SSC CGL - Detailed Guide 2025
Self-Paced Course

Gupta Empire & Post-Gupta Period
Reference: Lucent GK, NCERT Class 6–12
Gupta Empire (c. 320 CE – 550 CE)
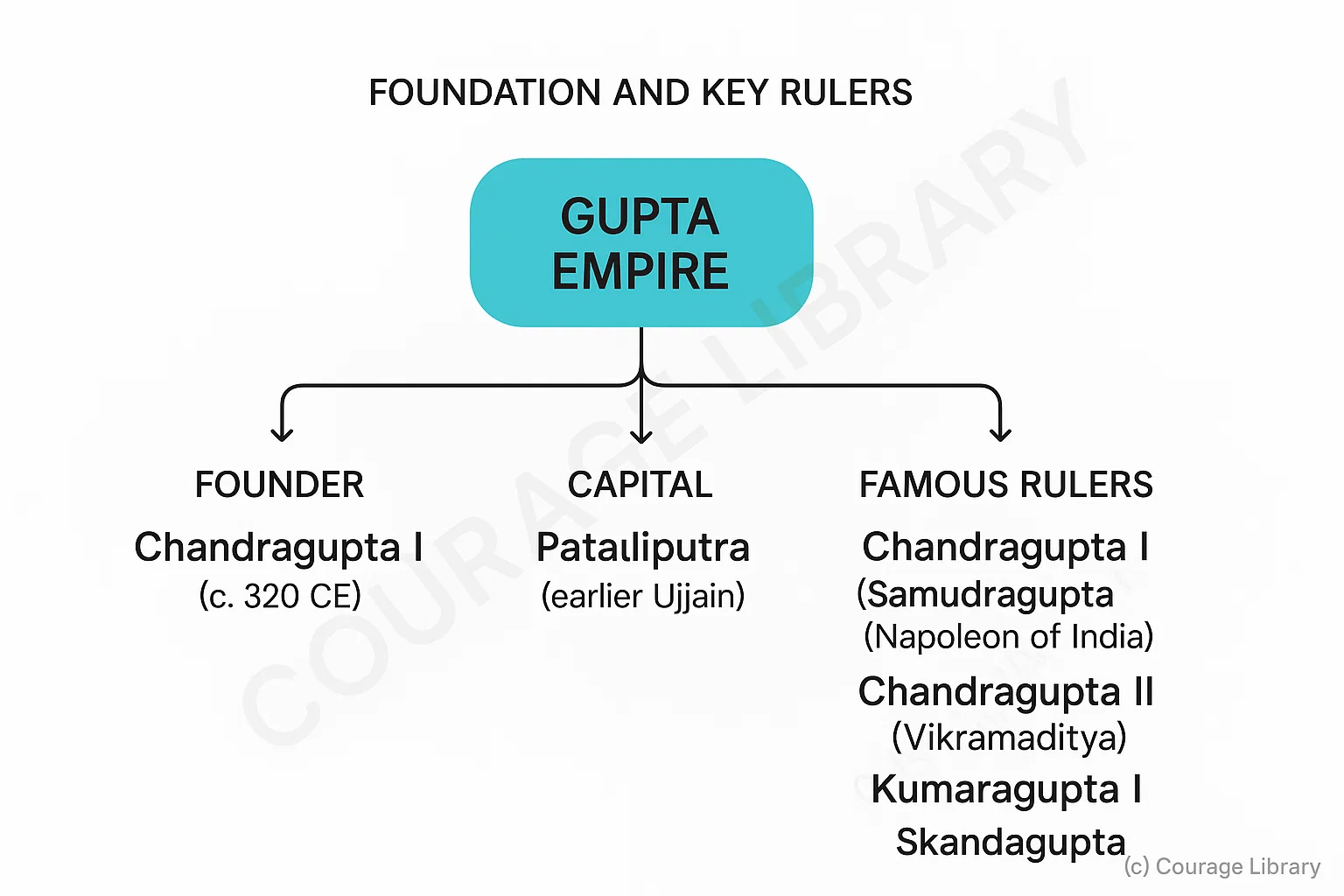
Foundation and Key Rulers
- Founder: Chandragupta I (c. 320 CE)
- Capital: Pataliputra (earlier also Ujjain)
-
Famous Rulers:
- Chandragupta I
- Samudragupta (the Napoleon of India)
- Chandragupta II (Vikramaditya)
- Kumaragupta I
- Skandagupta
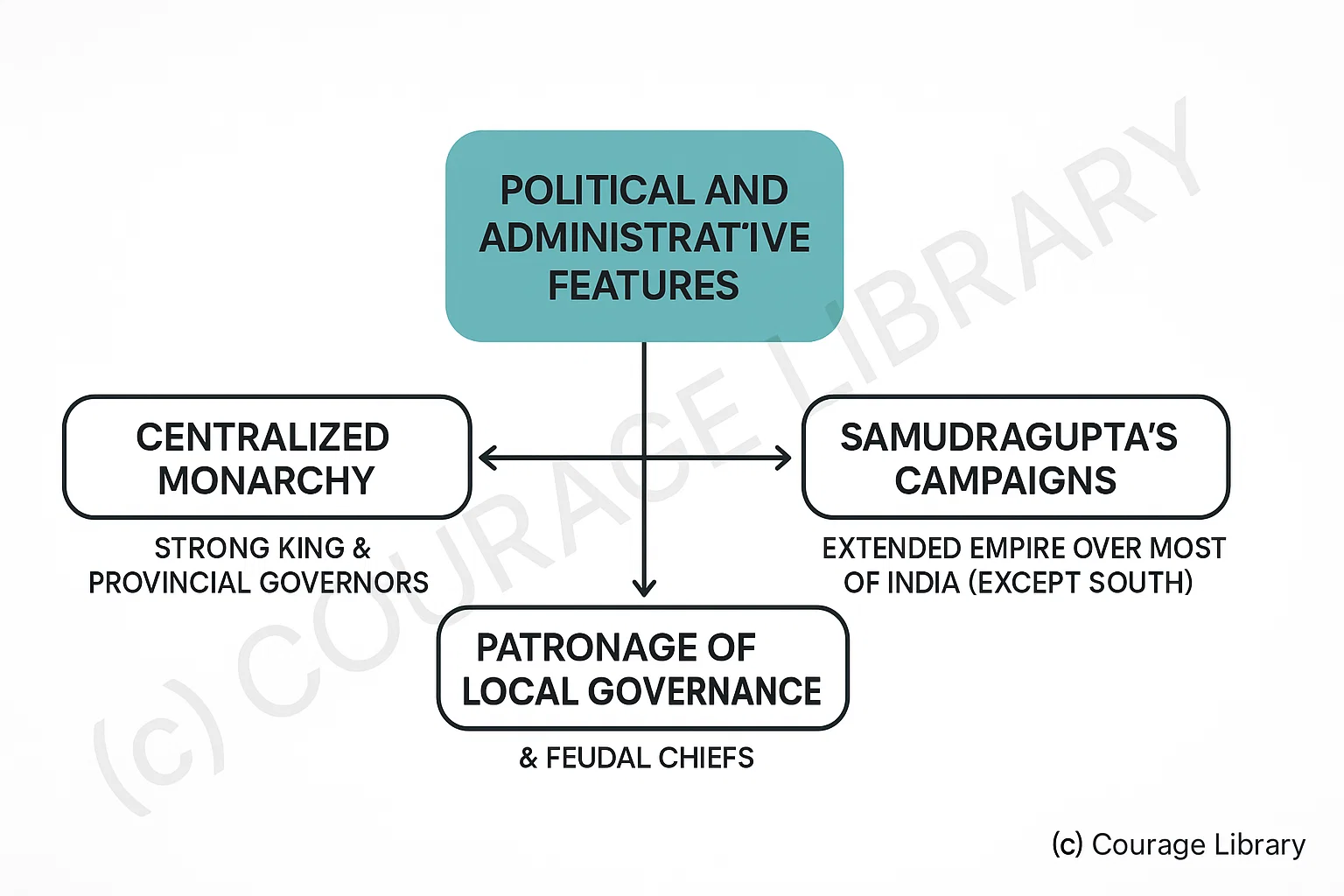
Political and Administrative Features
