SSC CGL - Detailed Guide 2025
Self-Paced Course

Constitutional Developments in India
Reference: Lucent GK, NCERT Class 6–12
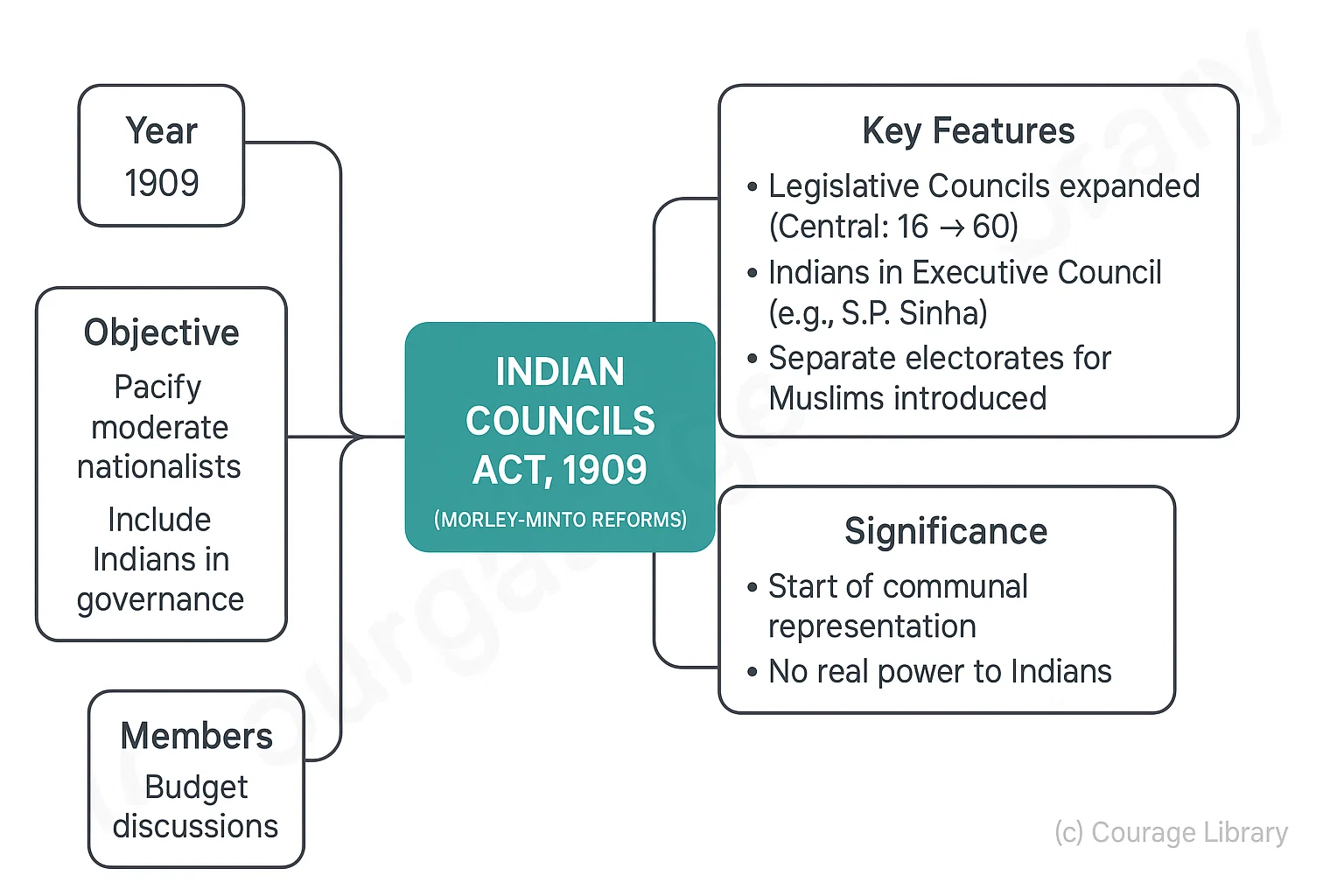
1. Indian Councils Act, 1909 (Morley-Minto Reforms)
- Year: 1909
- Objective: Pacify moderate nationalists, introduce Indians in governance.
