SSC CGL - Detailed Guide 2025
Self-Paced Course

Natural Vegetation & Wildlife
Reference: Lucent GK, NCERT Class 6–12
Forest Types in India
Forest classification in India is primarily based on rainfall, altitude, and temperature. As per the Champion & Seth classification, forests are categorized into several major types:
| Type | Rainfall / Climate | Regions | Key Species |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tropical Evergreen Forests | >200 cm, hot & humid | Western Ghats, NE India, Andamans | Ebony, Mahogany, Rosewood |
| Tropical Deciduous (Monsoon) Forests | 100–200 cm, seasonal rainfall | Central India, UP, Bihar, MP | Sal, Teak, Bamboo |
| Thorn & Scrub Forests | <75 cm, dry & arid | Rajasthan, Gujarat, Deccan Plateau | Acacia, Euphorbia |
| Montane Forests | Vary with altitude (1000–3500 m) | Himalayan region | Pine, Deodar, Spruce |
| Littoral & Swamp Forests (Mangroves) | Coastal/tidal areas | Sundarbans, Andaman, Mahanadi Delta | Sundari trees, Coconut, Palm |
- Tropical Deciduous Forests are the most widespread type in India.
- Sundarbans (West Bengal) has the world’s largest mangrove forest.
Biodiversity Hotspots
| Biodiversity Hotspot | Location | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Himalayas | Jammu & Kashmir to Arunachal Pradesh | Rare Himalayan flora & fauna |
| Western Ghats | Maharashtra, Kerala, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu | Endemic species like Lion-tailed macaque |
| Indo-Burma Region | NE states, Andaman Islands | High bird diversity |
| Sundaland (Nicobar Islands) | Nicobar Islands | Coral reefs, tropical forests |
Key Biodiversity Facts:
- ~7.6% of world’s mammals, 12.6% of birds, 6.2% of reptiles are found in India.
- Endemic species: Lion-tailed macaque, Nilgiri Tahr, Indian Giant Squirrel.
Wildlife Sanctuaries, National Parks, Biosphere Reserves
