SSC CGL - Detailed Guide 2025
Self-Paced Course

Transportation And Communication
Reference: Lucent GK, NCERT Class 6–12
Modes of Transport
India uses four major modes of transport:
| Mode | Key Features | Advantages | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Roadways | 65% of freight & 80% of passenger traffic; flexible | Cost-effective for short distances | Traffic congestion, pollution |
| Railways | Largest rail network in Asia; lifeline of Indian transport | Efficient for long distances & bulk goods | Overcrowding, outdated infrastructure |
| Waterways | Cheapest mode; underutilized inland water transport | Fuel-efficient, eco-friendly | Slow, limited connectivity |
| Airways | Fastest mode; increasing importance post-liberalization | Saves time, good for long distances | Expensive, weather-dependent |
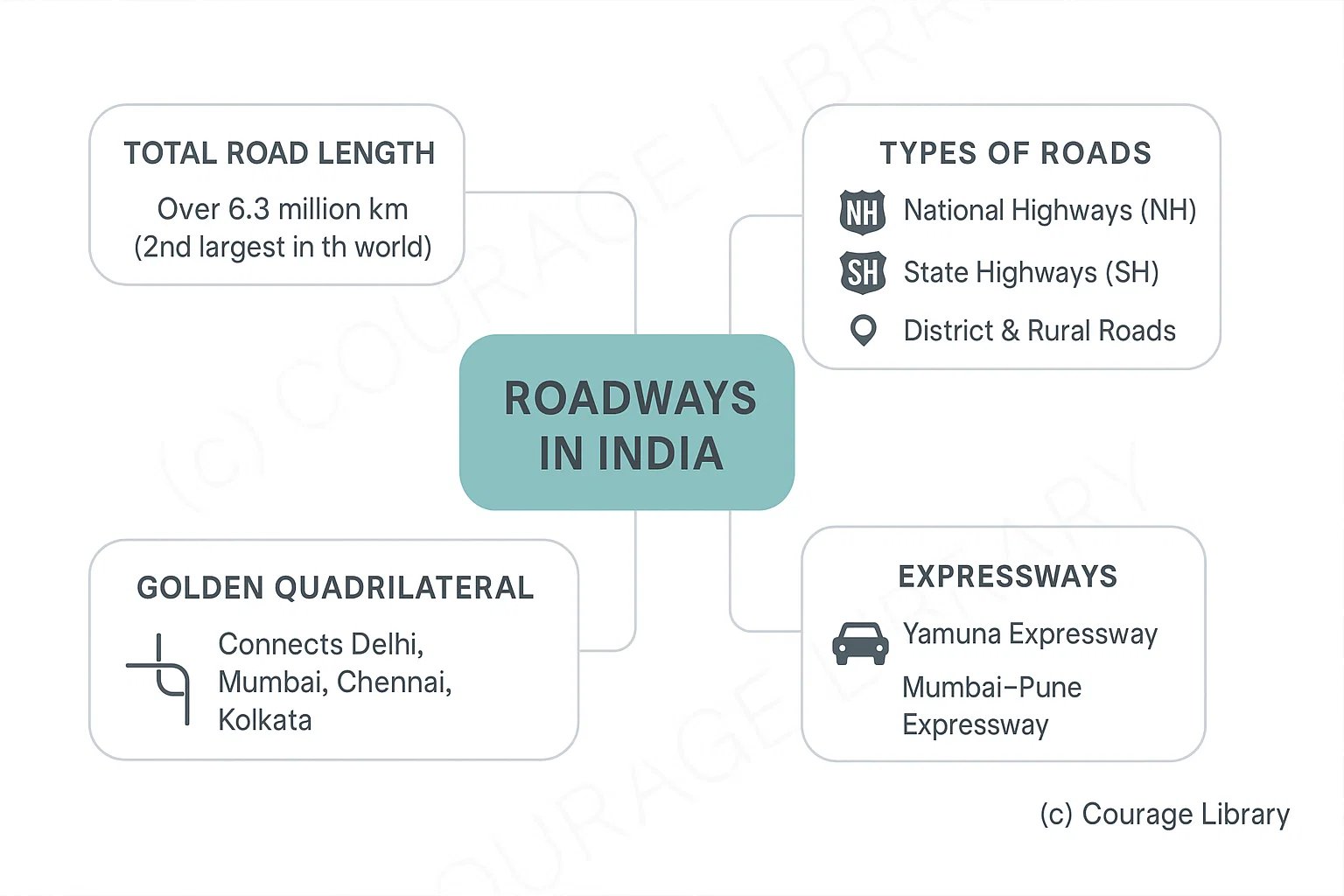
Roadways in India