- Key Features:
- Increased size of legislative councils (Central: 16 → 60)
- First time Indians allowed in Executive Council (e.g., S.P. Sinha)
- Separate electorates for Muslims introduced
- Members could discuss budgets, ask questions (limited power)
- Significance:
- Start of communal representation
- No real power to Indians
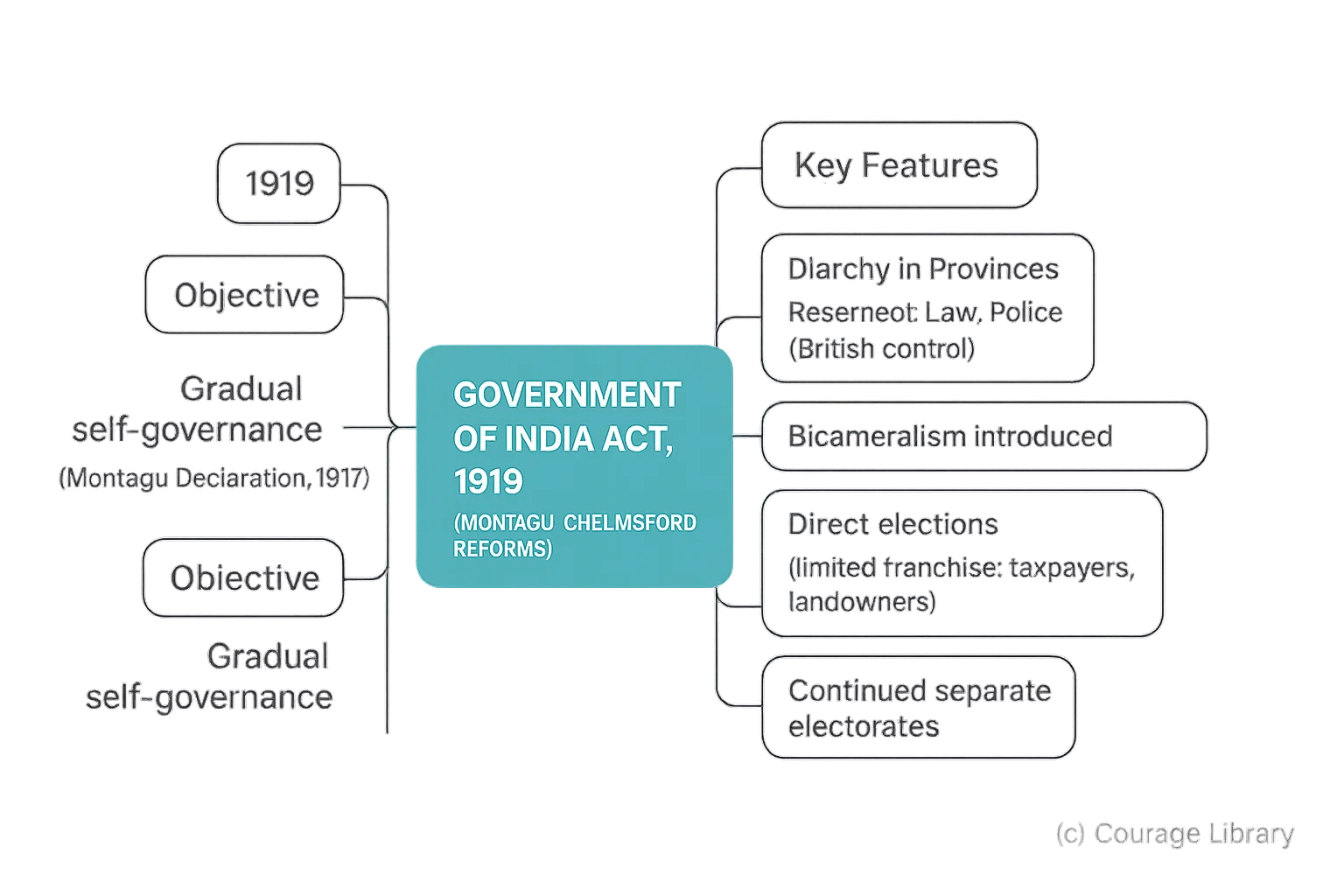
2. Government of India Act, 1919 (Montagu-Chelmsford Reforms)
- Year: 1919
- Objective: Fulfill Montagu Declaration (1917): gradual self-governance.
