SSC CGL - Detailed Guide 2025
Self-Paced Course

Fundamental Rights & Duties
Reference: Lucent GK, NCERT Class 6–12
6 Fundamental Rights (Articles 12–35)
Part III of the Constitution (Articles 12–35) guarantees six Fundamental Rights to all citizens of India:
| Right | Articles | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Right to Equality | 14–18 | Equality before law, no discrimination, equal access to public places. |
| Right to Freedom | 19–22 | Freedom of speech, assembly, association, movement, residence, profession; protection from arbitrary arrest. |
| Right against Exploitation | 23–24 | Prohibits human trafficking, forced labor, and child labor in factories/mines. |
| Right to Freedom of Religion | 25–28 | Freedom to profess, practice, and propagate any religion. |
| Right to Cultural & Educational | 29–30 | Protection of language, script, culture of minorities; minority educational rights. |
| Right to Constitutional Remedies | 32 | Right to move the Supreme Court for enforcement of rights. Called "Heart & Soul of the Constitution" – Dr. Ambedkar. |
Additional Notes:
- Article 13: Declares any law that violates Fundamental Rights as void.
- Rights are not absolute — subject to reasonable restrictions.
Key Amendments
| Amendment | Year | Change Made |
|---|---|---|
| 42nd Amendment | 1976 | Added words: Socialist, Secular, Integrity to Preamble; added Fundamental Duties (Part IVA) |
| 44th Amendment | 1978 | Removed Right to Property from Fundamental Rights (now a legal right under Article 300A) |
Note: Right to Property was originally Article 31. After 44th Amendment, it became a legal right.
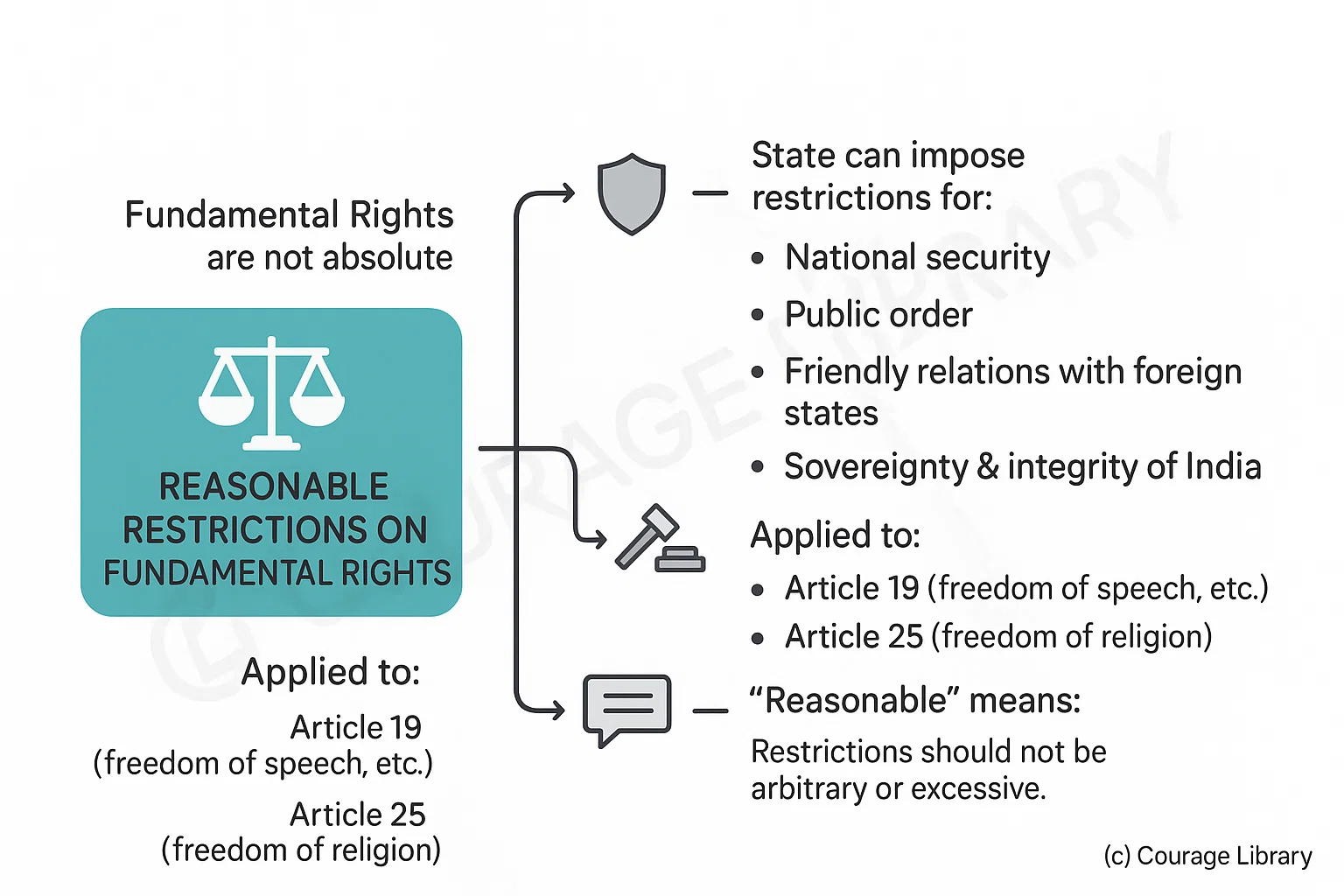
Reasonable Restrictions
Fundamental Rights are not absolute; the state can impose reasonable restrictions in the interest of:
- National security
- Public order
- Morality
- Friendly relations with foreign states
- Sovereignty and integrity of India
Applied especially to:
- Article 19 (freedom of speech, etc.)
- Article 25 (freedom of religion)
"Reasonable" means restrictions should not be arbitrary or excessive.
Fundamental Duties (Article 51A)
Part IVA (added by 42nd Amendment Act, 1976)
Article 51A lists 11 Fundamental Duties
| Duty No. | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Abide by Constitution and respect National Flag and Anthem |
| 2 | Cherish noble ideals of freedom struggle |
| 11 | (Added by 86th Amendment, 2002) — Ensure child's education (6–14 years) |
Unlike Fundamental Rights, Duties are non-justiciable (not enforceable by court), but morally binding.
Difference between Fundamental Rights and Duties
| Feature | Fundamental Rights | Fundamental Duties |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | Legal Rights (Justiciable) | Moral Obligations (Non-justiciable) |
| Enforceability | Can be enforced via courts | Not enforceable by law |
| Purpose | Protect individual liberty | Promote civic responsibility |
| Part of Constitution | Part III (Articles 12–35) | Part IVA (Article 51A) |
| Amendment Introduced | From beginning (1950) | 42nd Amendment (1976) |
| Who Benefits | Citizens (mostly); some to foreigners as well | Applies only to citizens |
Start Your SSC CGL Journey Now!
Join Courage Library to experience disciplined study and expert support.
Be a Couragian!