SSC CGL - Detailed Guide 2025
Self-Paced Course

Prehistoric Period
Reference: Lucent GK, NCERT Class 6–12
Introduction:
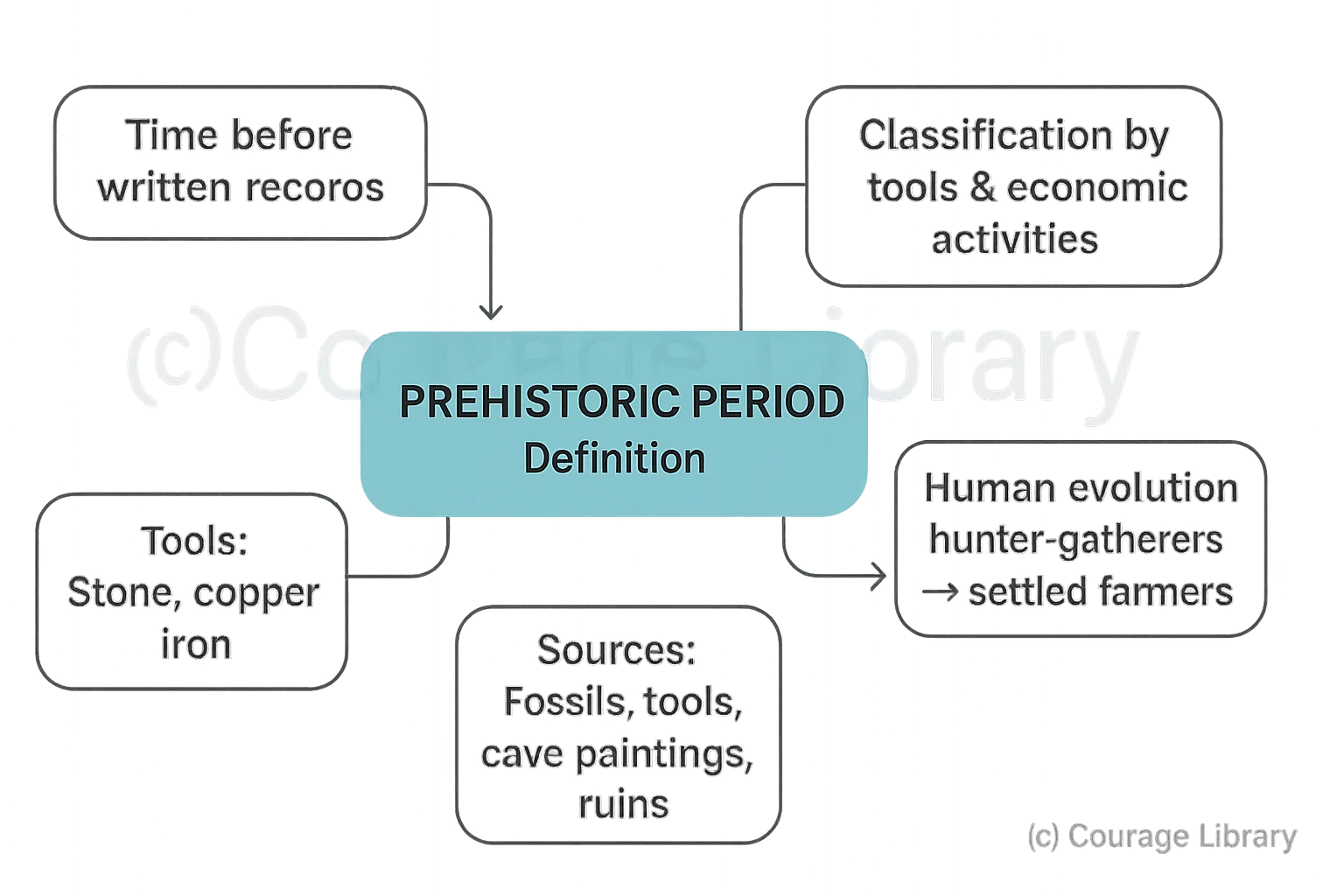
- The Prehistoric Period refers to the time before written records.
- Divided based on the tools used and economic activities.
- Covers human evolution from hunter-gatherers to settled farmers.
- Characterized by stone, copper, and iron tool usage.
- Information comes from fossils, tools, cave paintings, and ruins.
