SSC CGL - Detailed Guide 2025
Self-Paced Course

Mughal Empire (1526–1857)
Reference: Lucent GK, NCERT Class 6–12
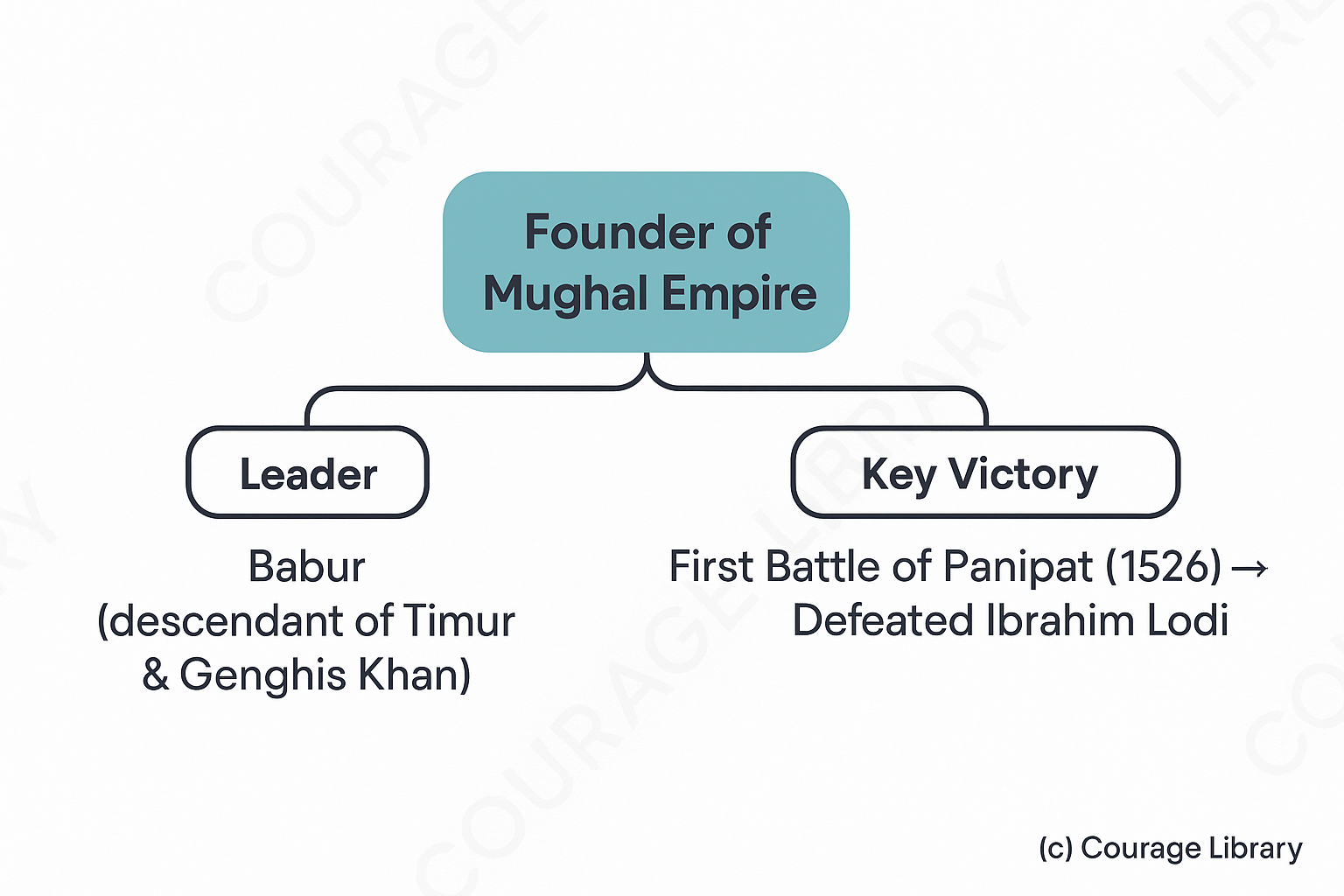
Founder
- Babur (descendant of Timur & Genghis Khan)
- Defeated Ibrahim Lodi in the First Battle of Panipat (1526)
Major Mughal Emperors
| Emperor | Reign | Key Points |
|---|---|---|
| Babur | 1526–1530 | - First Battle of Panipat (1526) - Battle of Khanwa (1527) vs. Rana Sanga |
| Humayun | 1530–1540, 1555–56 | - Lost to Sher Shah Suri - Died falling from library stairs |
| Akbar | 1556–1605 | - Second Battle of Panipat (1556) - Religious tolerance (Din-i-Ilahi) - Abolished Jizya tax - Navratnas (Birbal, Tansen, etc.) |