- Centralized monarchy with a strong king and provincial governors
- Samudragupta’s military campaigns extended empire over almost entire India (except south)
- Gupta rulers patronized local governance and feudal chiefs
- Well-organized bureaucracy and taxation system
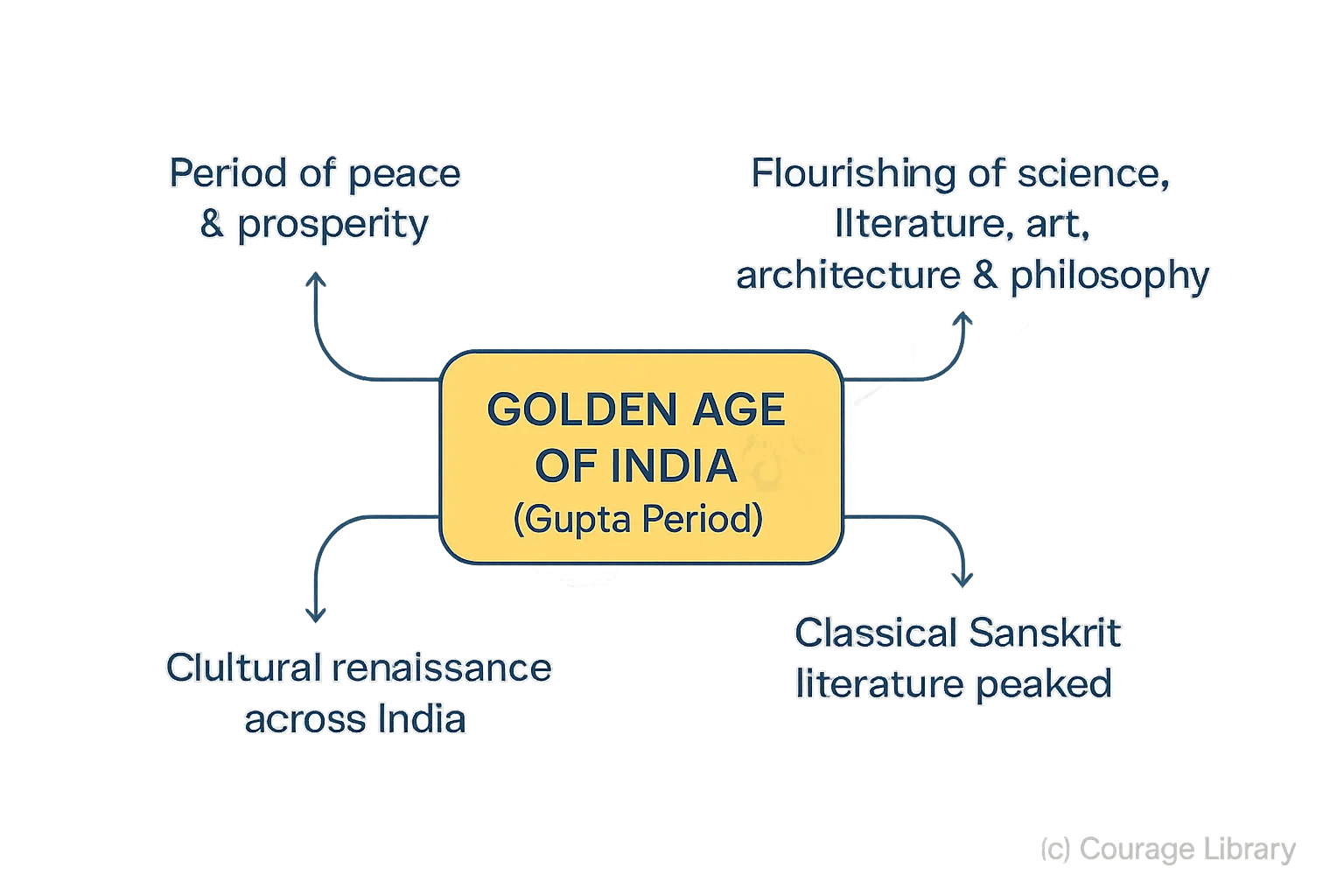
Golden Age of India
- Period of peace, prosperity, and cultural renaissance
- Flourishing of science, literature, art, architecture, and philosophy
- Classical Sanskrit literature reached its peak

Contributions of Key Rulers
-
Samudragupta:
- Military genius, recorded in Allahabad Pillar inscription
- Patron of arts and poetry
-
Chandragupta II (Vikramaditya)
- Expanded empire westwards
- Supported scholars like Kalidasa
- Promoted Hinduism alongside Buddhism and Jainism
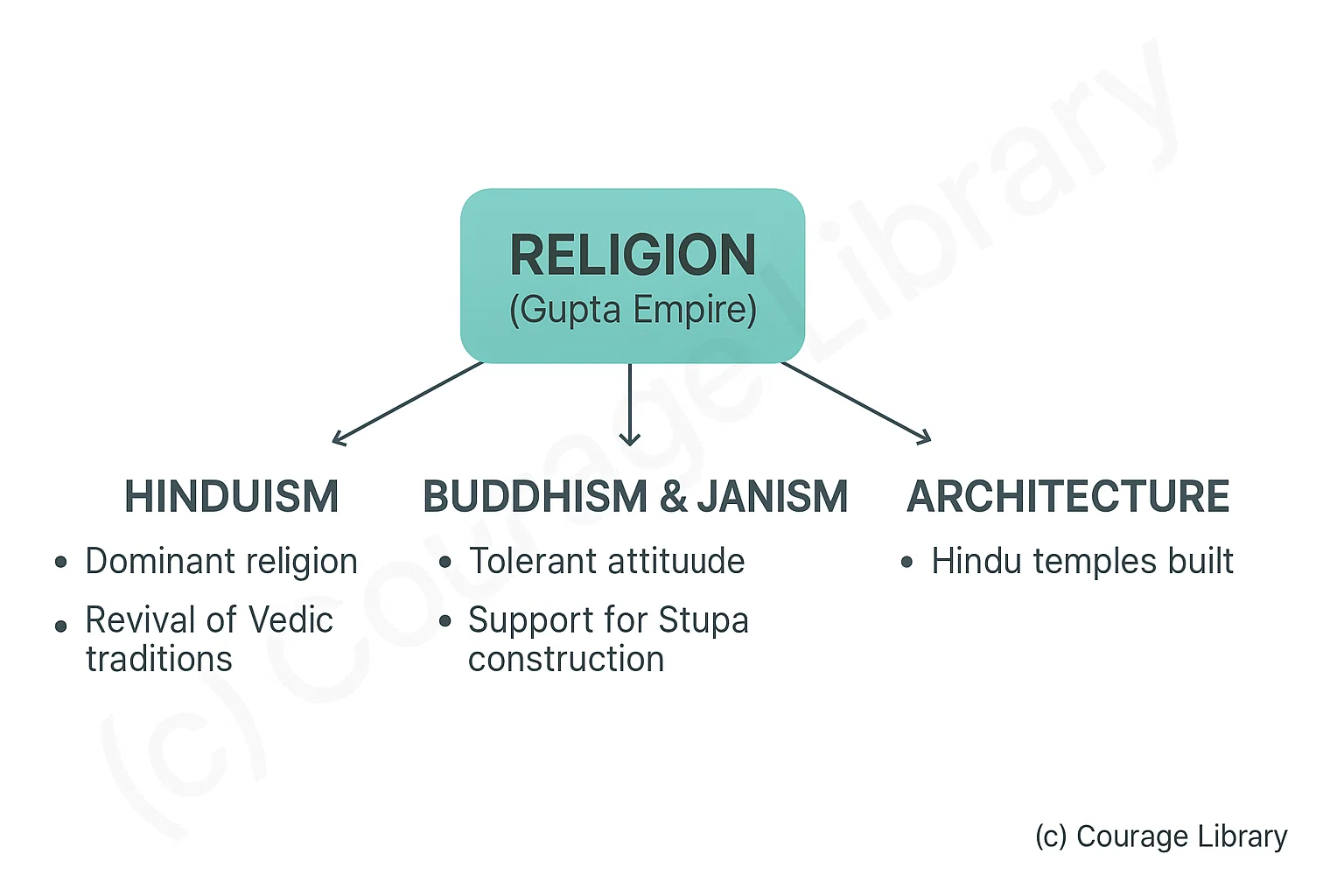
Religion
- Hinduism was dominant, revival of Vedic traditions
- Tolerant attitude towards Buddhism and Jainism
- Construction of Hindu temples and Buddhist Stupas
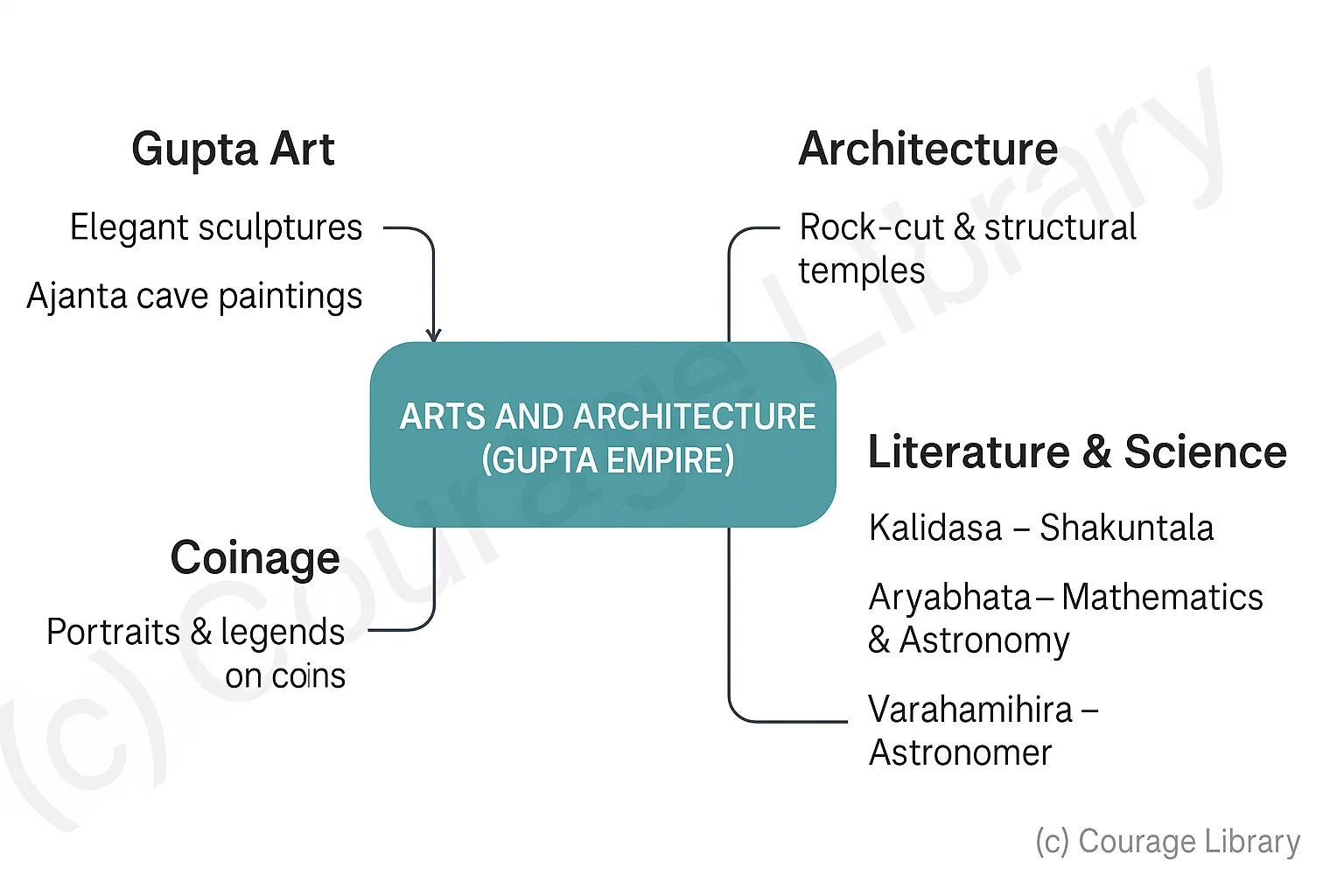
Arts and Architecture
