SSC CGL - Detailed Guide 2025
Self-Paced Course

British Expansion in India
Reference: Lucent GK, NCERT Class 6–12
1. Initial Establishment
- East India Company received Royal Charter in 1600
- First factory at Surat (1613) with permission from Jahangir
- Fort St. George (Madras), Bombay (dowry from Portuguese), and Calcutta established as presidencies
2. Major Battles that Enabled British Expansion
| Battle | Year | Fought Between | Outcome / Importance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battle of Plassey | 1757 | British (Clive) vs. Siraj-ud-Daulah | British victory → Start of political control |
| Battle of Buxar | 1764 | British vs. Mir Qasim + Shuja-ud-Daulah + Shah Alam II | Confirmed British supremacy in Bengal |
| 3rd Battle of Panipat | 1761 | Marathas vs. Ahmad Shah Abdali | Created a power vacuum exploited by British |
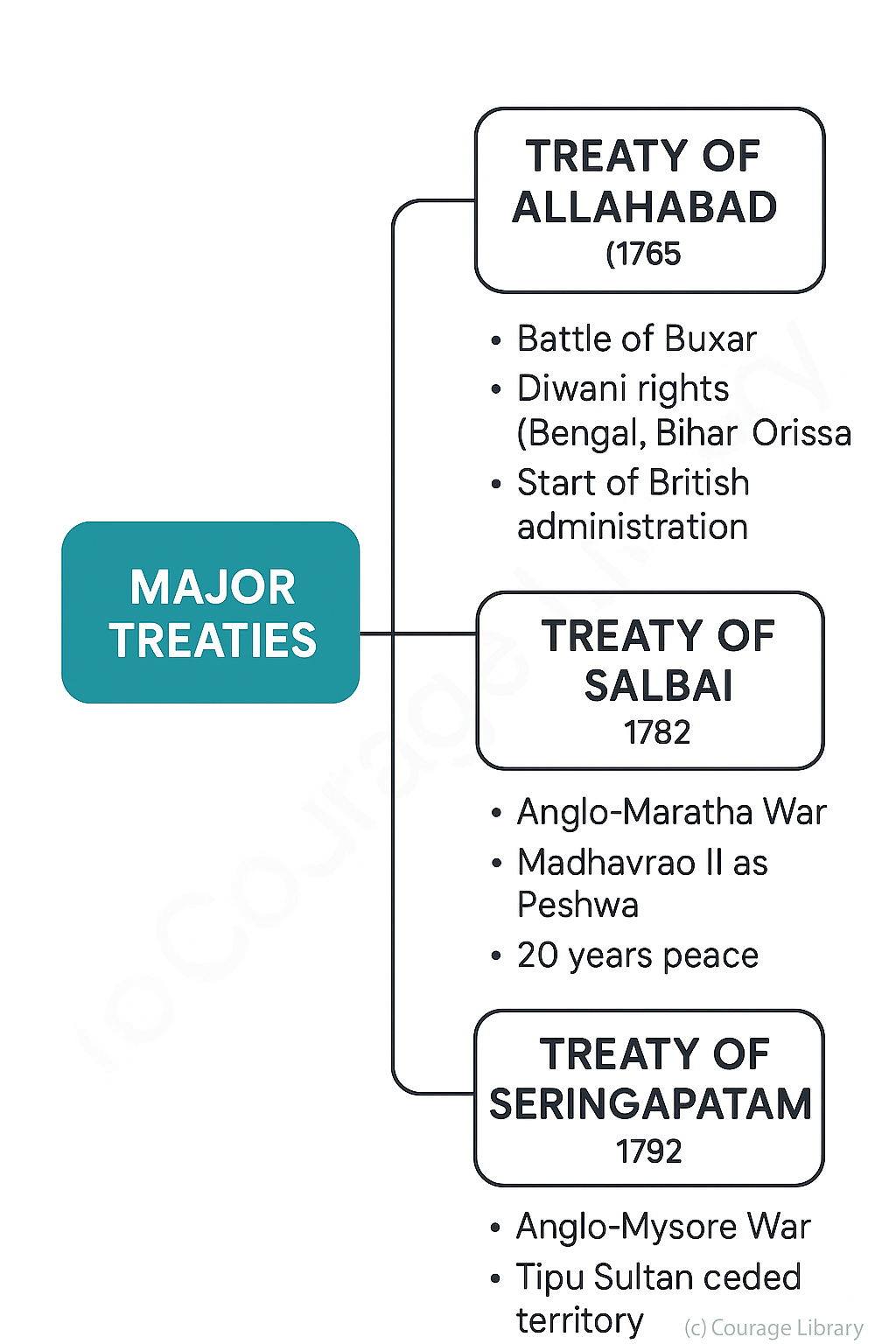
3. Major Treaties
Treaty of Allahabad (1765):
- Signed after Battle of Buxar.