| Jahangir | 1605–1627 | - Justice lover - Married to Nur Jahan - Mewar accepted Mughal suzerainty |
| Shah Jahan | 1628–1658 | - Built Taj Mahal - Period of architectural glory |
| Aurangzeb | 1658–1707 | - Expanded empire to its greatest extent - Imposed Jizya again - Known for religious orthodoxy |
Important Battles
| Battle | Year | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| First Battle of Panipat | 1526 | Babur vs. Ibrahim Lodi – foundation of Mughal rule |
| Battle of Khanwa | 1527 | Babur vs. Rana Sanga – Rajput resistance crushed |
| Second Battle of Panipat | 1556 | Akbar vs. Hemu – Consolidation of Akbar's rule |
| Battle of Haldighati | 1576 | Akbar vs. Maharana Pratap – Mughal partial victory |
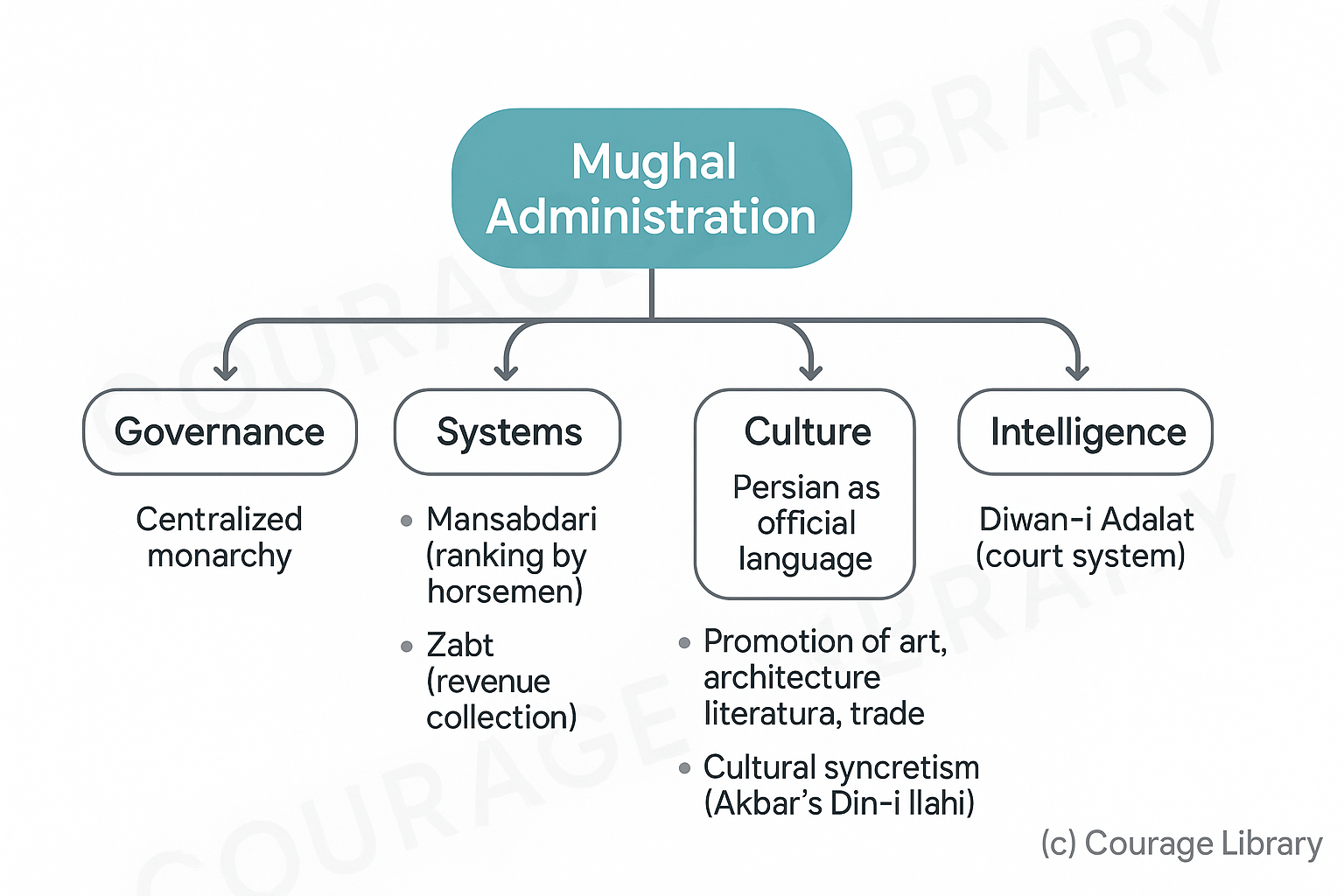
Mughal Administration
- Centralized monarchy
- Mansabdari System (ranking officials based on horsemen)
- Zabt system (revenue collection)
- Promotion of art, architecture, literature, and trade
- Use of Persian as the official language of administration
- Efficient court system and justice (Diwan-i-Adalat)
- Emphasis on cultural syncretism (e.g., Akbar’s Din-i-Ilahi)
- Strong intelligence network (Barid)
