SSC CGL - Detailed Guide 2025
Self-Paced Course

Indus Valley Civilization
Reference: Lucent GK, NCERT Class 6–12
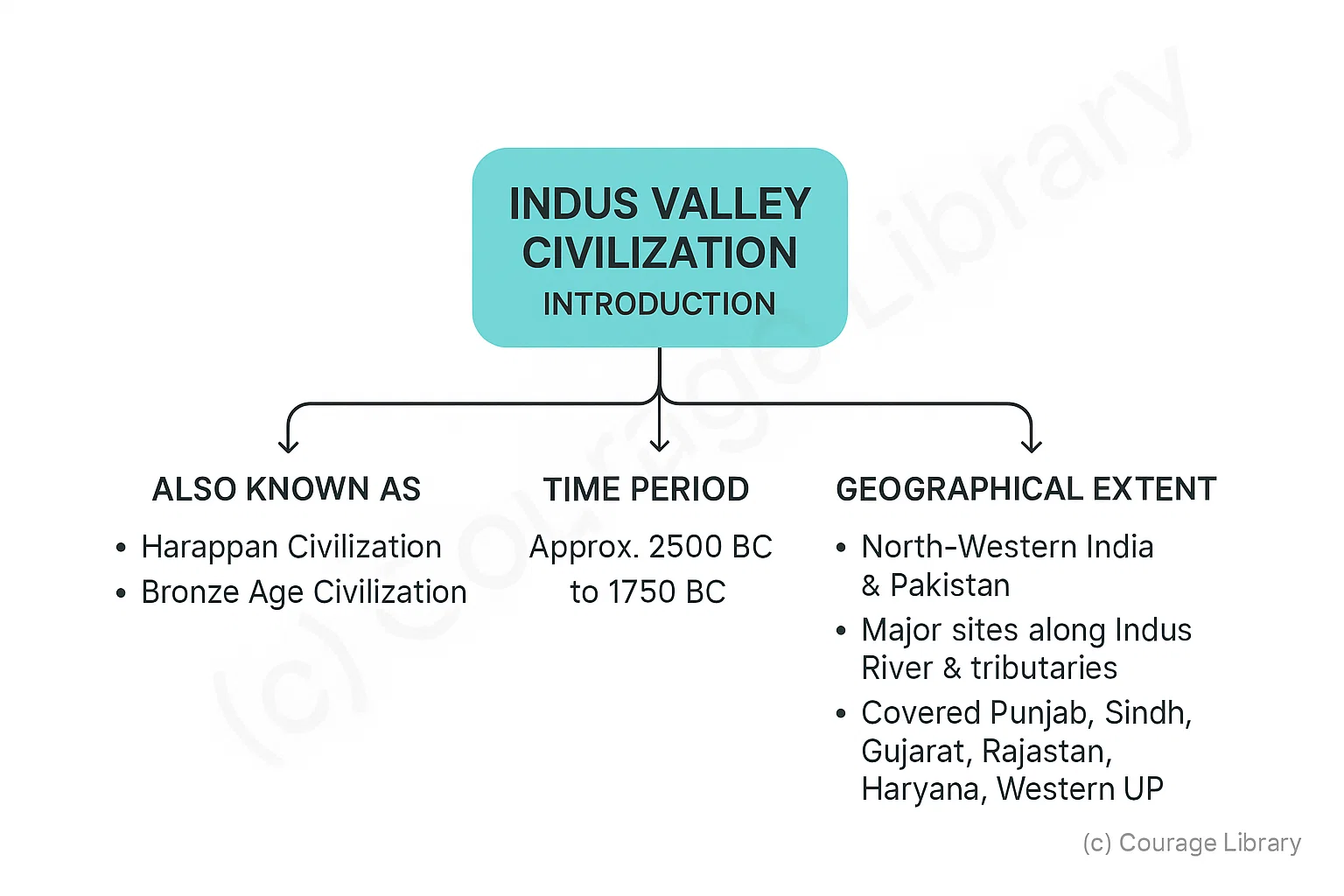
Introduction
-
Also known as:
- Harappan Civilization
- Bronze Age Civilization
-
Time Period: Approx. 2500 BC to 1750 BC -
Geogrphical Extent:
- Mainly in North-Western India and Pakistan
- Major sites along Indus River and its tributaries