- Mughal Emperor Shah Alam II granted Diwani rights (revenue collection) of Bengal, Bihar, and Orissa to British.
- Beginning of British administration.
Treaty of Salbai (1782):
- Signed after the First Anglo-Maratha War.
- Recognized Madhavrao II as the Peshwa of the Marathas.
- Brought 20 years of peace between the British and Marathas.
Treaty of Seringapatam (1792):
- Concluded the Third Anglo-Mysore War.
- Tipu Sultan ceded half of his territories to the British and their allies.
- Paid a large indemnity and surrendered two of his sons as hostages.
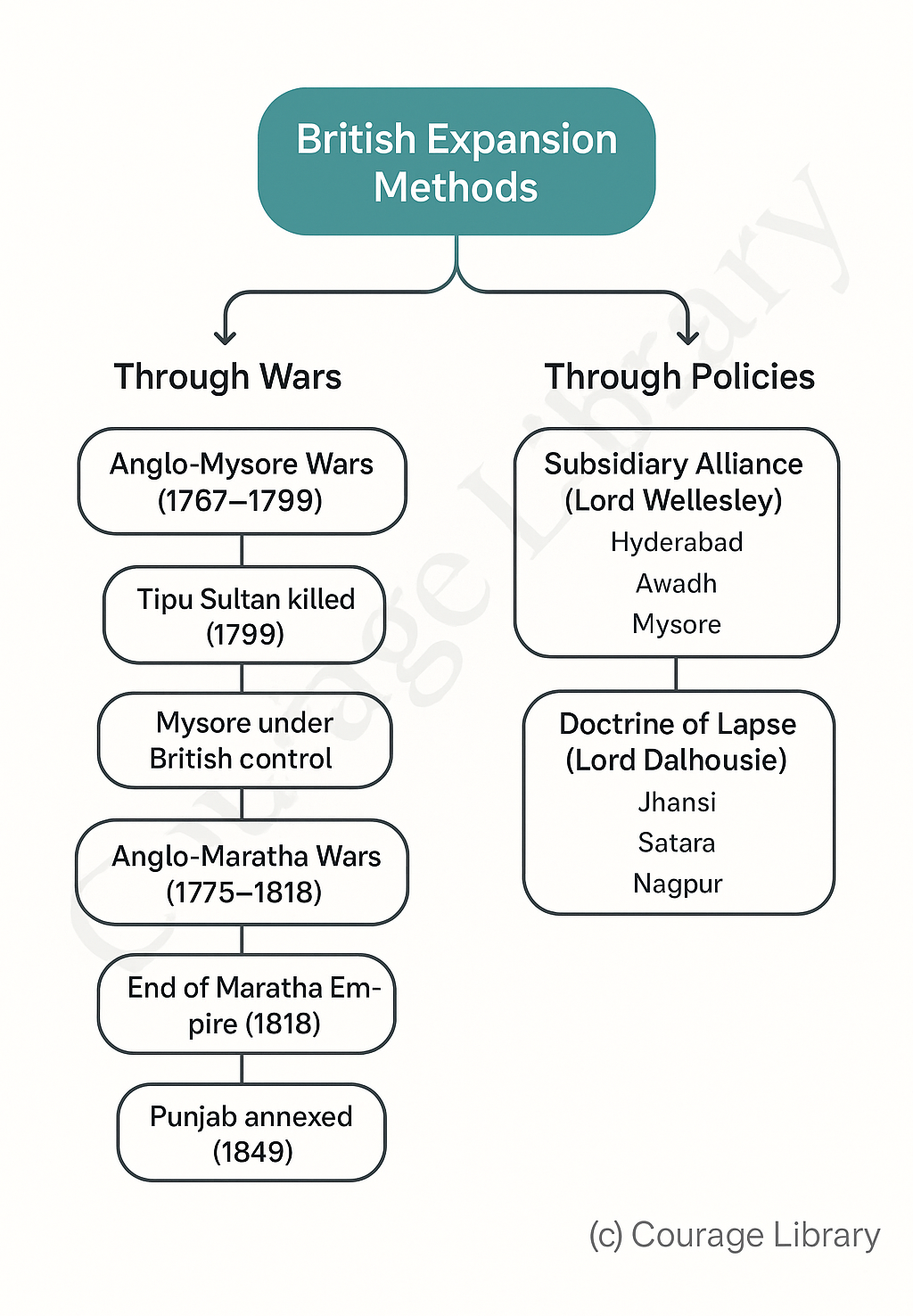
4. British Expansion Methods
Through Wars
-
Anglo-Mysore Wars (1767–1799): Fought between British and Hyder Ali/Tipu
Sultan of
Mysore.