- Total Road Length: Over 6.3 million km (2nd largest in the world)
- Types: National Highways (NH), State Highways (SH), District & Rural Roads
- Golden Quadrilateral: Connects Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, Kolkata
- Expressways: Yamuna Expressway, Mumbai–Pune Expressway
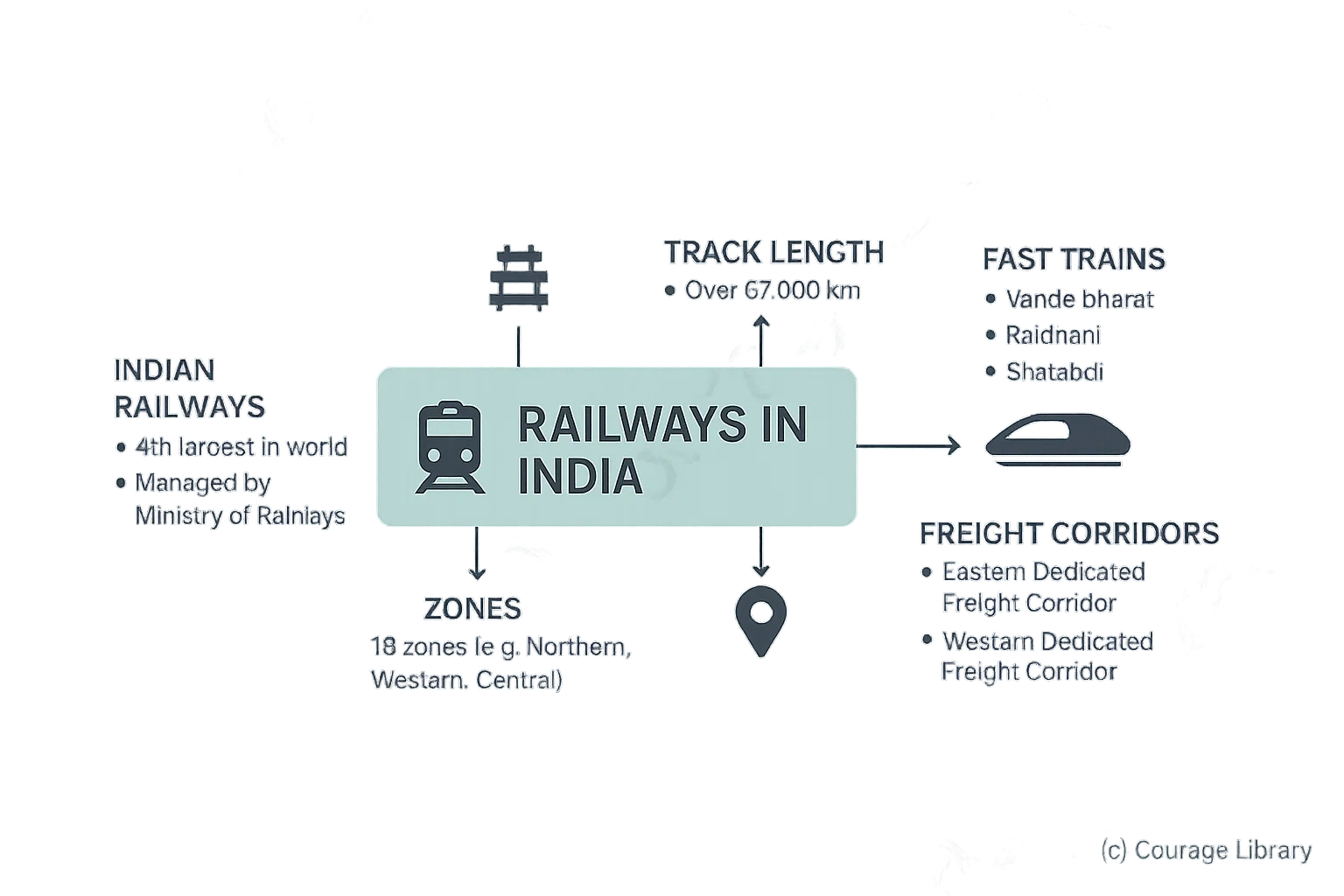
Railways in India
- Indian Railways: 4th largest in world; run by Ministry of Railways
- Track Length: Over 67,000 km
- Zones: 18 zones (e.g., Northern, Western, Central)
- Fast Trains: Vande Bharat, Rajdhani, Shatabdi
- Freight Corridors: Eastern & Western Dedicated Freight Corridors
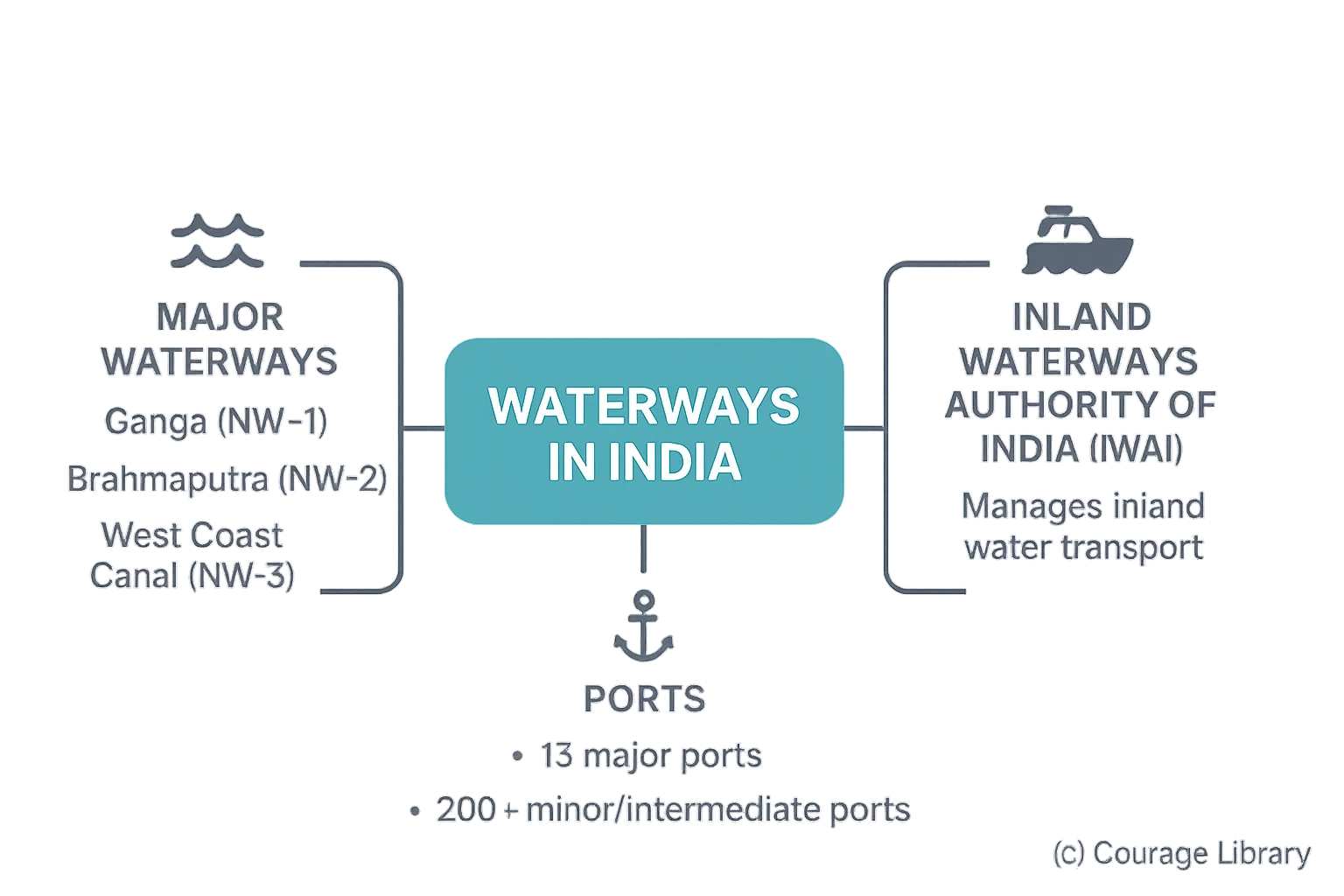
Waterways in India
- Major Waterways: Ganga (NW-1), Brahmaputra (NW-2), West Coast Canal (NW-3)
- Ports: 13 major ports + 200+ minor/intermediate ports
- Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI) manages inland water transport
