SSC CGL - Detailed Guide 2025
Self-Paced Course

India: Location & Structure
Reference: Lucent GK, NCERT Class 6–12
India’s Location (Latitudinal and Longitudinal Extent)
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Latitudinal Extent | 8°4′N to 37°6′N |
| Longitudinal Extent | 68°7′E to 97°25′E |
| North–South Length | ~3,214 km |
| East–West Width | ~2,933 km |
| Tropic of Cancer | 23°30′N – passes through 8 states |
| Standard Meridian | 82°30′E – basis for IST (UTC +5:30) |
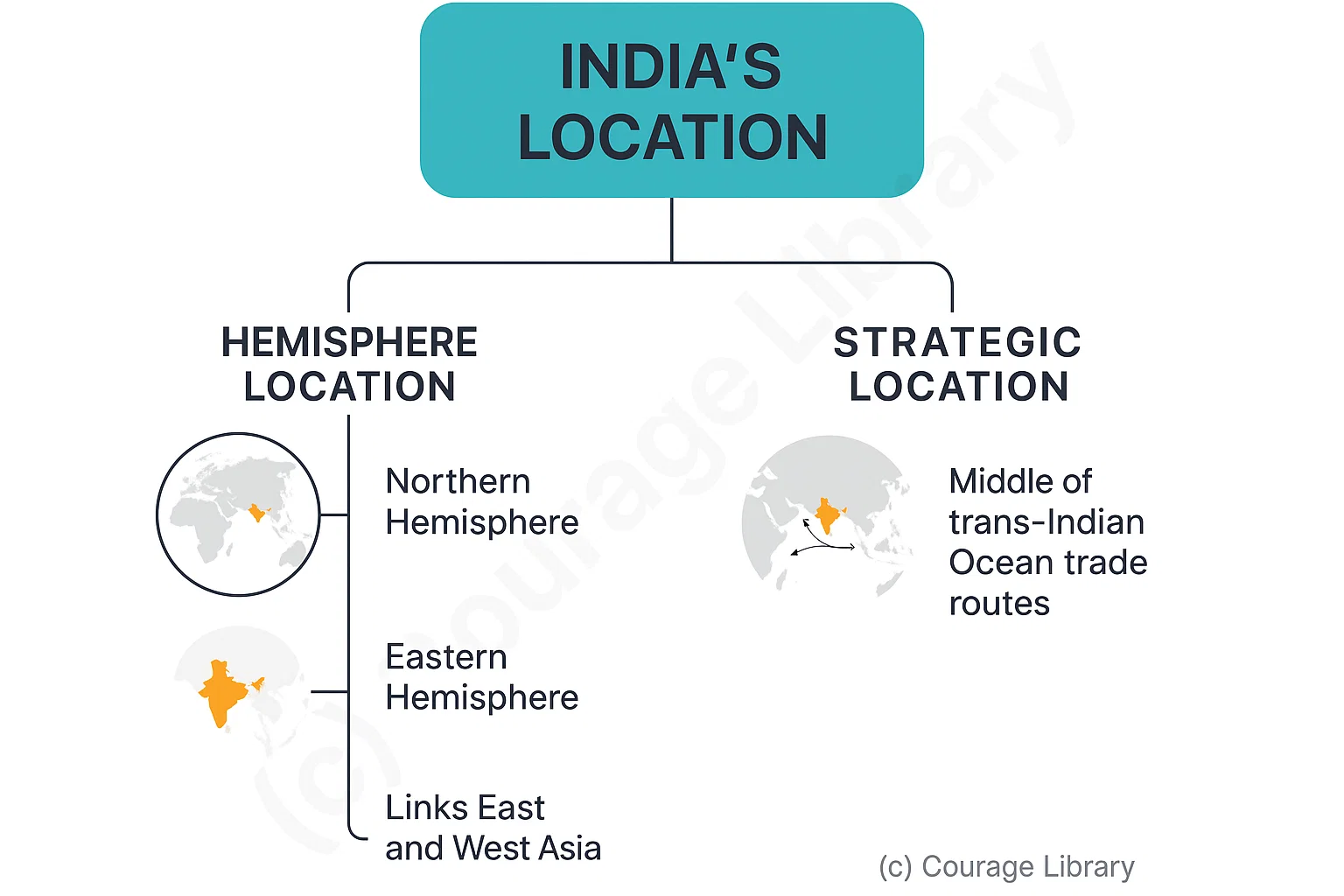
India lies entirely in the Northern and Eastern hemispheres.
India's location is strategic:
- Lies in the middle of the trans-Indian Ocean trade routes
- Links East and West Asia
Neighbors & Surrounding Water Bodies
| Direction | Neighboring Countries |
|---|---|
| North | China, Nepal, Bhutan |
| East | Bangladesh, Myanmar |
| West | Pakistan, Afghanistan (PoK region) |
| South (Sea) | Sri Lanka, Maldives (across Indian Ocean) |
India shares its borders with 7 countries and has the 3rd largest international border length after Russia and China.
| Water Body | Direction |
|---|---|
| Arabian Sea | West |
| Bay of Bengal | East |
| Indian Ocean | South |
Indian Ocean is the only ocean named after a country — India.