Main Phases of Prehistory
| Period | Time Approx. | Tools Used | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Paleolithic Age | 2 million – 10,000 BCE | Rough, chipped stone tools | Hunting-gathering, nomadic lifestyle |
| Mesolithic Age | 10,000 – 8,000 BCE | Microliths | Domestication, semi-nomadic |
| Neolithic Age | 8000 – 2000 BCE | Polished stone tools | Farming, settlements |
| Chalcolithic Age | 3000 – 1000 BCE | Copper + stone tools | Painted pottery, metals introduced |
| Iron Age | After 1000 BCE | Iron tools | Advanced agriculture, burials |
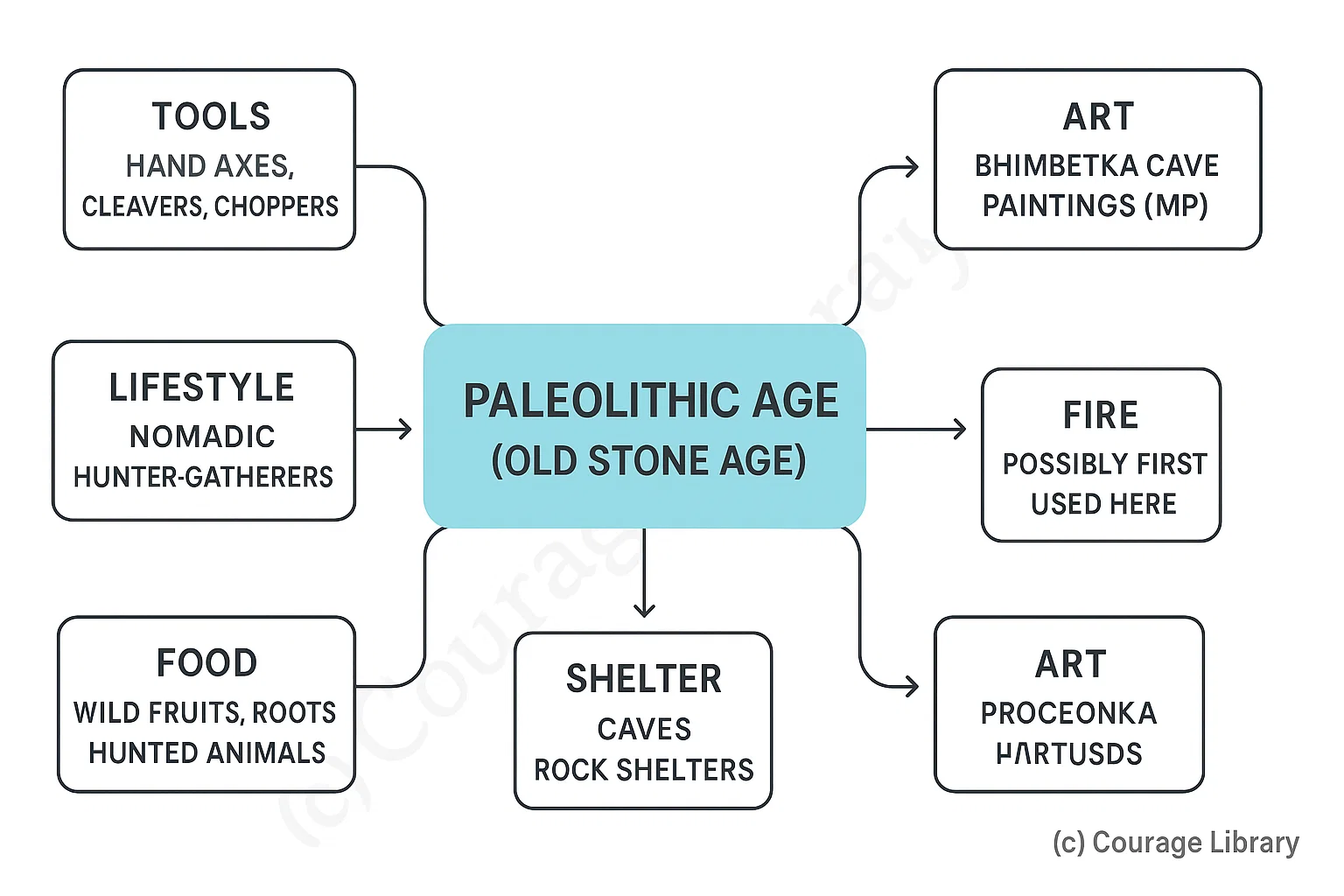
Paleolithic Age (Old Stone Age)
- Tools: Hand axes, cleavers, choppers
- Lifestyle: Nomadic, hunter-gatherers
- Food: Wild fruits, roots, hunted animals
- Shelter: Caves, rock shelters
- Art: Bhimbetka cave paintings (MP)
- Fire: Possibly first used here
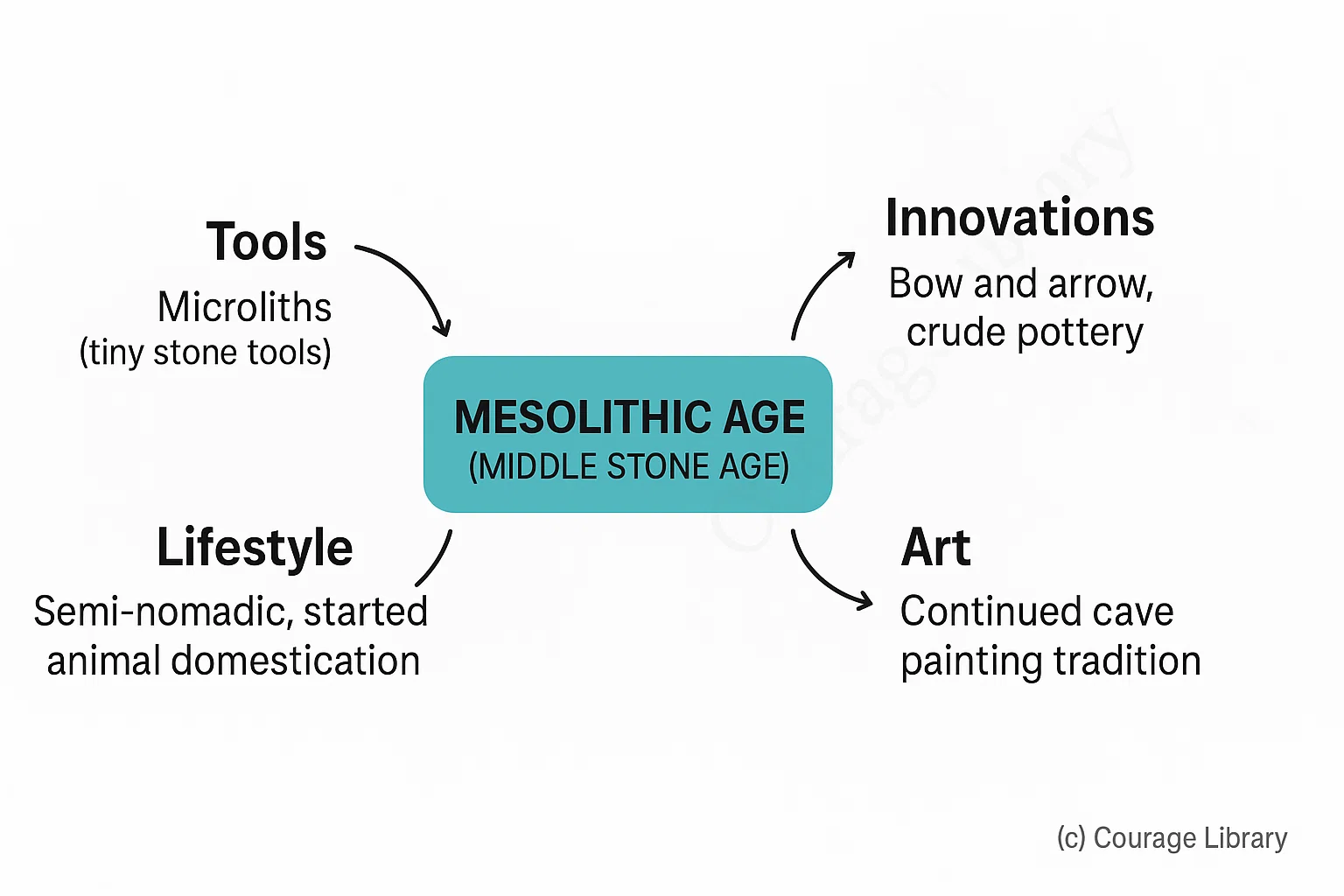
Mesolithic Age (Middle Stone Age)
- Tools: Microliths (tiny stone tools)