- Development of Gupta style of art: elegant sculptures,cave temples (Ajanta caves)
- Coinage with portraits and legends
- Temples started emerging with distinct architectural style (rock-cut and structural)
- Literature: Kalidasa(Shakuntala), Aryabhata (mathematician - astronomer), Varahamihira
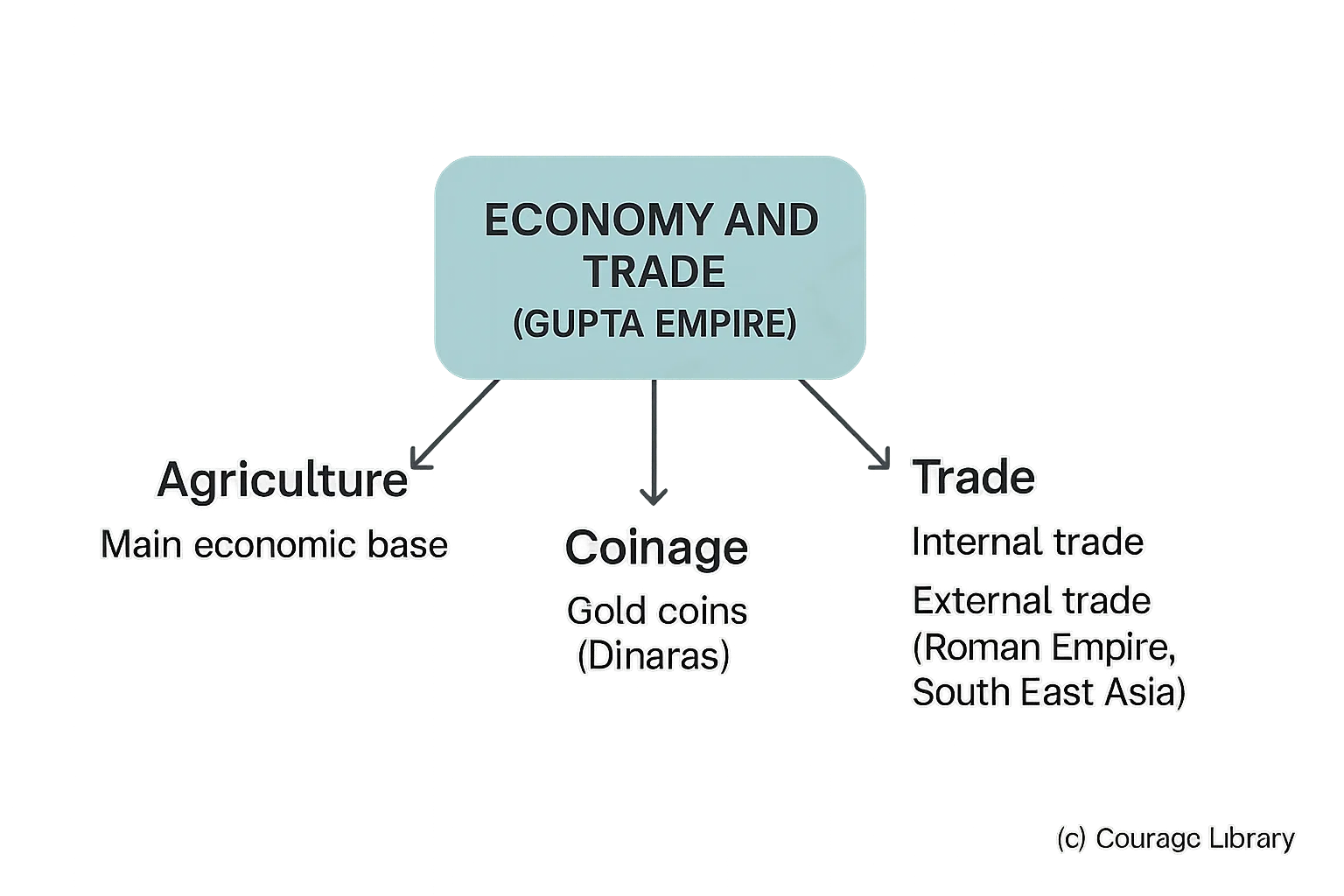
Economy and Trade
- Agriculture is the main economic base
- Growth in internal and external trade (contacts with Roman Empire and South East Asia)
- Use of gold coins (dinara)
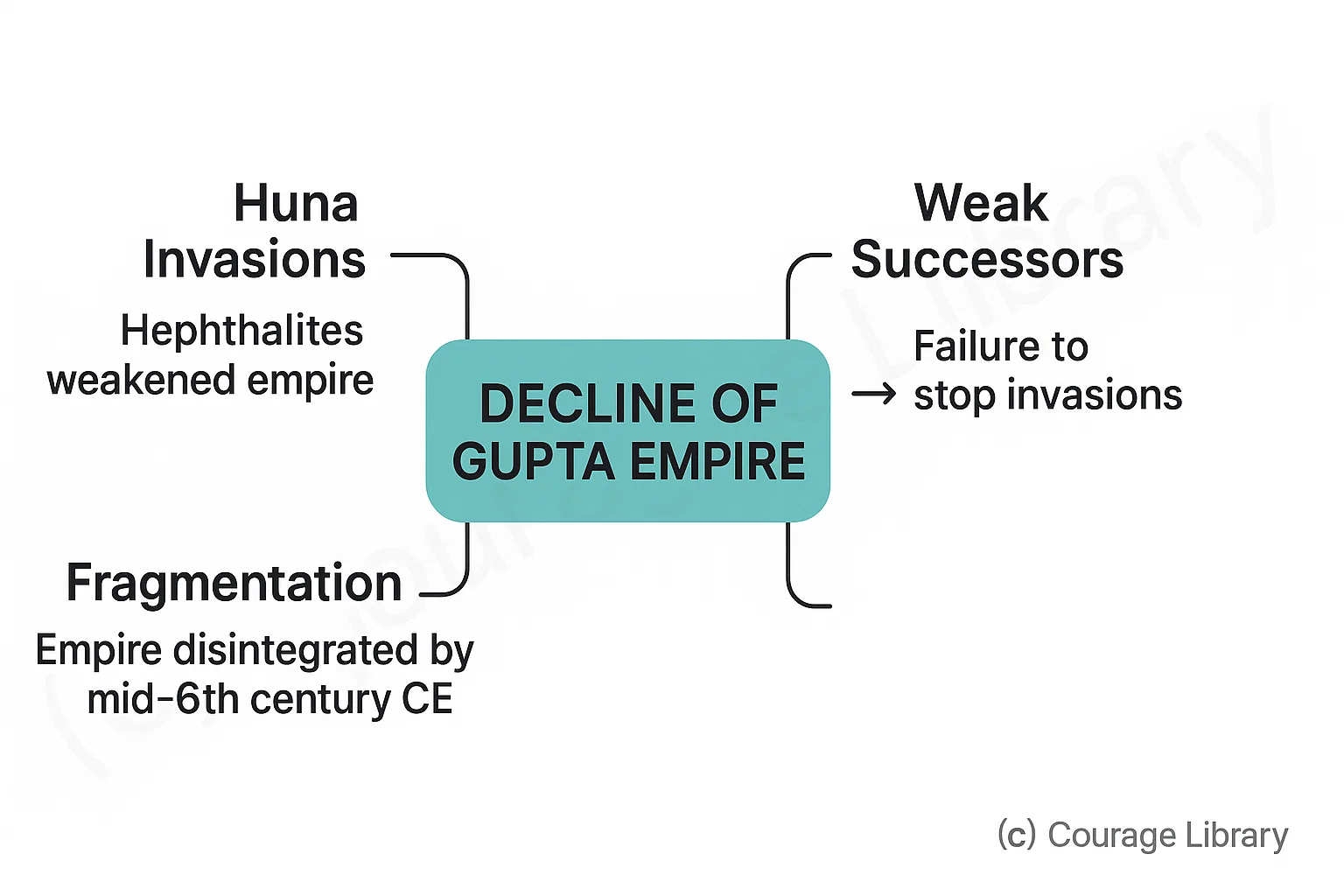
Decline