- Covered parts of Punjab, Sindh, Gujarat, Rajasthan, Haryana and Western UP
Major Sites and Discoveries
| Site | Modern Location | Important Findings |
|---|---|---|
| Harappa | Punjab, Pakistan | Granaries, Coffin burial, Stone symbols |
| Mohenjodaro | Sindh, Pakistan | Great Bath, Granary, Dancing girl(bronze), Pashupati seal |
| Dholavira | Gujarat | Water conservation system, signboard in Harappan script |
| Lothal | Gujarat | Dockyard, Rice husk, Beads, Fire altars |
| Kalibangan | Rajasthan | Fire altars, Ploughed fields |
| Banawali | Haryana | Barley cultivation, Fire altars |
| Rakhigarhi | Haryana | Largest known Indus Valley Civilization site in India |
| Chanhudaro | Sindh, Pakistan | Bead making factory, Ivory works |
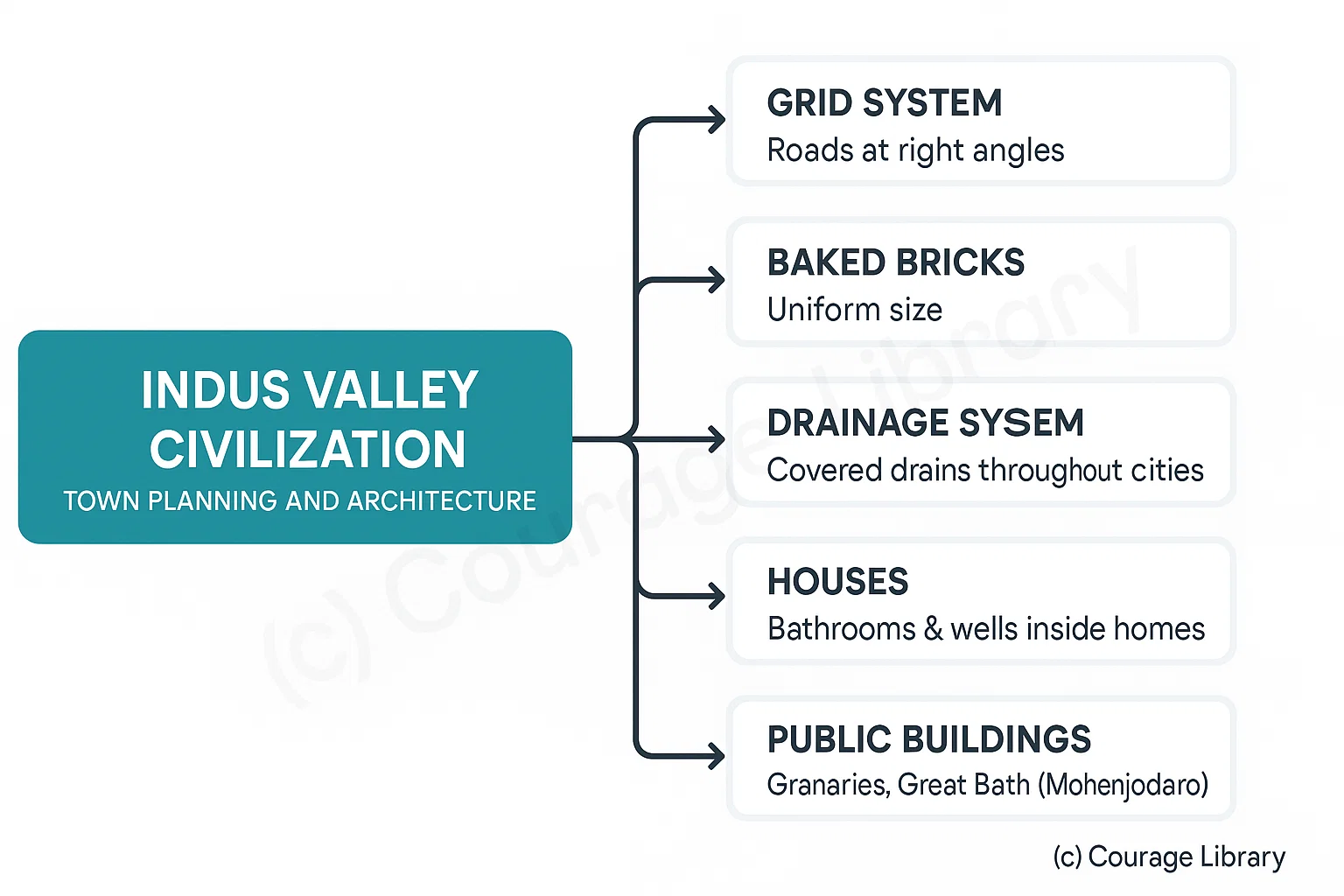
Town Planning and Architecture