These are protected areas categorized based on the degree of protection and ecological purpose.
| Category | Features | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Wildlife Sanctuary | Least restricted; human activity allowed (with control) | Periyar (Kerala), Bhadra (Karnataka) |
| National Park | Strictly protected; no human activity allowed | Jim Corbett (1st, Uttarakhand), Kaziranga (Assam) |
| Biosphere Reserve | Large areas; includes core, buffer & transition zones | Nilgiri, Sundarbans, Gulf of Mannar |
-
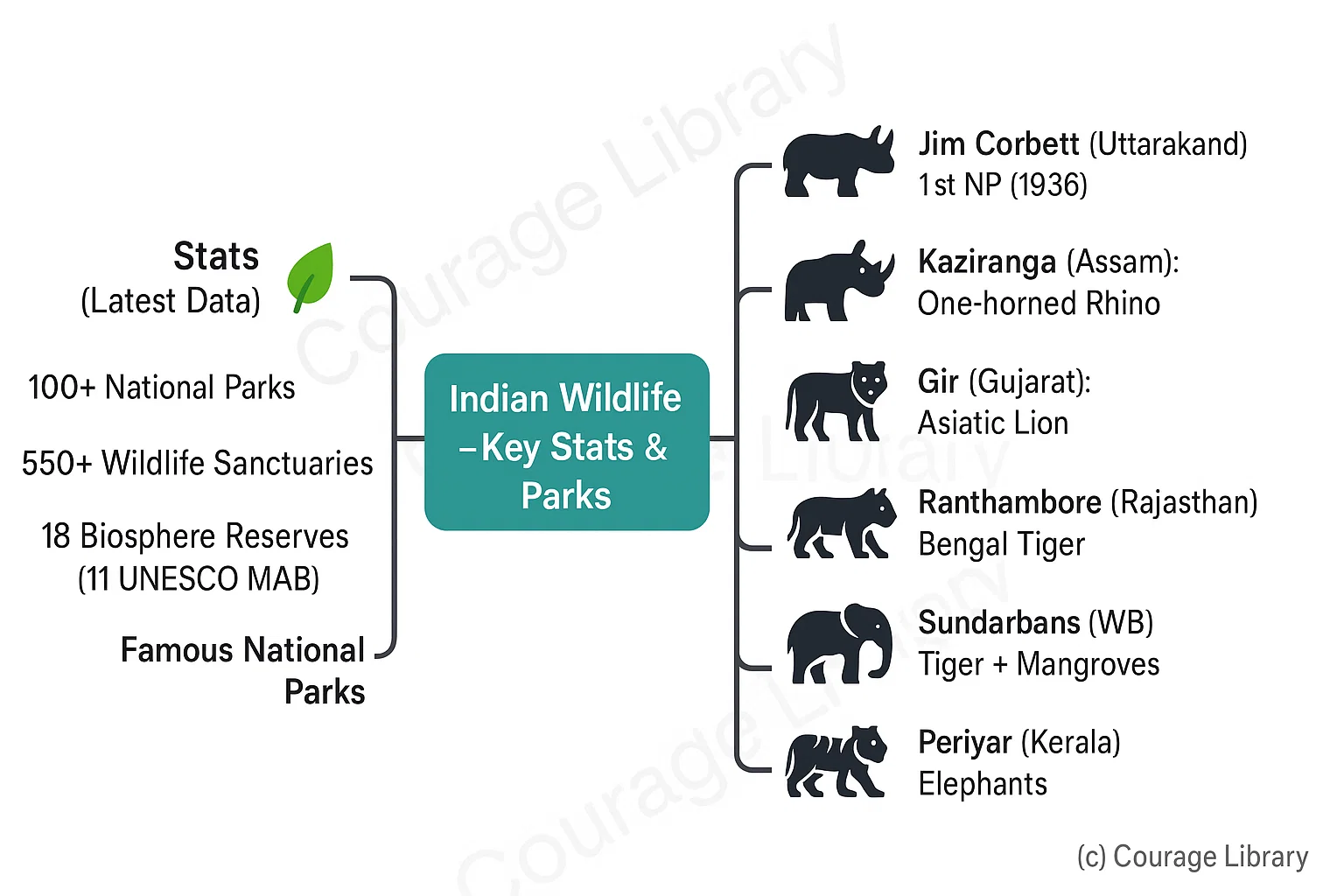
Numbers (as per latest available data):
- 100+ National Parks
- 550+ Wildlife Sanctuaries
- 18 Biosphere Reserves (11 recognized under UNESCO’s MAB)
-
Famous National Parks:
- Jim Corbett (Uttarakhand) – First NP of India (1936)
- Kaziranga (Assam) – One-horned Rhino
- Gir (Gujarat) – Asiatic Lion
- Ranthambore (Rajasthan) – Bengal Tiger
- Sundarbans (WB) – Royal Bengal Tiger + Mangroves
- Periyar (Kerala) – Elephants
Conservation Projects
| Project Name | Year Started | Aim | Key Focus Area / Animal |
|---|---|---|---|
| Project Elephant | 1992 | Elephant conservation & corridor management | Assam, Kerala, Jharkhand |
| Crocodile Breeding | 1975 | Protect freshwater, saltwater & gharial | Odisha, Bihar |
| Project Snow Leopard | 2009 | Conservation in Himalayan states | Ladakh, Himachal, Uttarakhand |
| Project Rhino (Assam) | State-level | Increase Rhino population | Kaziranga |
| Project Lion | 1972 | Protect Asiatic Lions | Gir National Park |
-
Other efforts:
- Wildlife Protection Act (1972)
- Forest Conservation Act (1980)
- CAMPA Fund (Compensatory Afforestation)
- National Board for Wildlife (NBWL)
Developed By Roopasree Challa
Next
Start Your SSC CGL Journey Now!
Join Courage Library to experience disciplined study and expert support.
Be a Couragian!