- Fourth war (1799): Tipu Sultan killed, Mysore under British control.
-
Anglo-Maratha Wars (1775–1818): 3 wars in total.
- Third war (1817–1818): British defeated Peshwa Bajirao II.
- Marked the end of Maratha Empire.
-
Anglo-Sikh Wars (1845–1849): After death of Ranjit Singh.
- Second war (1849): Punjab annexed by British.
Through Policies
-
Subsidiary Alliance – Introduced by Lord Wellesley:
- Native rulers had to maintain British army at their expense.
- Example: Hyderabad, Awadh, Mysore.
-
Doctrine of Lapse – Introduced by Lord Dalhousie:
- If ruler died without a male heir, territory annexed by British.
- Example: Jhansi, Satara, Nagpur.
5. Important Governors-General & Their Role in Expansion
| Governor-General | Contribution to British Expansion |
|---|---|
| Robert Clive | Battle of Plassey, dual system in Bengal |
| Warren Hastings | Regulating Act (1773), Rohilla War, 1st Anglo-Maratha war |
| Lord Cornwallis | Permanent Settlement (1793) |
| Lord Wellesley | Subsidiary Alliance |
| Lord Hastings | End of Maratha power (1818) |
| Lord Dalhousie | Doctrine of Lapse, Railways, Telegraph |
6. Territories Annexed by British
| Territory | Method Used | Annexed Under |
|---|---|---|
| Bengal | Battle of Plassey | Robert Clive |
| Awadh | Subsidiary Alliance | Lord Wellesley |
| Punjab | Anglo-Sikh War | Lord Dalhousie |
| Jhansi | Doctrine of Lapse | Lord Dalhousie |
| Mysore | Anglo-Mysore Wars | Tipu Sultan defeated |
7. Timeline of British Expansion in India
- 1600 – British East India Company formed.
- 1608 – First British ship docks at Surat.
- 1613 – First British factory established at Masulipatnam (Andhra Pradesh).
- 1757 – Battle of Plassey: British establish political control in Bengal.
- 1764 – Battle of Buxar: Confirms British dominance in Bengal.
- 1765 – Treaty of Allahabad: British granted Diwani rights in Bengal, Bihar, Orissa.
- 1767–1799 – Anglo-Mysore Wars: Mysore defeated by British (Tipu Sultan dies in 1799).
- 1775–1818 – Anglo-Maratha Wars: Marathas defeated, British supremacy in Deccan.
- 1793 – Permanent Settlement introduced by Lord Cornwallis.
- 1798–1805 – Lord Wellesley's Subsidiary Alliance expands British control.
- 1845–1849 – Anglo-Sikh Wars: Punjab annexed by British.
- 1848–1856 – Doctrine of Lapse policy: territories like Jhansi annexed.
- 1857 – First War of Independence / Sepoy Mutiny challenges British rule.
- 1858 – End of Company rule, British Crown takes direct control (start of British Raj).
Developed By Satyam Kumar
Next
Start Your SSC CGL Journey Now!
Join Courage Library to experience disciplined study and expert support.
Be a Couragian!