- Lifestyle: Semi-nomadic, started animal domestication
- Innovations: Bow and arrow, crude pottery
- Art: Continued cave painting tradition
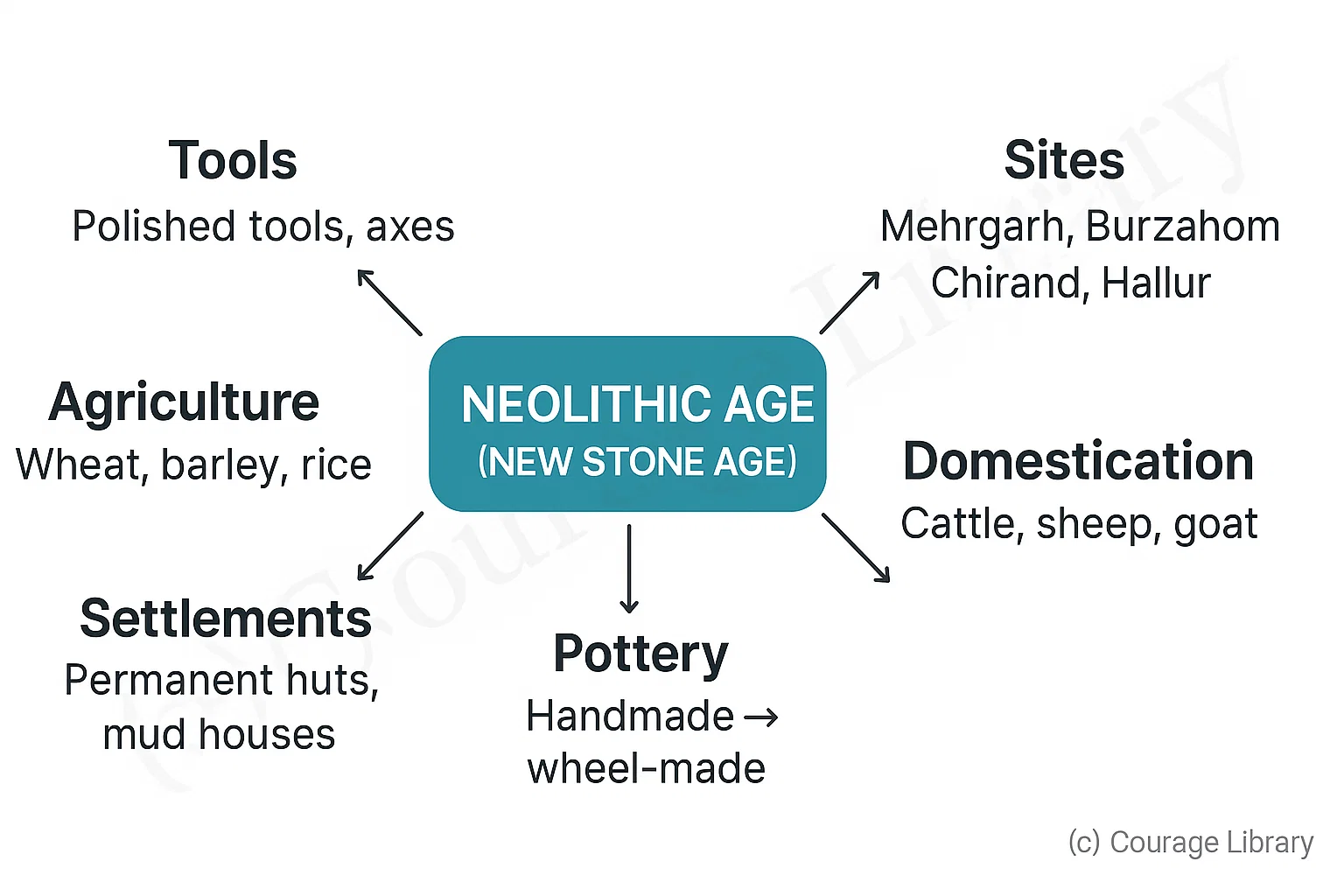
Neolithic Age (New Stone Age)
- Tools: Polished tools, axes
- Agriculture: Wheat, barley, rice
- Domestication: Cattle, sheep, goat
- Settlements: Permanent huts, mud houses
- Pottery: Handmade → wheel-made
- Sites: Mehrgarh, Burzahom, Chirand, Hallur
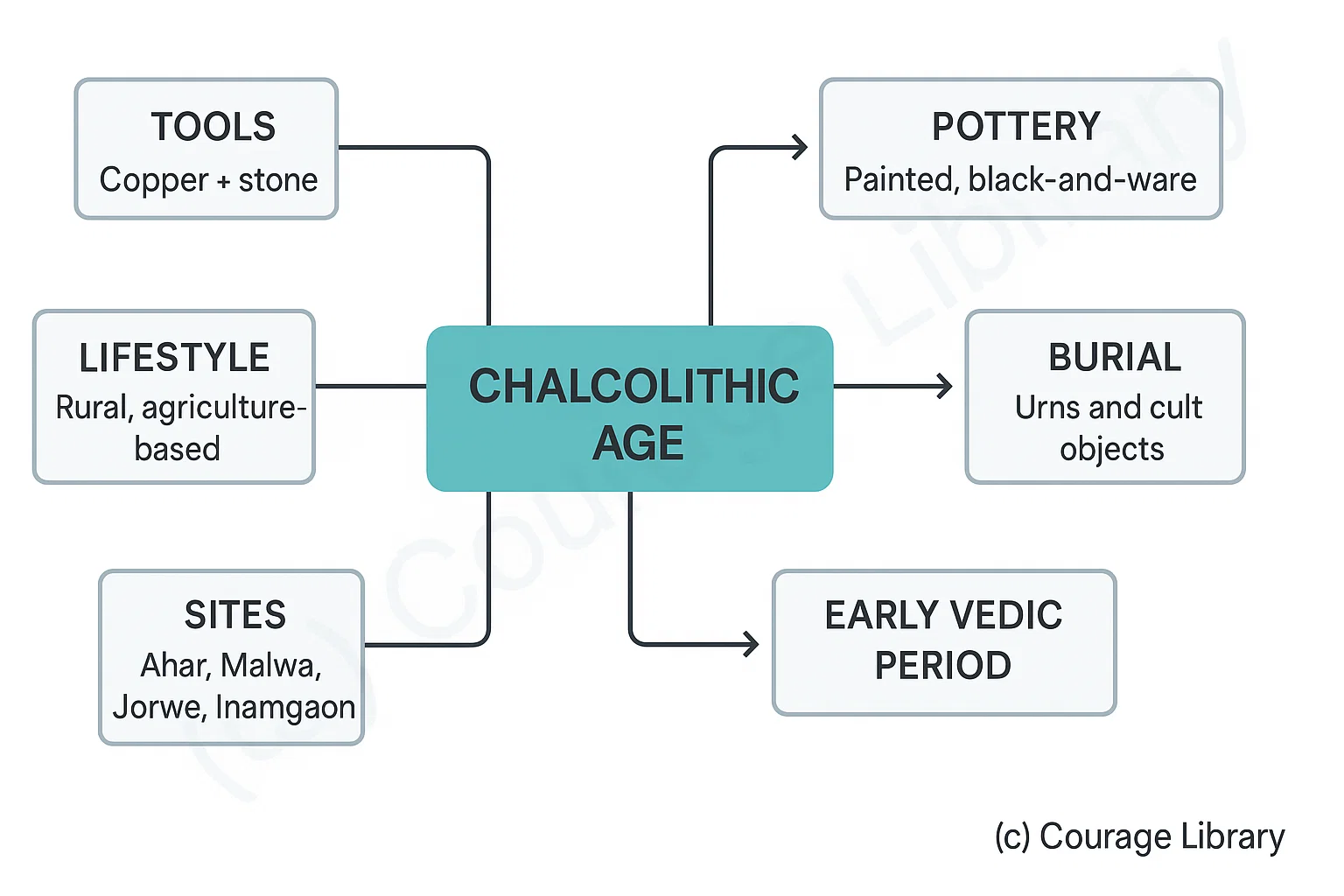
Chalcolithic Age