Mughal Architecture Highlights
| Monument | Built By | Location |
|---|---|---|
| Taj Mahal | Shah Jahan | Agra |
| Red Fort | Shah Jahan | Delhi |
| Buland Darwaza | Akbar | Fatehpur Sikri |
| Humayun’s Tomb | Akbar (for Humayun) | Delhi |
| Bibi Ka Maqbara | Aurangzeb (for wife) | Aurangabad |
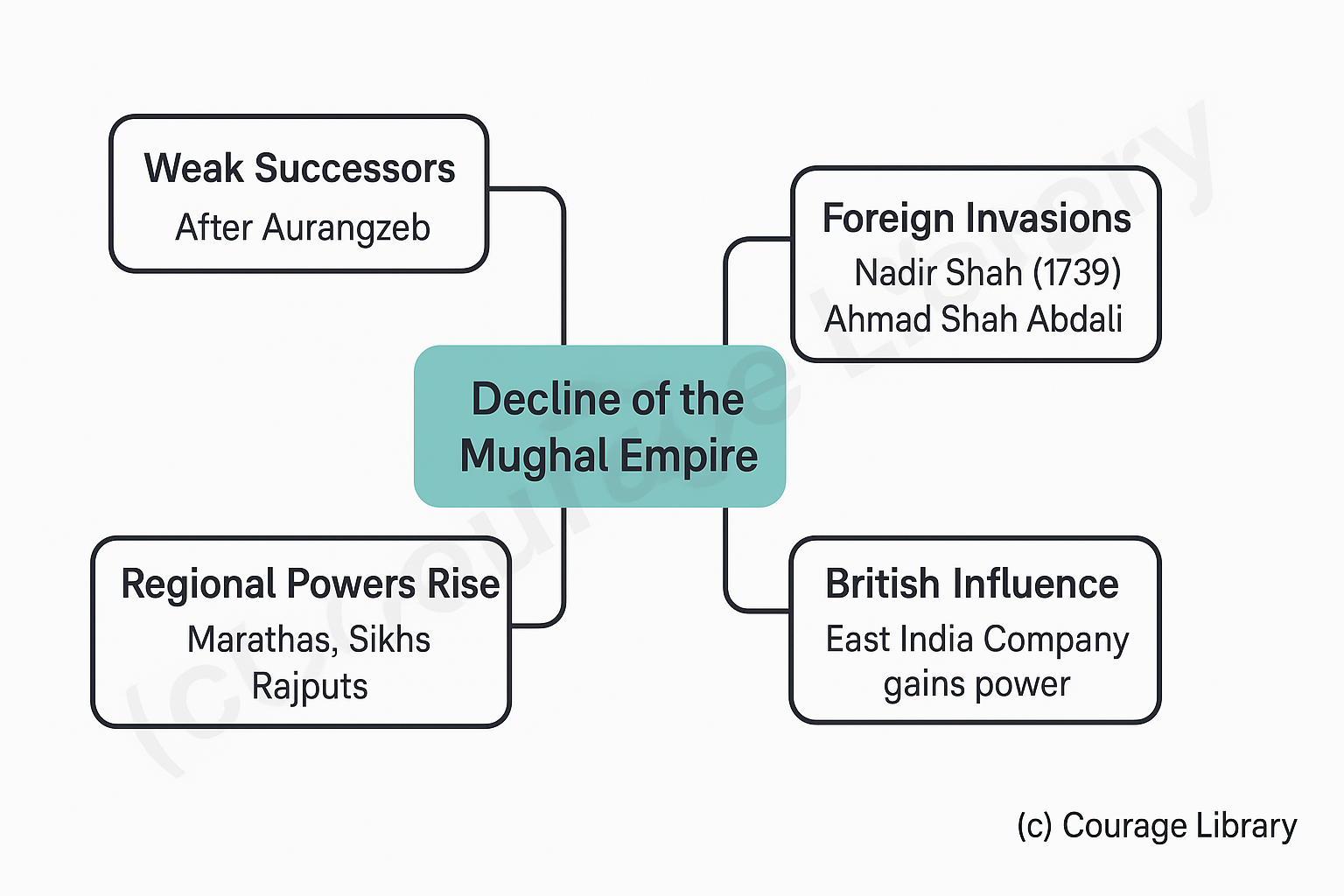
Decline of the Mughal Empire
Causes:
- Weak successors after Aurangzeb
- Rise of regional powers (Marathas, Sikhs, Rajputs)
- Foreign invasions (Nadir Shah in 1739, Ahmad Shah Abdali)
- British East India Company gaining power
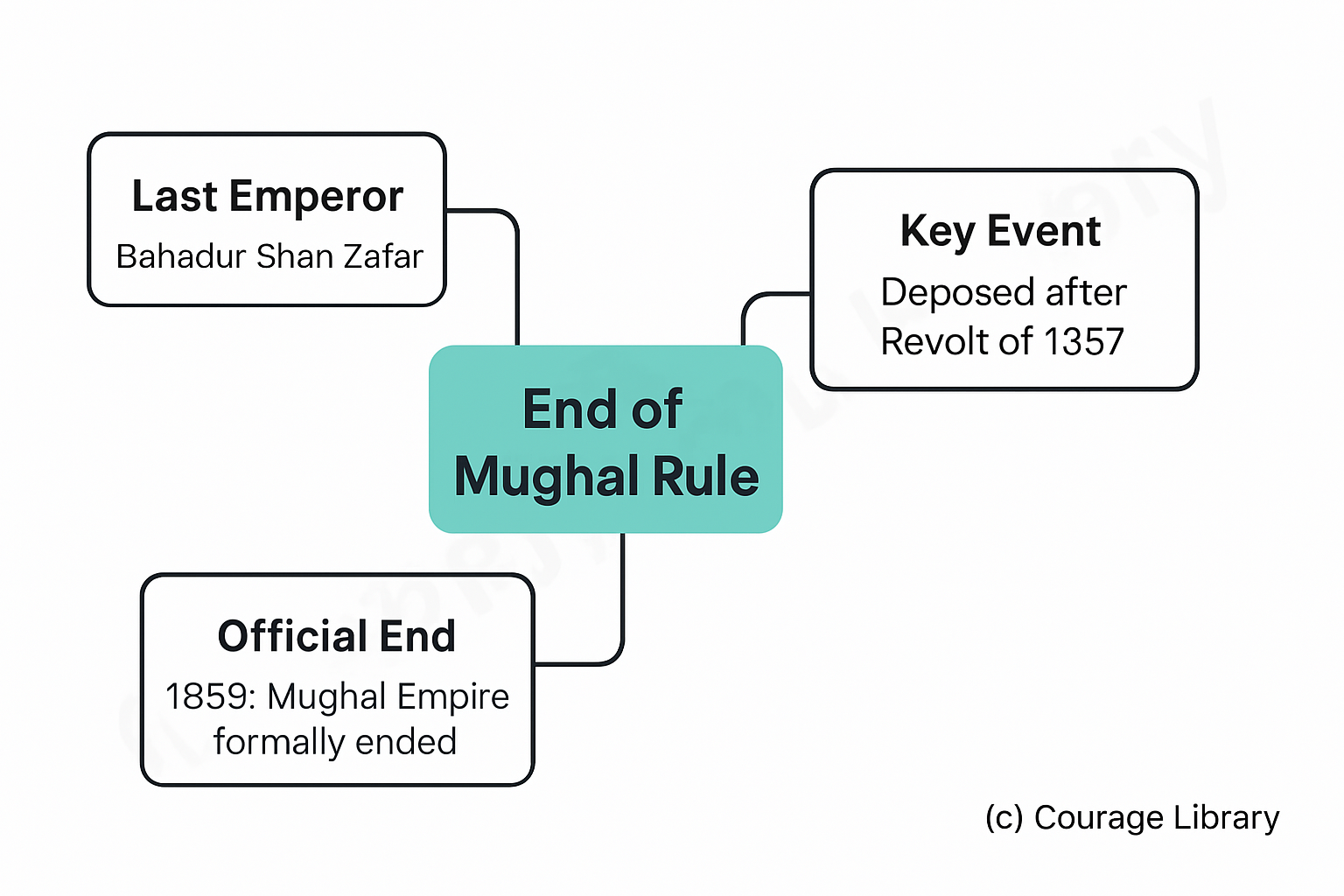
