SSC CGL - Detailed Guide 2025
Self-Paced Course

Introduction to Indian Polity
Reference: Lucent GK, NCERT Class 6–12
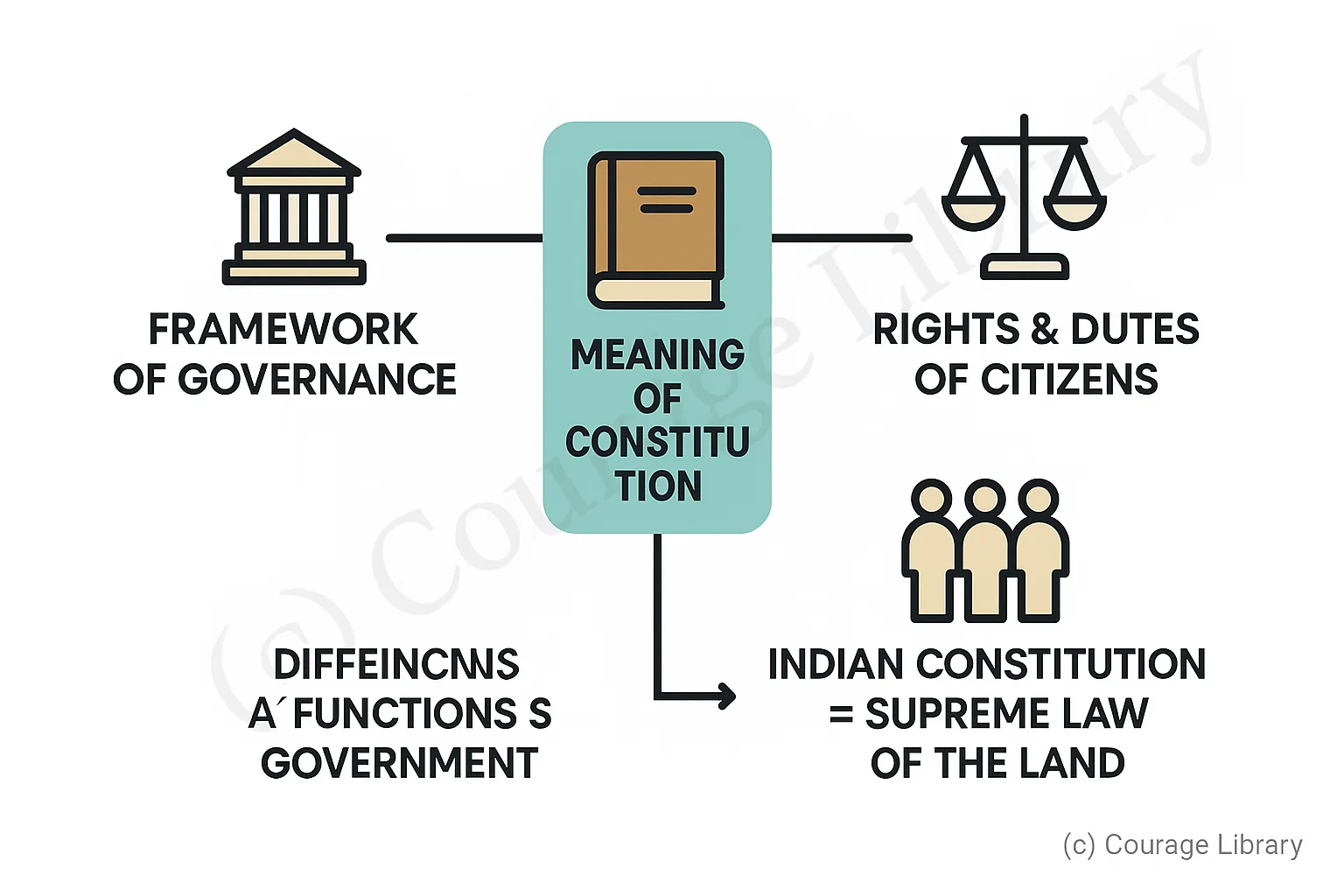
Meaning of Constitution
-
A constitution is the fundamental legal document that:
- Lays down the framework of governance.
- Defines the powers and functions of government organs.
- Provides rights and duties to citizens.
- Indian Constitution = supreme law of the land.
Features of Indian Constitution
| Feature | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Lengthiest Constitution | Originally 395 Articles, 22 Parts, 8 Schedules. Now has 470+ Articles. |
| Parliamentary System | Based on UK model: PM is real executive; President is nominal. |
| Written Constitution | Fully written and codified document. |
| Federal in Form, Unitary in Spirit | Strong Centre (e.g., single Constitution, All-India Services). |
| Blend of Rigidity and Flexibility | Some provisions require special majority; some by simple majority. |
| Fundamental Rights & Duties | Inspired by US; guaranteed by Constitution. |
| Secular State | Equal respect to all religions. |
| Universal Adult Franchise | Every citizen above 18 years can vote. |
| Independent Judiciary | Supreme Court ensures constitutional supremacy. |
| Single Citizenship | All Indians are citizens of India only. |
| Directive Principles | Socio-economic goals for government (from Ireland). |
| Emergency Provisions | Allows Centre to take control during crisis. |
Sources of Indian Constitution
| Provision Borrowed | Source Country |
|---|---|
| Fundamental Rights | USA |
| Directive Principles of State Policy | Ireland (Irish Constitution) |
| Parliamentary System | UK |
| Federation with strong Centre | Canada |
| Fundamental Duties | USSR (Russia) |
| Procedure for Amendment | South Africa |
| Suspension of Fundamental Rights | Germany (Weimar Constitution) |
| Concurrent List | Australia |
| Idea of Justice, Liberty, Equality | France (Preamble ideas) |
Preamble of the Constitution
The Preamble is the introduction to the Constitution. It declares:
"We, the People of India, having solemnly resolved to constitute India into a:
Sovereign,
Socialist,
Secular,
Democratic,
Republic
and to secure to all its citizens:
Justice — social, economic and political
Liberty — of thought, expression, belief, faith and worship
Equality — of status and of opportunity
Fraternity — assuring the dignity of the individual and the unity and integrity
of the nation..."
Added by 42nd Amendment (1976): "Socialist", "Secular", and "Integrity".
The Preamble is non-justiciable (not enforceable by courts) but helps in interpreting the
Constitution.

Union vs State Features
| Aspect | Union Features (Centralized) | State Features (Decentralized) |
|---|---|---|
| Constitution | Single Constitution for Centre & States | States cannot frame their own constitution |
| Citizenship | Single citizenship for all Indians | No separate state citizenship |
| Parliament Powers | Parliament can override State laws on Concurrent List | States can legislate on State List only |
| All-India Services | IAS, IPS, etc. common to both Centre and States | Appointed by Centre |
| Emergency Powers | During emergencies, Centre gains full control | States’ autonomy is curtailed |
| Appointment of Governor | By President (i.e., Centre) | Acts as Centre’s agent in state |
| Unequal Division of Powers | More subjects and stronger hold with Centre | States have fewer subjects (66 vs 47 in Lists) |
| Judiciary | Single, integrated judiciary system | No separate High Court system |
So, India is federal in structure, but unitary in essence during emergencies.
Start Your SSC CGL Journey Now!
Join Courage Library to experience disciplined study and expert support.
Be a Couragian!