- Tools: Copper + stone
- Lifestyle: Rural, agriculture-based
- Pottery: Painted, black-and-red ware
- Burial: Urns and cult objects
- Sites: Ahar, Malwa, Jorwe, Inamgaon
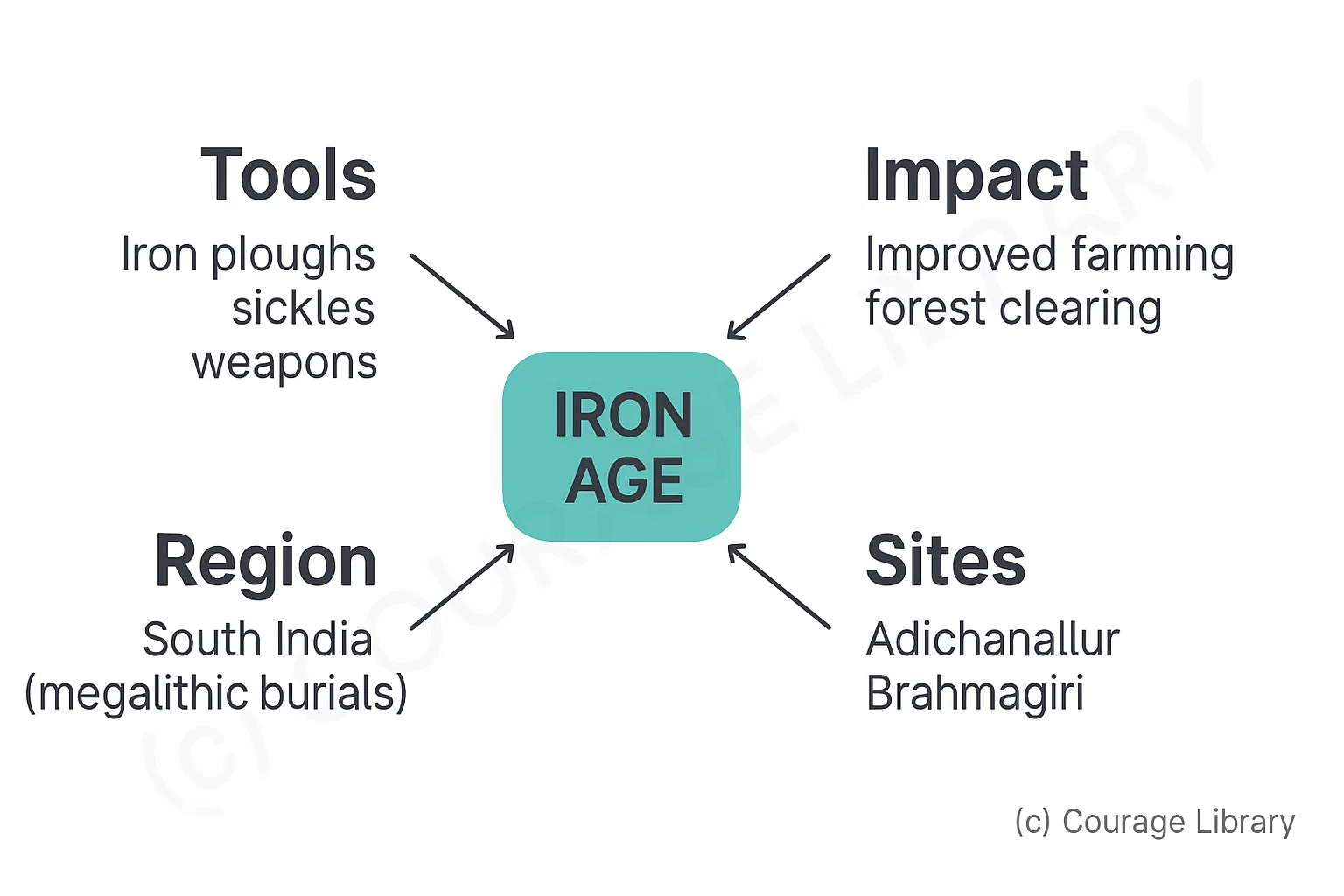
Iron Age
- Tools: Iron ploughs, sickles, weapons
- Impact: Improved farming, forest clearing
- Region: South India (megalithic burials)
- Sites: Adichanallur, Brahmagiri
Important Prehistoric Sites in India
| Site | State | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Bhimbetka | Madhya Pradesh | Rock art & cave paintings |
| Mehrgarh | Balochistan (Pakistan) | Early farming site |
| Burzahom | Jammu & Kashmir | Pit dwellings, stone tools |
| Chirand | Bihar | Neolithic + Chalcolithic |
| Hallur | Karnataka | Neolithic-Chalcolithic |
| Jorwe | Maharashtra | Chalcolithic pottery & burial |
Developed By Jan Mohammad
Next
Start Your SSC CGL Journey Now!
Join Courage Library to experience disciplined study and expert support.
Be a Couragian!