- Key Features:
- Diarchy in provinces:
- Reserved: Law, Police (British control)
- Transferred: Education, Health (Indian ministers)
- Introduced Bicameralism at Centre
- Direct elections for first time
- Franchise limited to taxpayers, landowners
- Continued separate electorates
- Diarchy in provinces:
3. Government of India Act, 1935
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Year | 1935 |
| Objective | Provide complete provincial autonomy |
| Key Features |
|
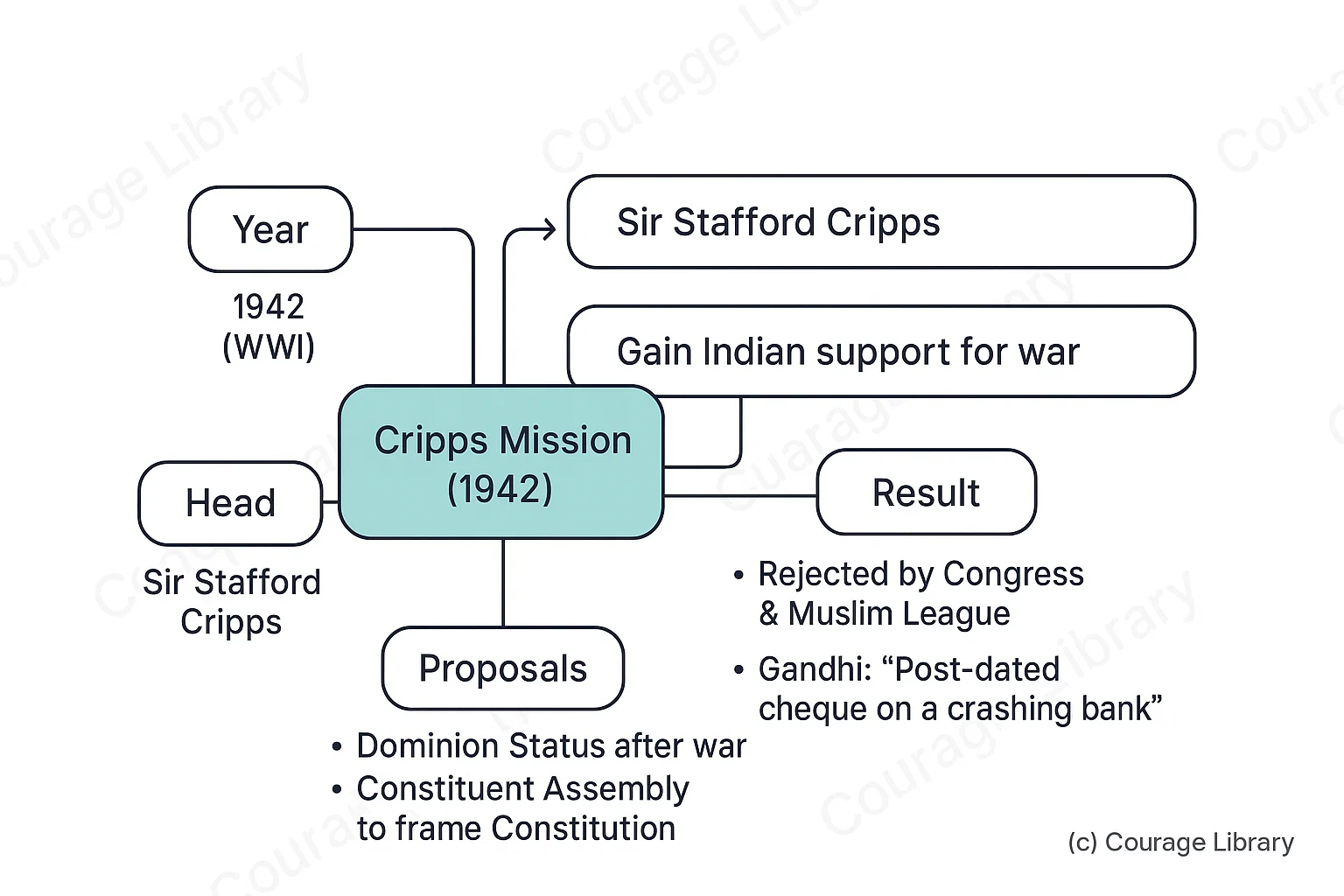
4. Cripps Mission (1942)
- Year: 1942 (during WWII)
- Head: Sir Stafford Cripps
- Objective: Gain Indian support for war
- Proposals:
- Dominion Status after war
- Constituent Assembly to frame Constitution
- Provinces can opt out of Indian Union
- Result:
- Rejected by Congress & Muslim League
- Called by Gandhi: "Post-dated cheque on a crashing bank"
5. Cabinet Mission Plan (1946)
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Year | 1946 |
| Members | Pethick-Lawrence, Cripps, Alexander |
| Objective | Transfer power & form Constituent Assembly |
| Proposals |
|
| Reaction |
|
Developed By Satyam Kumar
Next
Start Your SSC CGL Journey Now!
Join Courage Library to experience disciplined study and expert support.
Be a Couragian!