in force OR
- Election Commission certifies that elections can’t be held
-
Bommai Judgment (1994):
- President’s Rule is subject to judicial review
- Floor test in Assembly is mandatory to prove majority
-
Examples of Use:
Very frequently used in the past – over 125 times since Independence. Misused for political reasons.
3. Financial Emergency (Article 360)
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Reason | Threat to the financial stability or credit of India |
| Proclamation | By President; must be approved within 2 months by both Houses |
| Effect on States | Centre can direct State governments on financial matters |
| Impact on Salaries | Salaries of judges, officials (including SC/HC) can be reduced |
| Employment Security | Can direct reduction in government jobs or other austerity measures |
| Has it been used? | NO – Never invoked in Indian history |
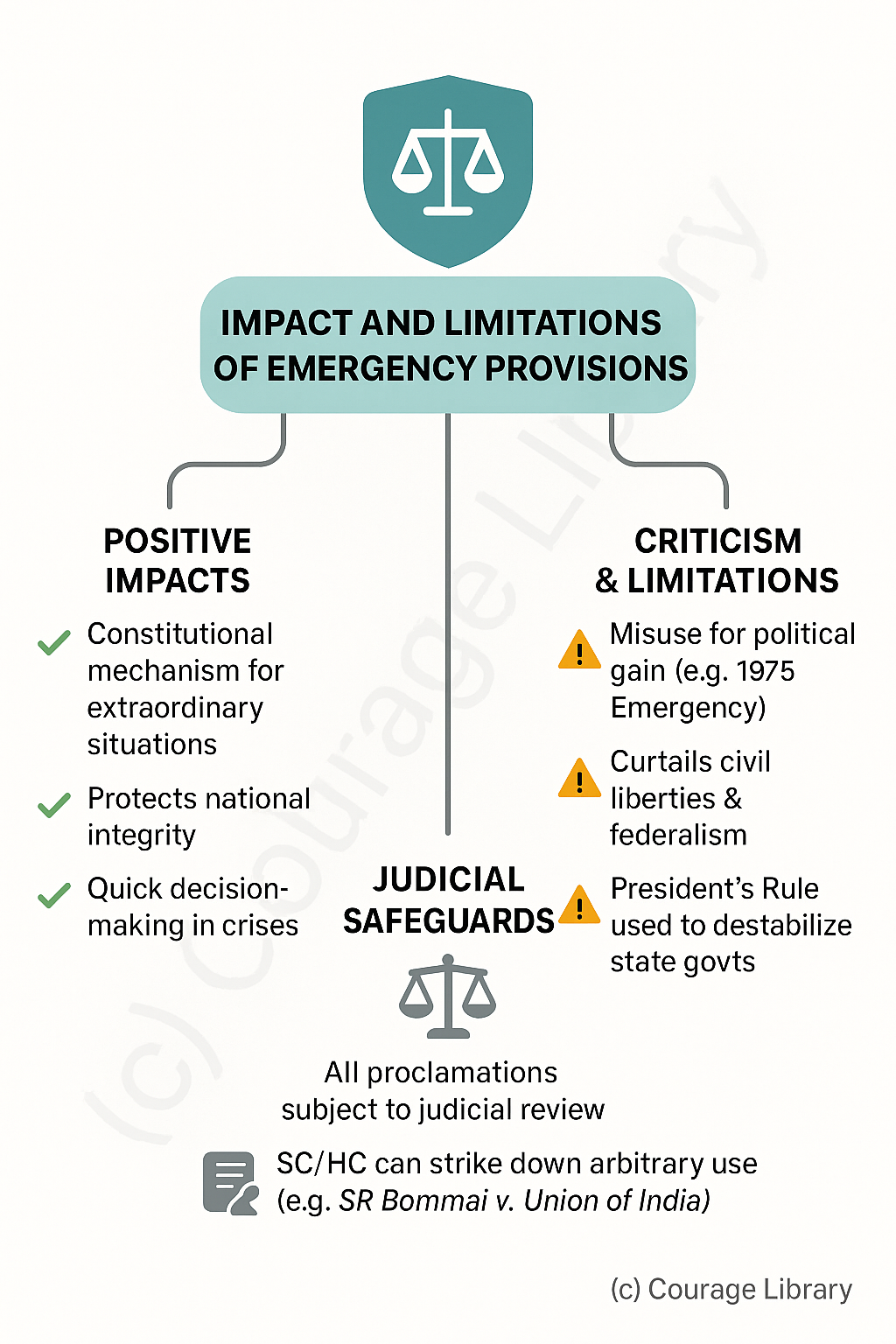
Impact and Limitations of Emergency Provisions
-
Positive Impacts:
- Provide constitutional mechanism to handle extraordinary situations
- Protect national integrity and ensure continuity of governance
- Enable quick decision-making in crisis
-
Criticism & Limitations:
- Can be misused for political gain (e.g., 1975 Emergency)
- Curtails civil liberties and federalism
- President’s Rule used to destabilize state governments
- Judiciary now plays an active role in checking misuse (Bommai case)
-
Judicial Safeguards:
- All emergency proclamations subject to Judicial Review
- SC/HC can strike down arbitrary use (e.g., SR Bommai v. Union of India)
Summary Table:
| Type of Emergency | Article | Reason | Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| National Emergency | 352 | War, external aggression, armed rebellion | Centre assumes control; FRs may be suspended |
| President’s Rule | 356 | Breakdown of constitutional machinery in a State | State under direct Centre control |
| Financial Emergency | 360 | Financial instability | Financial control of Centre over States |
Developed By Roopasree Challa
Next
Start Your SSC CGL Journey Now!
Join Courage Library to experience disciplined study and expert support.
Be a Couragian!