- Well-planned grid system (roads at right angles)
- Use of baked bricks
- Drainage system (covered drains)
- Houses with bathrooms and wells
- Citadel (Upper Town) and Lower Town
- Public buildings like Granaries and Great Bath (Mohenjodaro)
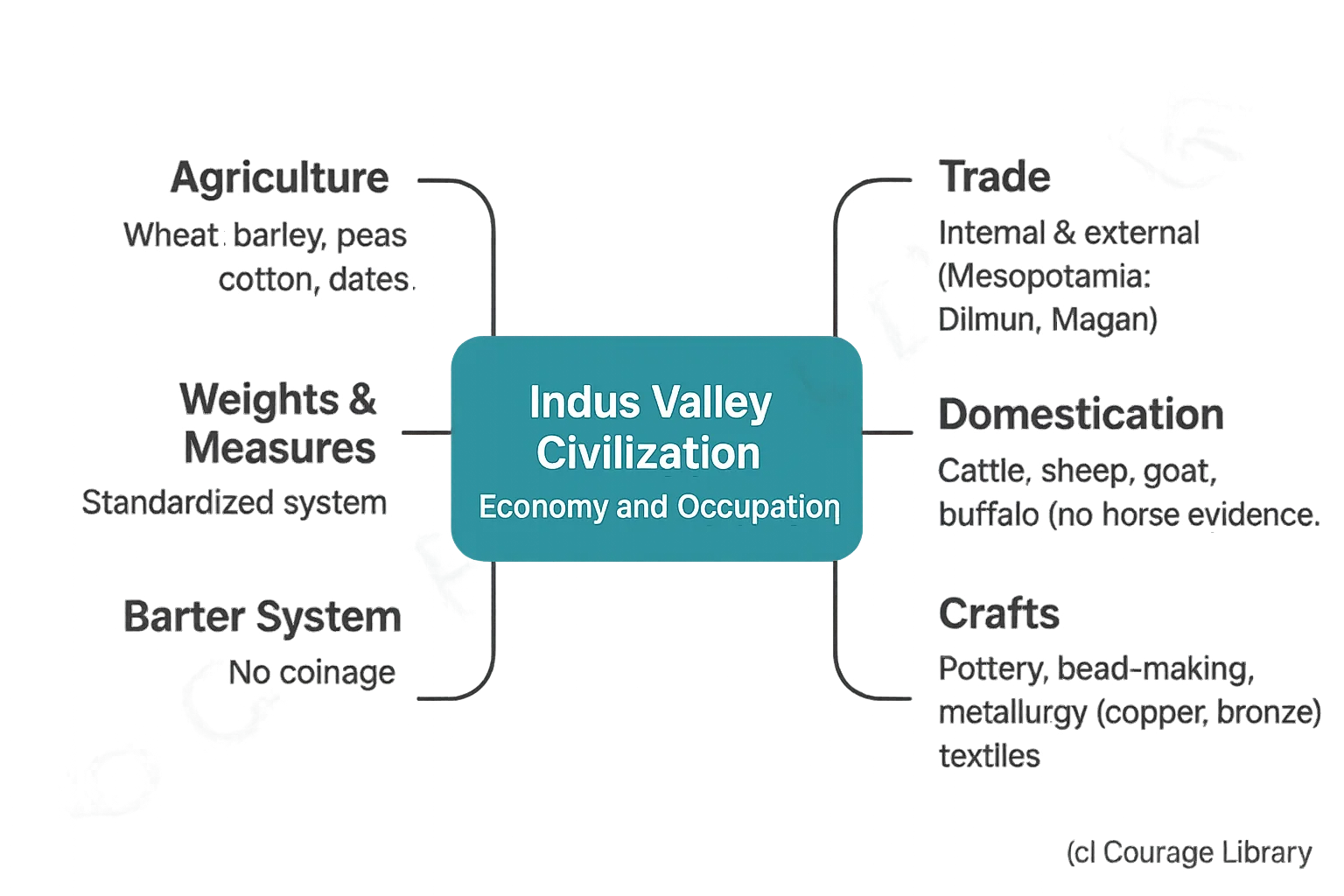
Economy and Occupation
- Agriculture: Wheat, barley, peas, cotton, dates
-
Trade:
- Internal and external (e.g., Mesopotamia - Dilmun, Magan)
- Use of weights and measures
- No coinage; relied on barter system
- Crafts: Pottery, bead-making, metallurgy (copper, bronze), textiles
- Domestication: Cattle, sheep, goat, buffalo; no clear evidence of horses
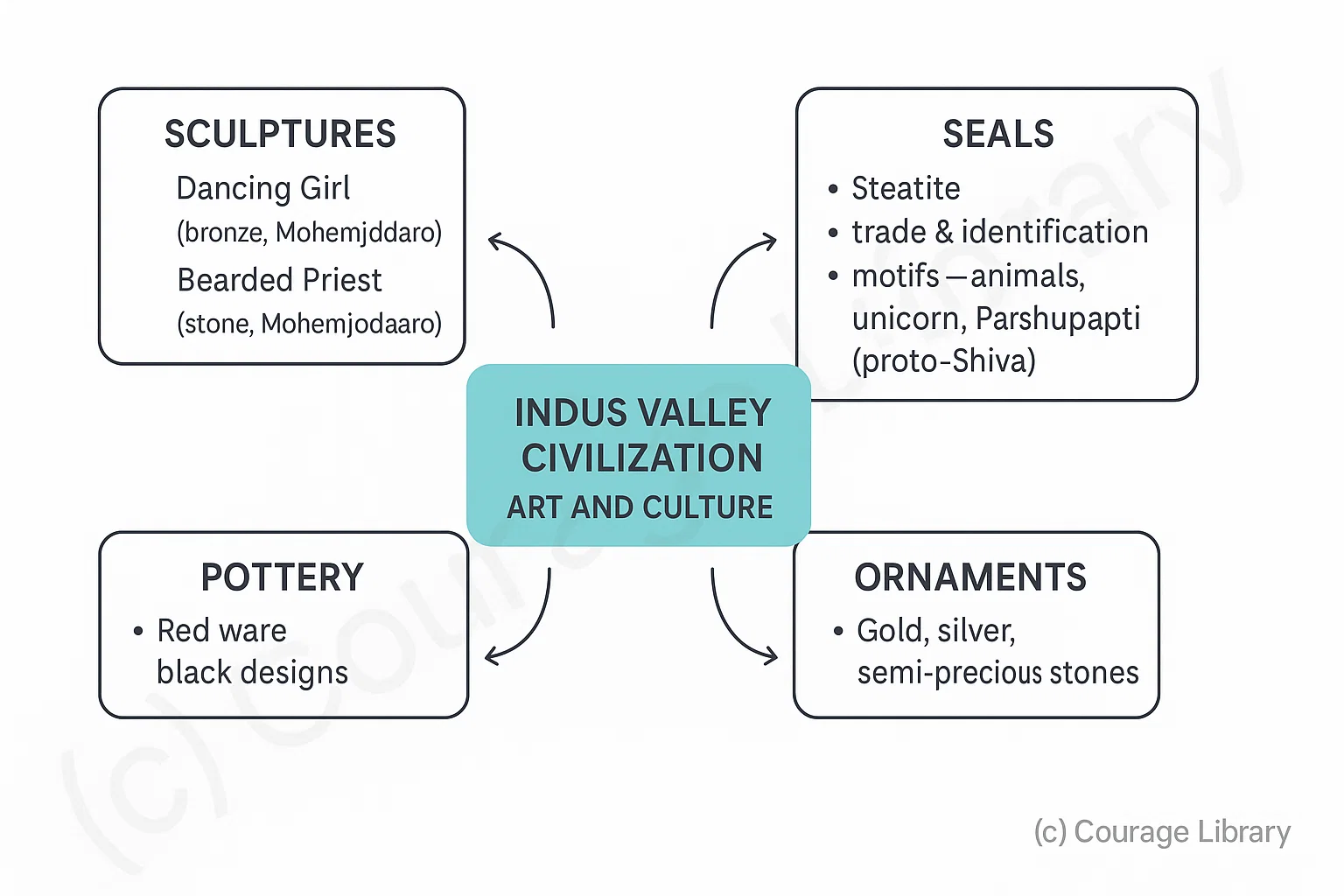
Art and Culture
-
Sculptures:
- Dancing Girl (bronze, Mohenjodaro)
- Bearded Priest (stone, Mohenjodaro)
-