- Invasion by the Huns (Hephthalites) weakened empire
- Later Gupta rulers failed to stop invasions, empire fragmented by mid 6th century CE
Post-Gupta Period (c. 550 CE-750 CE)
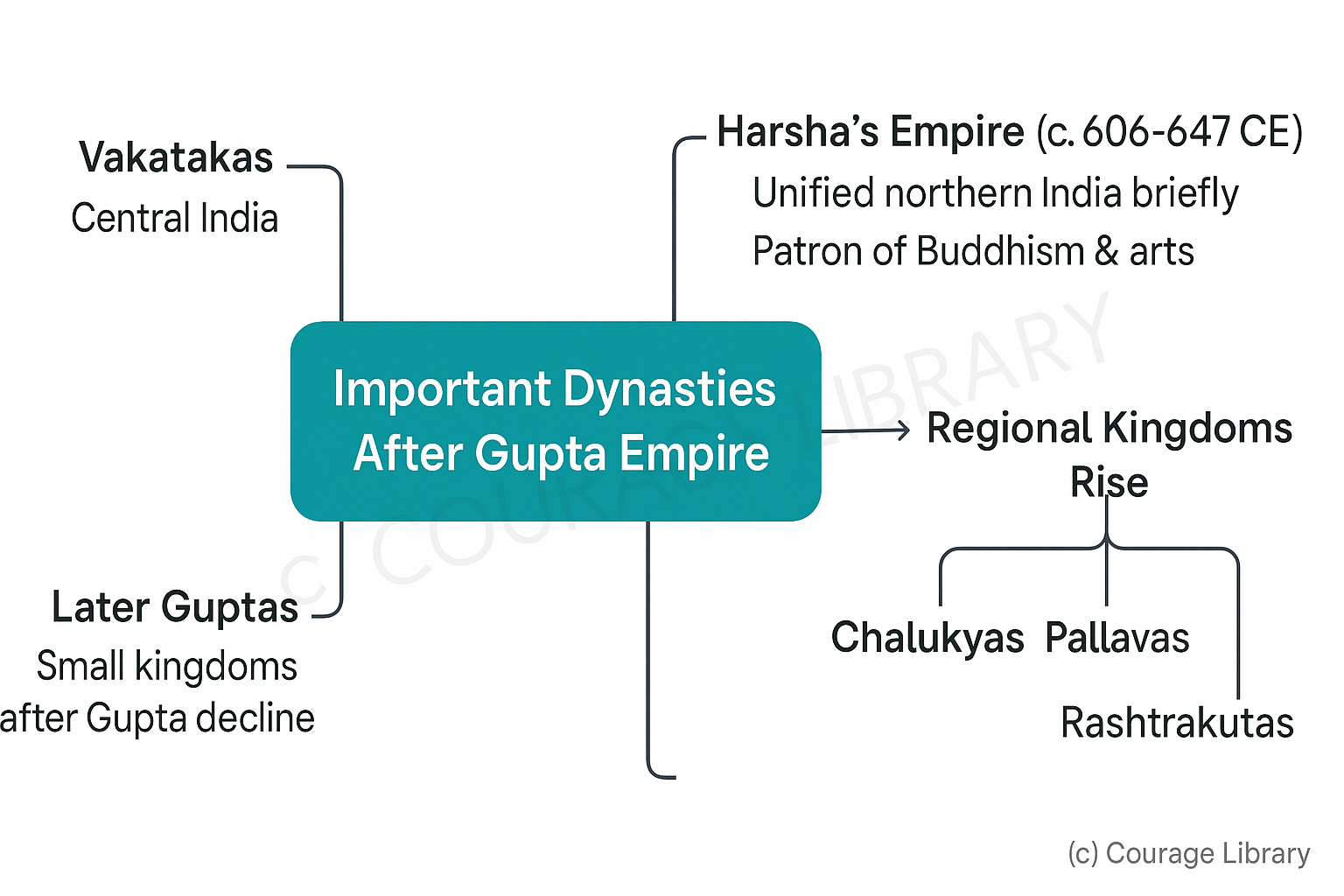
Important Dynasties
- Vakatakas (Central India)
-
Harsha's Empire (c. 606-647 CE)
- Harshavardhana ruled from Kanauj
- Unified northern India briefly after Gupta decline
- Patron of Buddhism and arts
- Later Guptas (small kingdoms)
- Rise of regional kingdoms: Chalukyas, Pallavas, Rashtrakutas
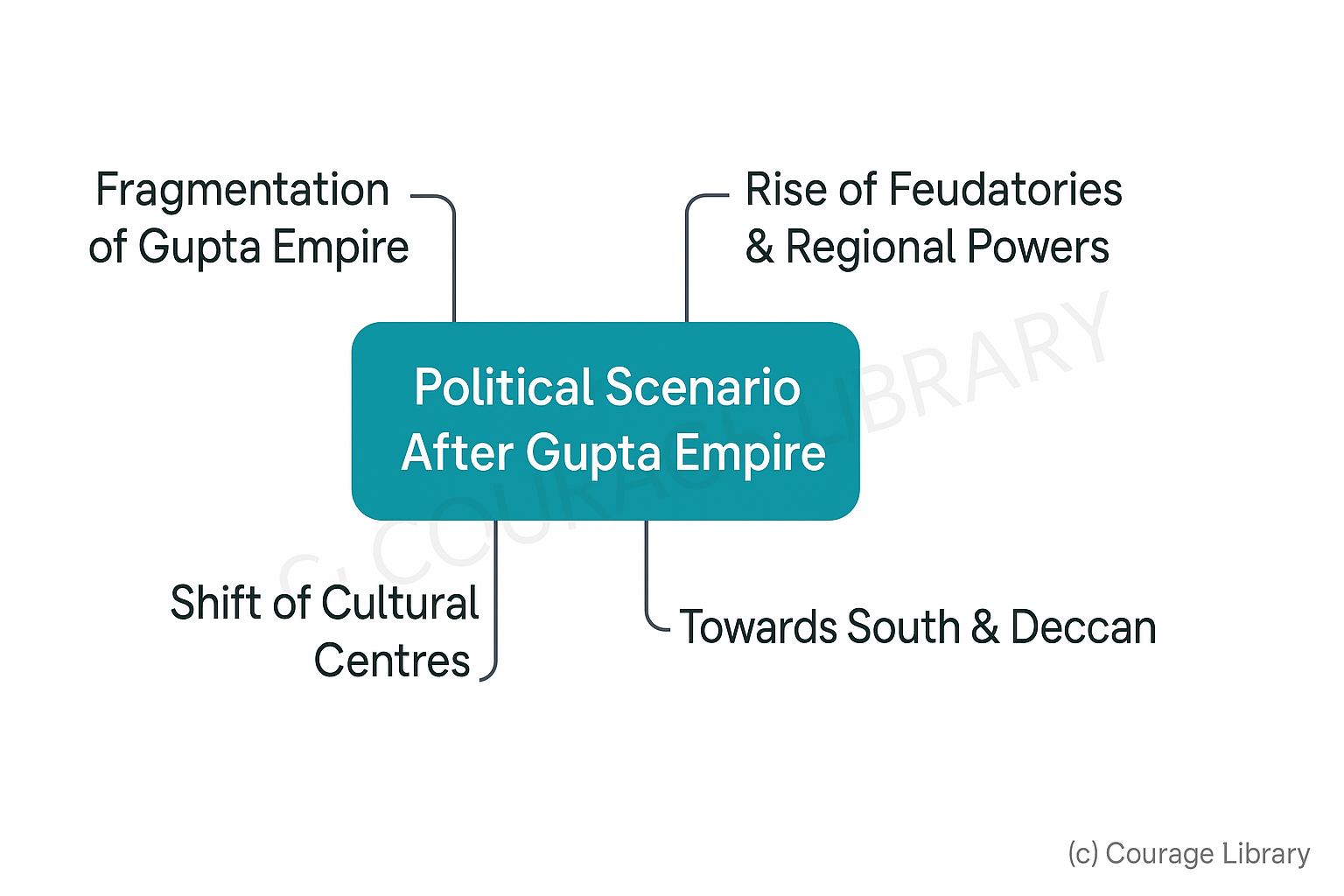