States, UTs & International Borders
| Category | Count |
|---|---|
| States | 28 |
| Union Territories | 8 |
| Longest Border With | Bangladesh (~4,096 km) |
| Smallest Border With | Afghanistan (~106 km) |
Notable International Borders
| Country | Bordering States/UTs |
|---|---|
| Pakistan | J&K, Punjab, Rajasthan, Gujarat |
| China | J&K, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, Arunachal |
| Nepal | Uttarakhand, UP, Bihar, Sikkim, West Bengal |
| Bhutan | Sikkim, West Bengal, Assam, Arunachal |
| Bangladesh | West Bengal, Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura, Mizoram |
| Myanmar | Arunachal, Nagaland, Manipur, Mizoram |
Geological Structure of India
India is divided into three major geological regions:
Peninsular Block
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Age | Very old – Precambrian (over 2.5 billion years) |
| Stability | Tectonically stable, no major earthquakes |
| Rock Type | Hard crystalline igneous and metamorphic rocks |
| Regions | Deccan Plateau, Chotanagpur Plateau, Western & Eastern Ghats |
| Resources | Rich in minerals like coal, iron, manganese, mica |
It forms the core of the Indian landmass.
Himalayan Region
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Formation | Result of collision between Indian & Eurasian plates (~40-50 million years ago) |
| Nature | Tectonically unstable, prone to earthquakes |
| Rock Type | Fold mountains – sedimentary rocks |
| Divisions | Western Himalayas, Central Himalayas, Eastern Himalayas |
| Major Ranges | Greater Himalayas (Himadri), Lesser Himalayas (Himachal), Shiwaliks |
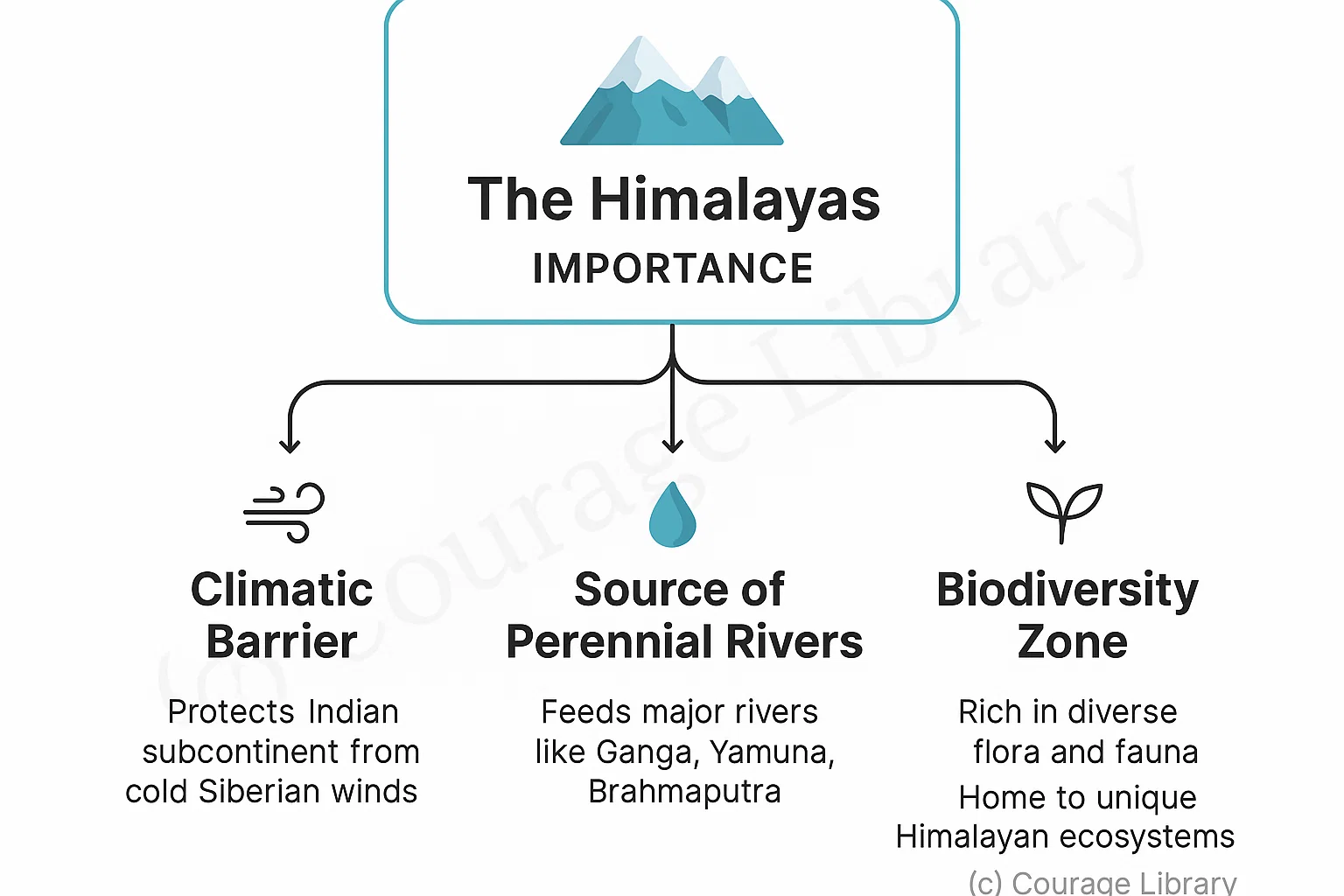
The Himalayas act as:
- A climatic barrier (protects from cold winds)
- A source of perennial rivers
- A rich biodiversity zone
Indo-Gangetic-Brahmaputra Plain
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Formation | Formed by alluvial deposits from Himalayan rivers |
| Fertility | Extremely fertile – intensive agriculture |
| Flatness | Almost featureless plain – ideal for transportation & irrigation |
| Extent | From Punjab to Assam (North India) |
Developed By Roopasree Challa
Next
Start Your SSC CGL Journey Now!
Join Courage Library to experience disciplined study and expert support.
Be a Couragian!