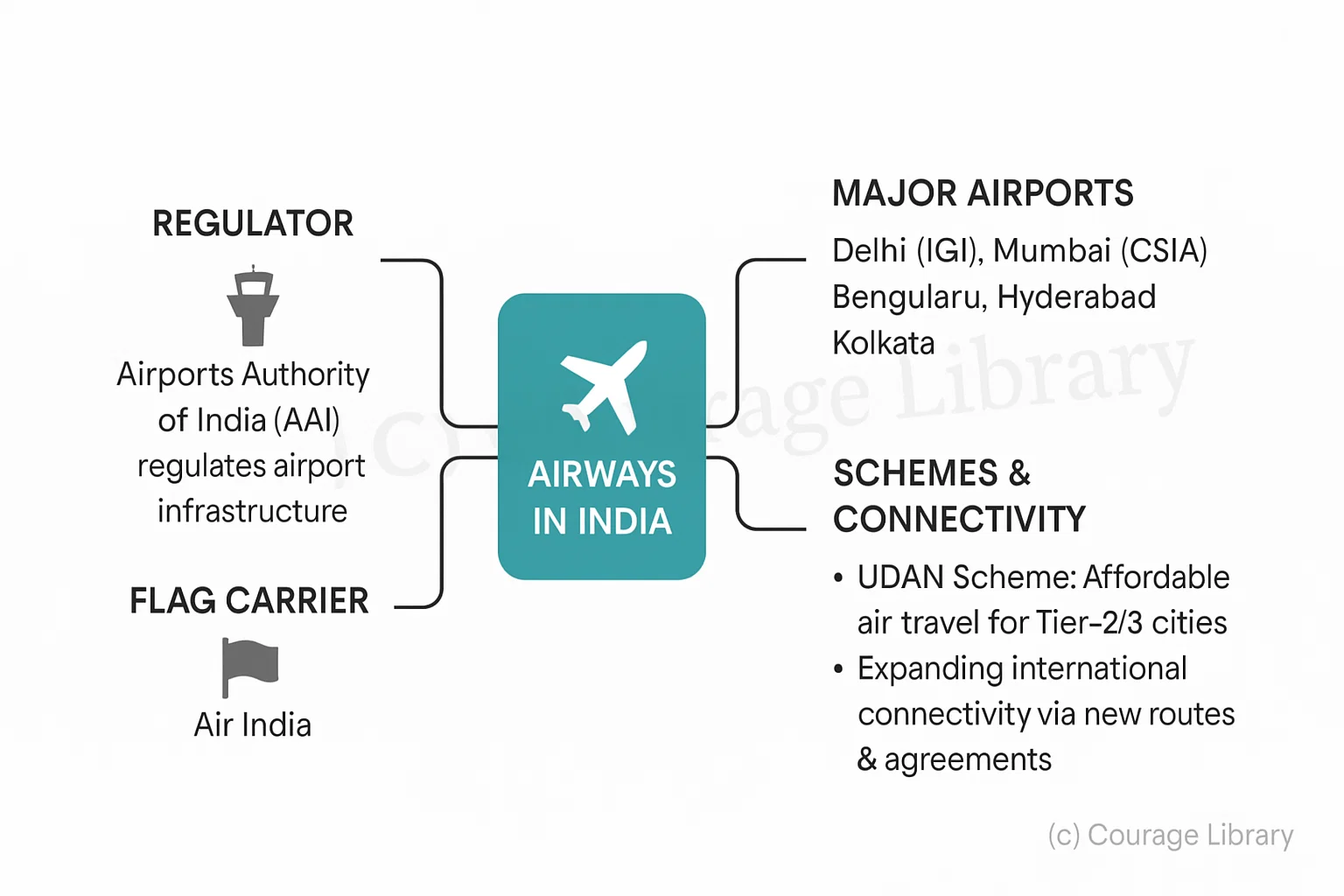
Airways in India
- Airports Authority of India (AAI) regulates airport infrastructure
- Major Airports: Delhi (IGI), Mumbai (CSIA), Bengaluru, Hyderabad, Kolkata
- Flag Carrier: Air India
- UDAN Scheme: Affordable air travel to Tier-2/3 cities
- International Connectivity: Expanding with new routes & bilateral agreements
Major Ports & Airports
Major Ports (13 total: 12 Govt + 1 Private)
| Region | Ports |
|---|---|
| West Coast | Mumbai, Kandla (Deendayal), Mormugao, New Mangalore, Kochi |
| East Coast | Kolkata (Haldia), Paradip, Visakhapatnam, Chennai, Tuticorin (V.O. Chidambaranar) |
| Union Territory | Port Blair (Andaman & Nicobar) |
- Largest Port by Volume: Kandla (Deendayal)
- Deepest Port: Visakhapatnam
- First major private port: Mundra (Gujarat)
Major Airports
| Airport | City | Special Note |