Seals:
- Made of steatite; used for trade and identification
- Common motifs: animals, unicorn, Pashupati (proto-Shiva)
- Pottery: Red ware with black designs
- Ornaments: Gold, Silver, semi-precious stones
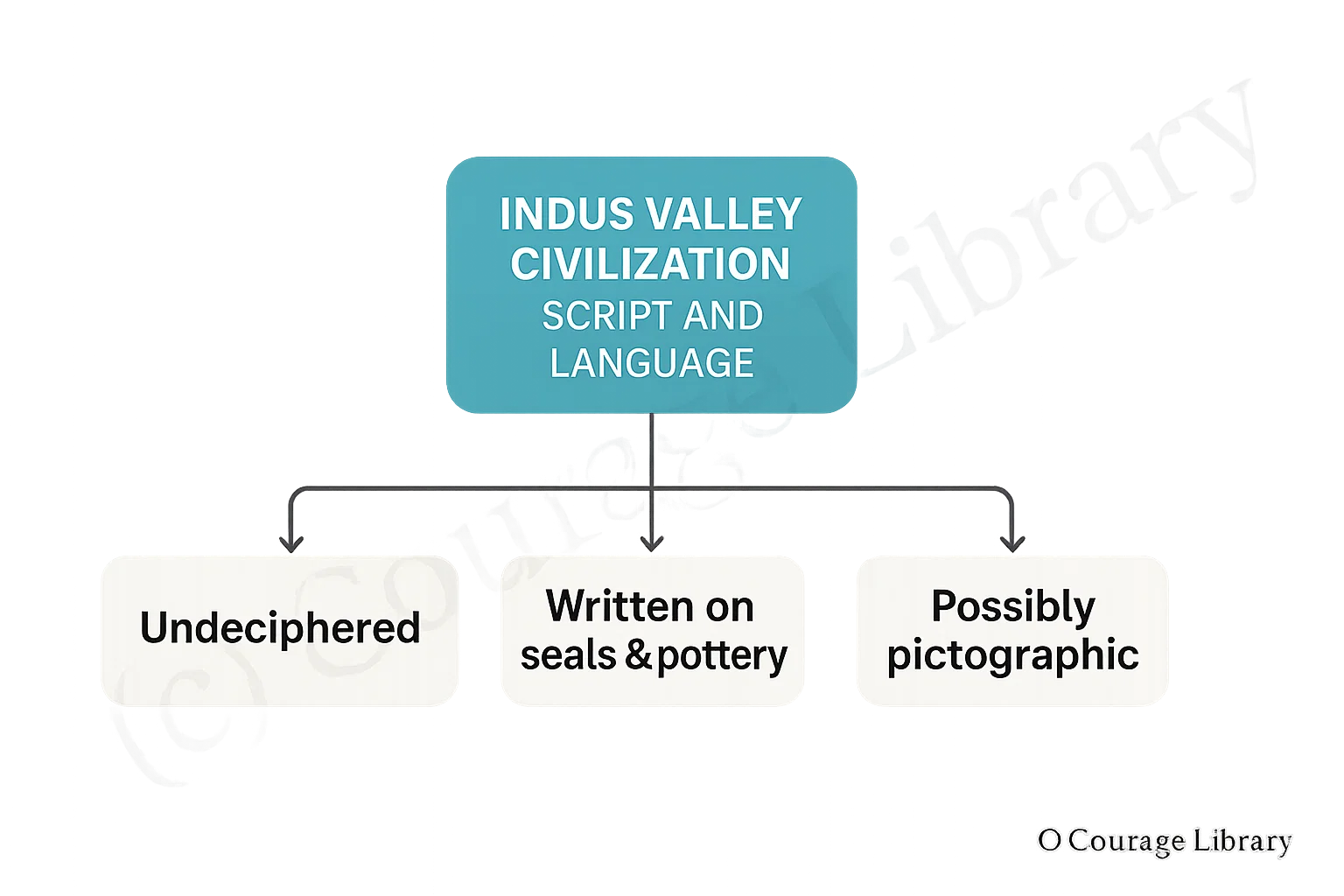
Script and Language
- Script: Undeciphered
- Written on seals and pottery
- Possibly pictographic in nature
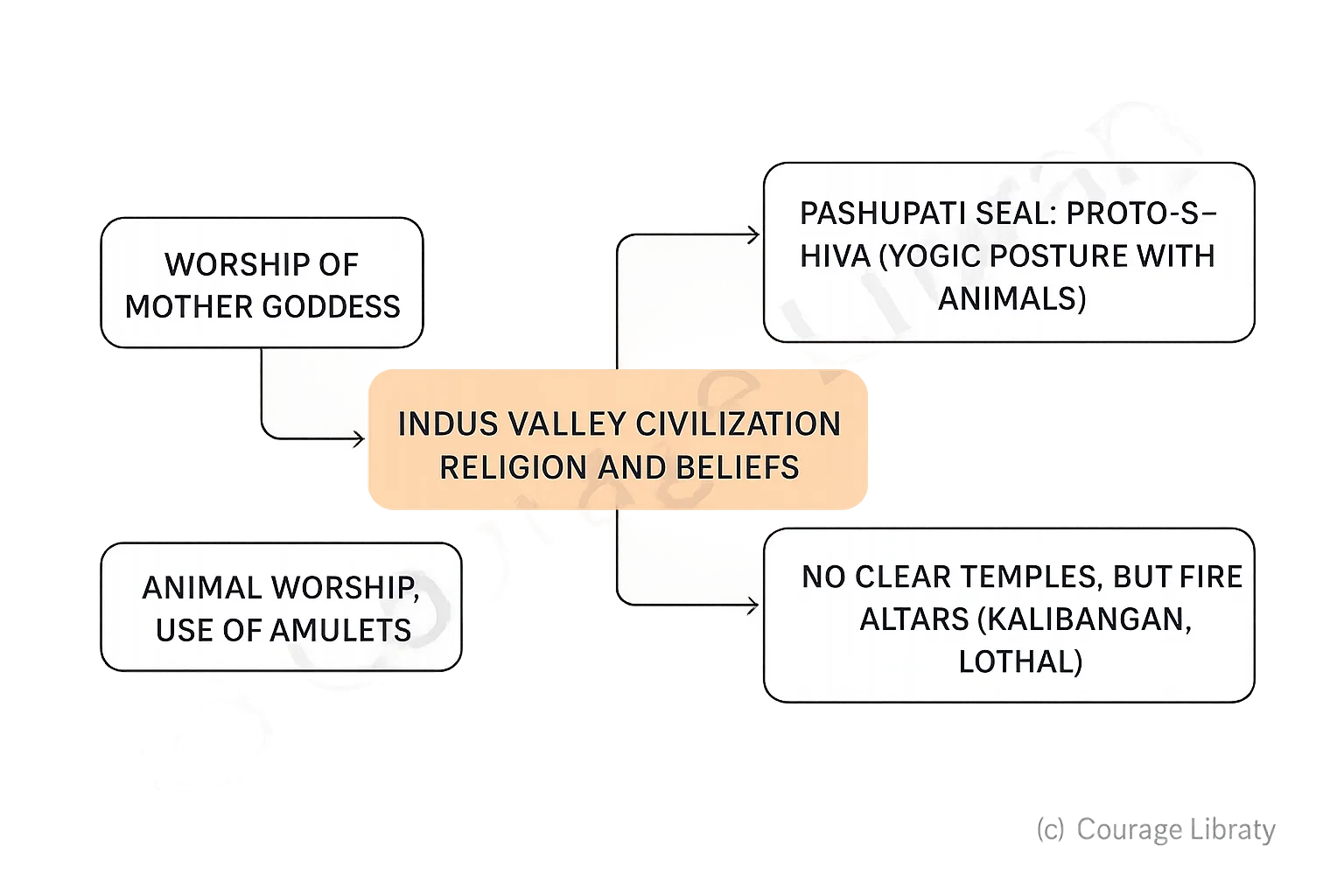
