SSC CGL - Detailed Guide 2025
Self-Paced Course

Mineral and Energy Resources of India
Reference: Lucent GK, NCERT Class 6–12
Metallic & Non-Metallic Minerals
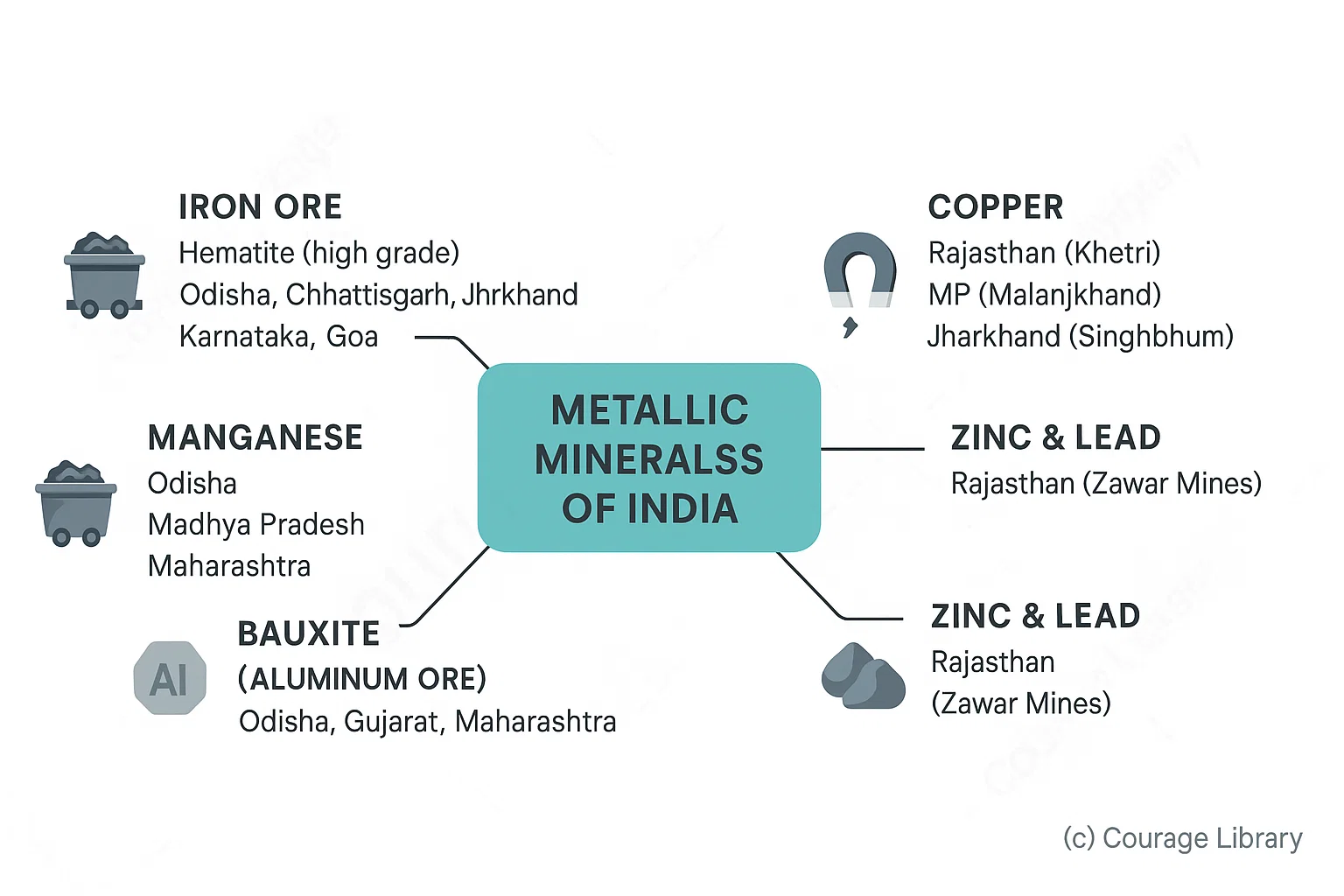
Metallic Minerals
| Type | Examples | Key States / Regions | Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ferrous Minerals | Iron ore, Manganese, Chromium | Odisha, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Karnataka | Steel, alloys, construction |
| Non-Ferrous Minerals | Bauxite, Copper, Zinc, Lead | MP, Rajasthan, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh | Electrical wires, alloys, transport |
Important Metallic Minerals:
-
Iron Ore:
- Hematite (high grade): Odisha, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Karnataka
- Magnetite (high magnetism): Karnataka, Goa
- Manganese: Odisha, MP, Maharashtra
- Bauxite (Aluminium ore): Odisha, Gujarat, Maharashtra
- Copper: Rajasthan (Khetri), MP (Malanjkhand), Jharkhand (Singhbhum)
- Zinc & Lead: Rajasthan (Zawar Mines)
Non-Metallic Minerals
| Mineral | States Found | Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Mica | Jharkhand, Andhra Pradesh, Rajasthan | Electronics, insulation |
| Limestone | MP, Rajasthan, Andhra Pradesh | Cement, construction |
| Gypsum | Rajasthan, HP | Fertilizers, cement |
| Salt | Gujarat, Rajasthan, TN | Edible & industrial salt |
| Dolomite | Odisha, Chhattisgarh | Iron & steel industry |
India is a major producer of mica and ranks high in iron ore reserves.
Energy Resources of India
India has both conventional and non-conventional sources of energy. The sector is key for development and sustainability.
Conventional Energy Sources
| Source | Details | Key States |
|---|---|---|
| Coal | India’s most abundant fossil fuel. Used in power and steel sectors. | Jharkhand, Odisha, Chhattisgarh, West Bengal, MP |
| Petroleum | Limited domestic reserves. Mostly imported. | Offshore Mumbai (Bombay High), Assam, Gujarat |