End of Mughal Rule
- Bahadur Shah Zafar (last Mughal Emperor)
- Deposed after Revolt of 1857
- Mughal Empire officially ended in 1858
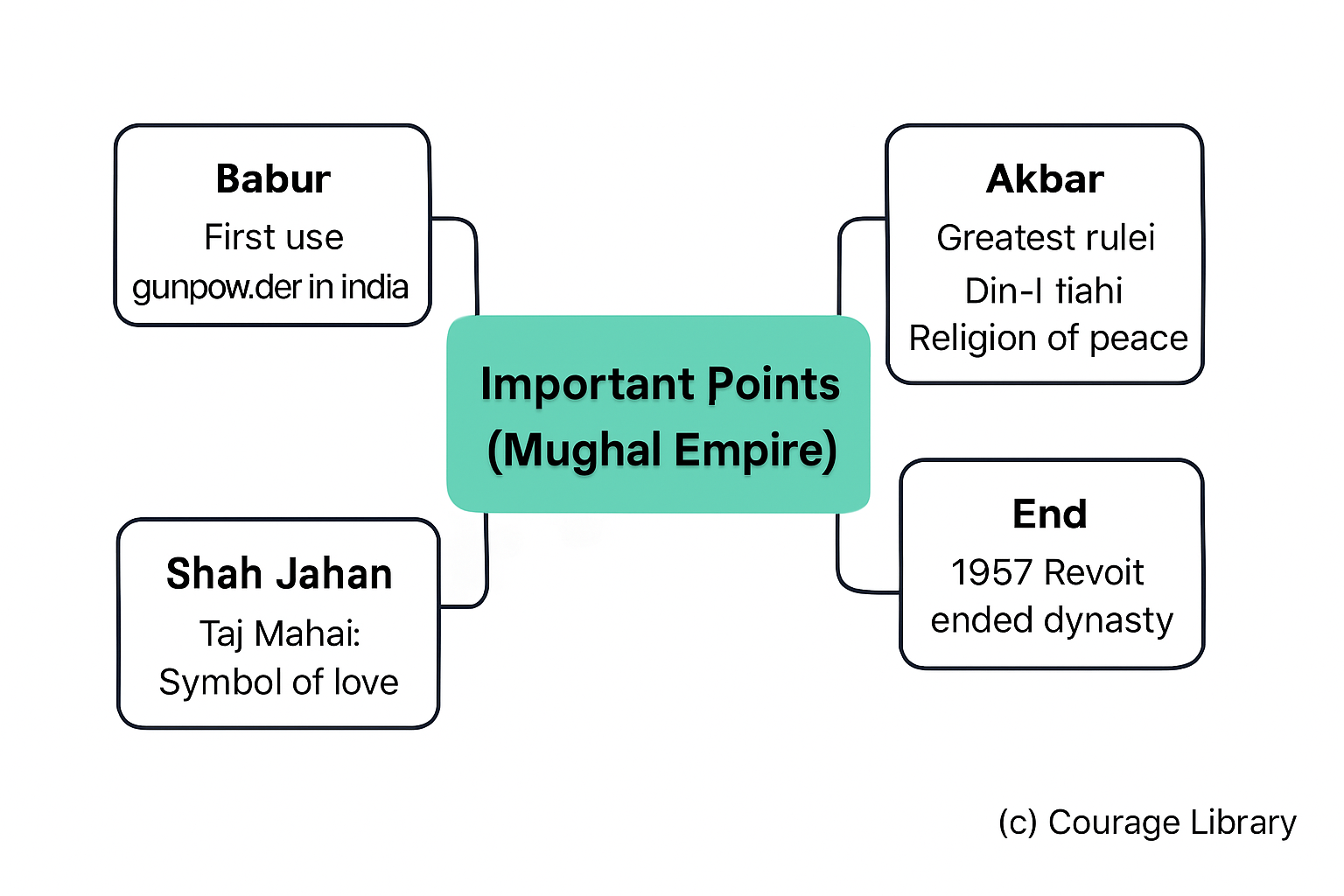
Important SSC Points to Remember
- Babur used gunpowder first in India.
- Akbar was the greatest Mughal ruler.
- Din-i-Ilahi: Akbar’s religion of peace.
- Taj Mahal: Symbol of love built by Shah Jahan.
- Aurangzeb: Last major ruler, known for orthodox policies.
- 1857 Revolt ended the Mughal dynasty.
Developed By Satyam Kumar
Next
Start Your SSC CGL Journey Now!
Join Courage Library to experience disciplined study and expert support.
Be a Couragian!