|---|---|---|
| Indira Gandhi International (IGI) | Delhi | Busiest airport in India |
| Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj (CSIA) | Mumbai | Major international hub |
| Kempegowda International | Bengaluru | Tech hub air gateway |
| Rajiv Gandhi International | Hyderabad | Known for cargo handling |
| Netaji Subhas Chandra Bose | Kolkata | Major airport of Eastern India |
Communication Networks (with Digital India relevance)
Types of Communication
| Type | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Personal | Between individuals | Mobile calls, SMS, Email |
| Mass Communication | Reaches large population | Television, Radio, Newspapers |
| Digital Communication | Internet-based, fast & interactive | WhatsApp, Social Media, UPI apps |
Communication in India – Key Facts
- Telecom: India is the 2nd largest telecom network in the world
- Internet: Over 850+ million users (as of 2024)
- Mobile Penetration: >90% coverage in rural areas
- Postal Network: Largest in the world (~1.5 lakh post offices)
Digital India Mission (Launched 2015)
| Pillar | Objective |
|---|---|
| Broadband Highways | Connect rural & remote areas |
| Universal Access to Phones | Digital inclusion through mobile connectivity |
| e-Governance | Online services for transparency & speed |
| e-Kranti | Digital delivery of government services |
| Public Internet Access | CSCs (Common Service Centres), Wi-Fi Hotspots |
| Digital Literacy | Digital Saksharta Abhiyan (DISHA) |
| Make in India | Promote electronics manufacturing |
BharatNet: World's largest rural broadband project (optical fiber to Gram Panchayats)
Developed By Md. Parvez
Next
Start Your SSC CGL Journey Now!
Join Courage Library to experience disciplined study and expert support.
Be a Couragian!