Political Scenario
- Fragmentation of Gupta Empire
- Rise of feudatories and regional powers
- Shift of cultural centres towards south and Deccan
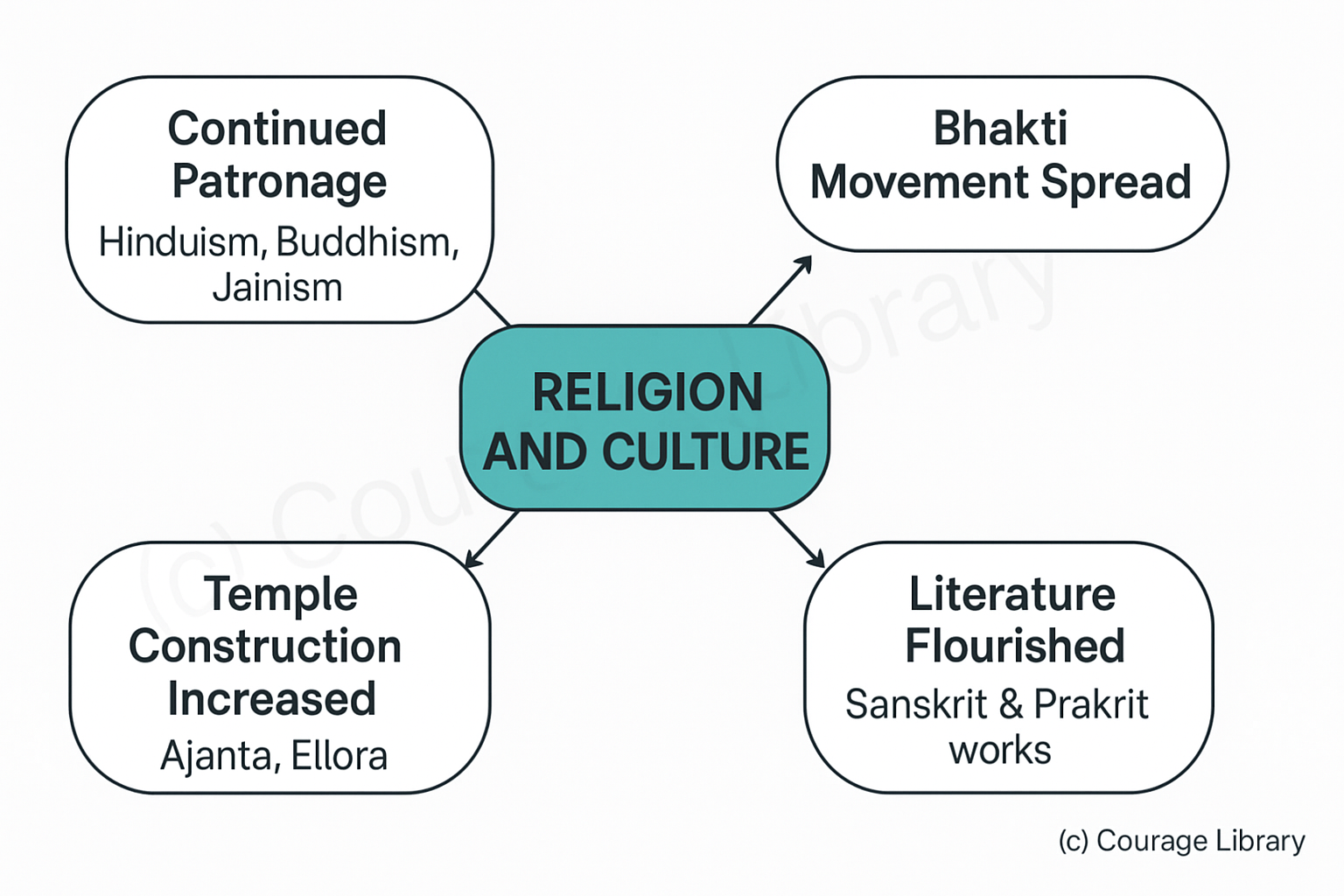
Religion and Culture
- Continued patronage of Hinduism, Buddhism and Jainism
- Spread of Bhakti movement
- Construction of temples increased (e.g., Ajanta, Ellora)
- Developments in Sanskrit and Prakrit literature
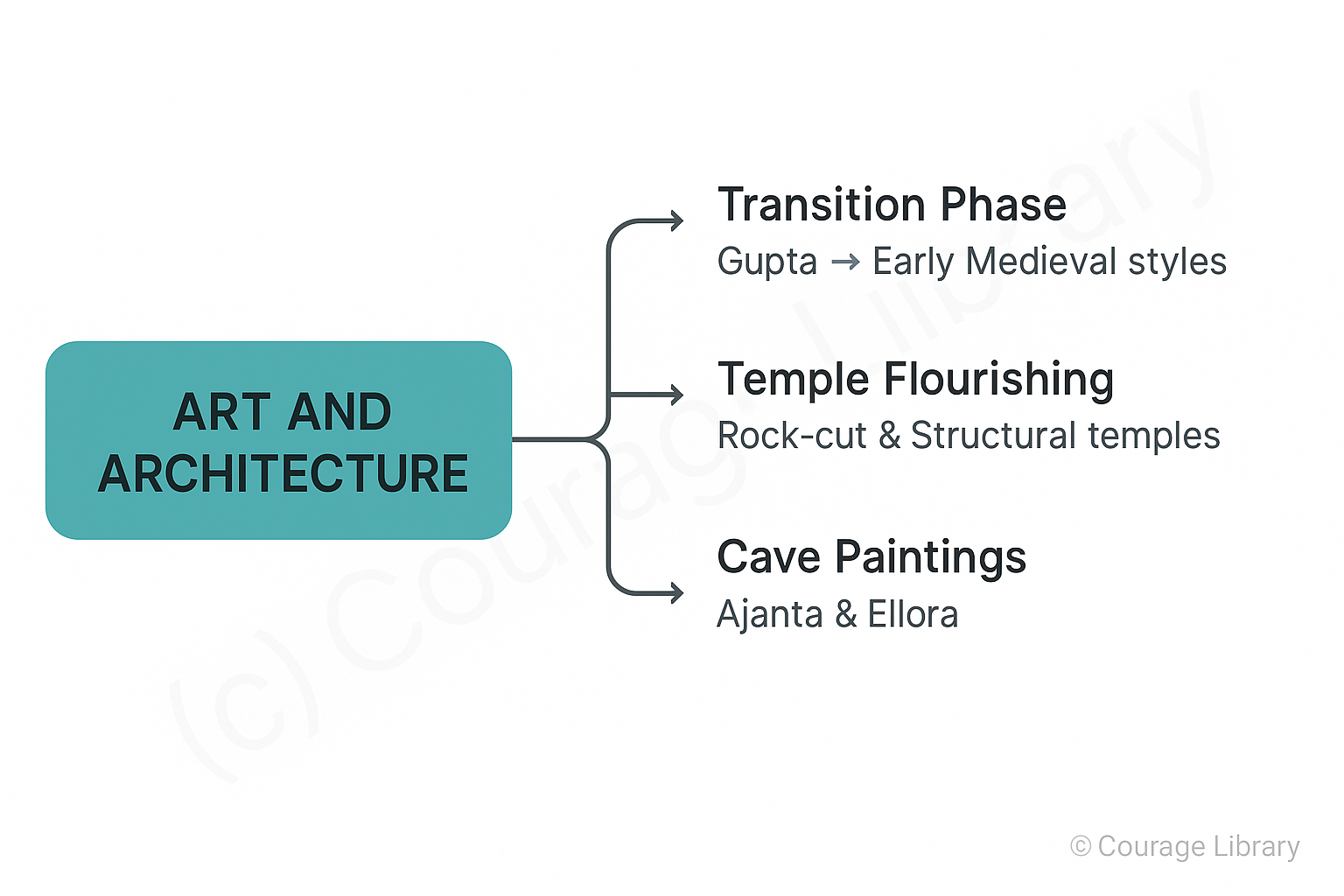
Art and Architecture
- Transition from Gupta to early medieval styles
- Temple architecture flourished: rock-cut and structural temples
- Paintings at Ajanta and Ellora caves
Quick facts
| Topic | Important Point |
|---|---|
| Gupta founder | Chandragupta I |
| Famous Gupta ruler | Samudragupta (military) and Chandragupta II (culture) |
| Gupta capital | Pataliputra |
| Gupta period known as | Golden Age of India |
| Famous scholar | Kalidasa, Aryabhatta |
| Invasion causing decline | Huns (Hephthalites) |
| Post-Gupta ruler | Harshavardhana |
| Harsha's capital | Kanauj |
| Art style | Gupta art (Ajanta caves, sculptures) |
| Gupta coin called | Dinara |
Important Exam Points
- Samudragupta's military campaigns (Allahabad Pillar inscription)
- Chandragupta II's patronage of arts and literature
- Gupta's era as "Classical Age" of Indian culture
- Harsha's role in temporarily uniting northern India post-Gupta
- Art and architecture: Ajanta caves, Gupta sculpture style
- Decline due to Hun invasions
Developed By Roopasree Challa
Next
Start Your SSC CGL Journey Now!
Join Courage Library to experience disciplined study and expert support.
Be a Couragian!