| Natural Gas | Cleaner fuel than coal; used in power, cooking, fertilizers | Krishna-Godavari basin, Assam, Tripura |
| Nuclear Energy | Used for electricity generation via nuclear fission. | Maharashtra (Tarapur), TN (Kalpakkam), Gujarat (Kakrapar), Rajasthan (Rawatbhata) |
India has 4th largest coal reserves in the world.
Non-Conventional/Renewable Energy Sources
| Source | Features | Major Regions/Projects |
|---|---|---|
| Hydroelectric | Clean, renewable; uses river flow | Tehri (UK), Sardar Sarovar (Gujarat), Bhakra-Nangal (HP/Punjab) |
| Solar | Abundant in Rajasthan, Gujarat, Telangana | Largest project: Bhadla Solar Park (Rajasthan) |
| Wind | High potential in Tamil Nadu, Gujarat | Muppandal (TN), Kutch (Gujarat) |
| Biomass | Organic waste-based energy | Rural India, sugar industry regions |
| Tidal | Least developed; potential in coastal areas | Gulf of Kutch, Sunderbans |
India ranks among top countries in installed solar and wind energy capacities.
Major Mining Areas & Distribution
| Mineral | Major Mining Areas |
|---|---|
| Iron Ore | Odisha (Keonjhar, Sundargarh), Chhattisgarh (Bailadila), Karnataka (Bellary), Jharkhand (Singhbhum) |
| Coal | Jharkhand (Jharia, Bokaro), Odisha (Talcher), Chhattisgarh (Korba), West Bengal (Raniganj) |
| Bauxite | Odisha (Kalahandi, Koraput), Maharashtra (Kolhapur), Gujarat |
| Copper | Rajasthan (Khetri), MP (Malanjkhand), Jharkhand (Singhbhum) |
| Mica | Jharkhand (Kodarma), AP (Nellore), Rajasthan |
| Gold | Karnataka (Kolar, Hutti mines), Jharkhand (Lawa, Singhbhum) |
| Uranium | Jharkhand (Jaduguda), AP (Tummalapalle) |
| Limestone | Rajasthan, MP, Tamil Nadu |
Note:
- Jharkhand is the mineral-richest state of India.
- Most of India’s mining belts lie in the peninsular plateau region.
Developed By Roopasree Challa
Next
Start Your SSC CGL Journey Now!
Join Courage Library to experience disciplined study and expert support.
Be a Couragian!