Religion and Beliefs
- Worship of Mother Goddess
- Pashupati Seal: Proto-Shiva (sitting in yogic posture with animals)
- No clear temples, but presence of fire altars (Kalibangan, Lothal)
- Animal worship, use of amulets
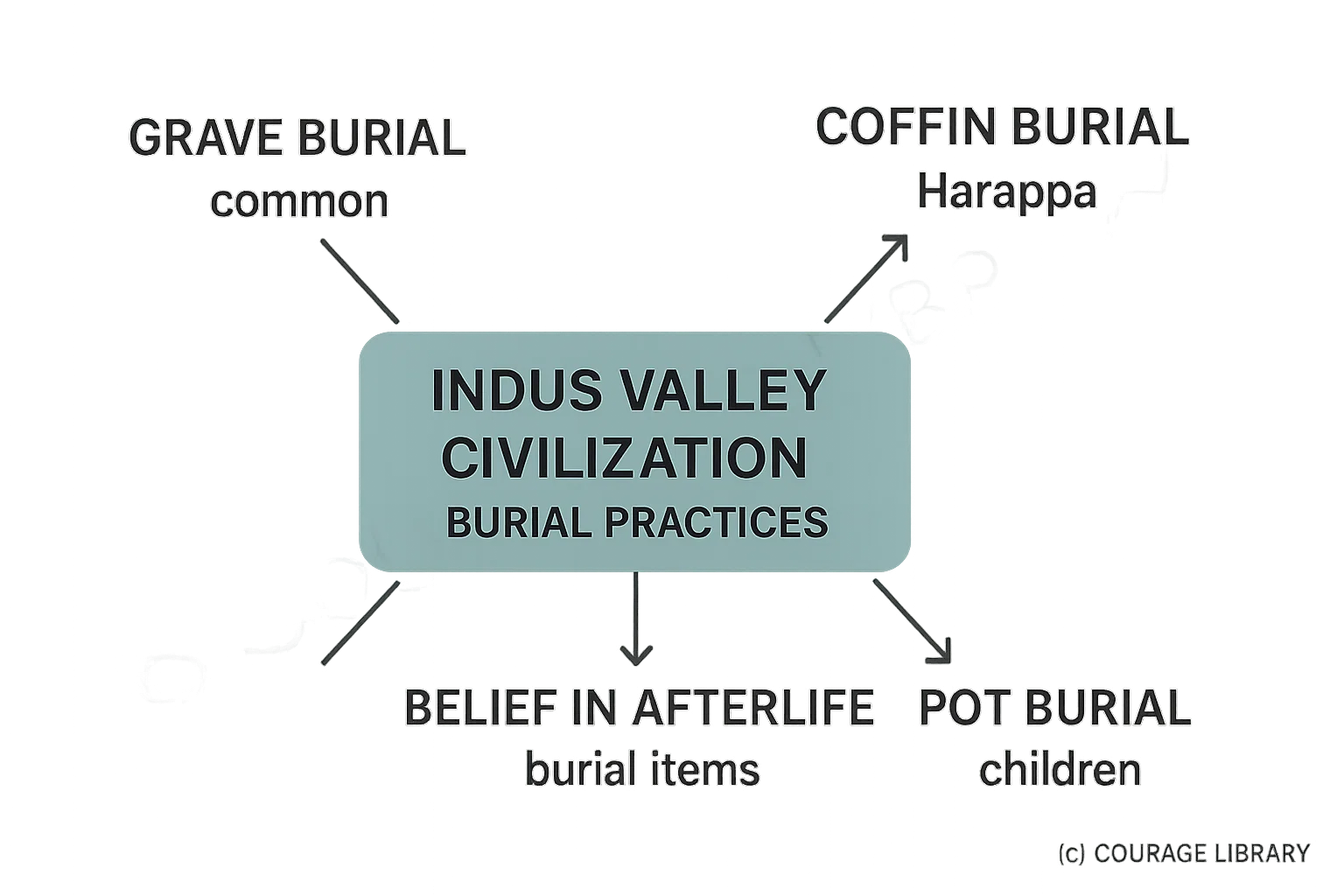
Burial Practices
- Grave burial (common)
- Coffin burail (Harappa)
- Pot burial (children)
- Belief in afterlife evident from burial items
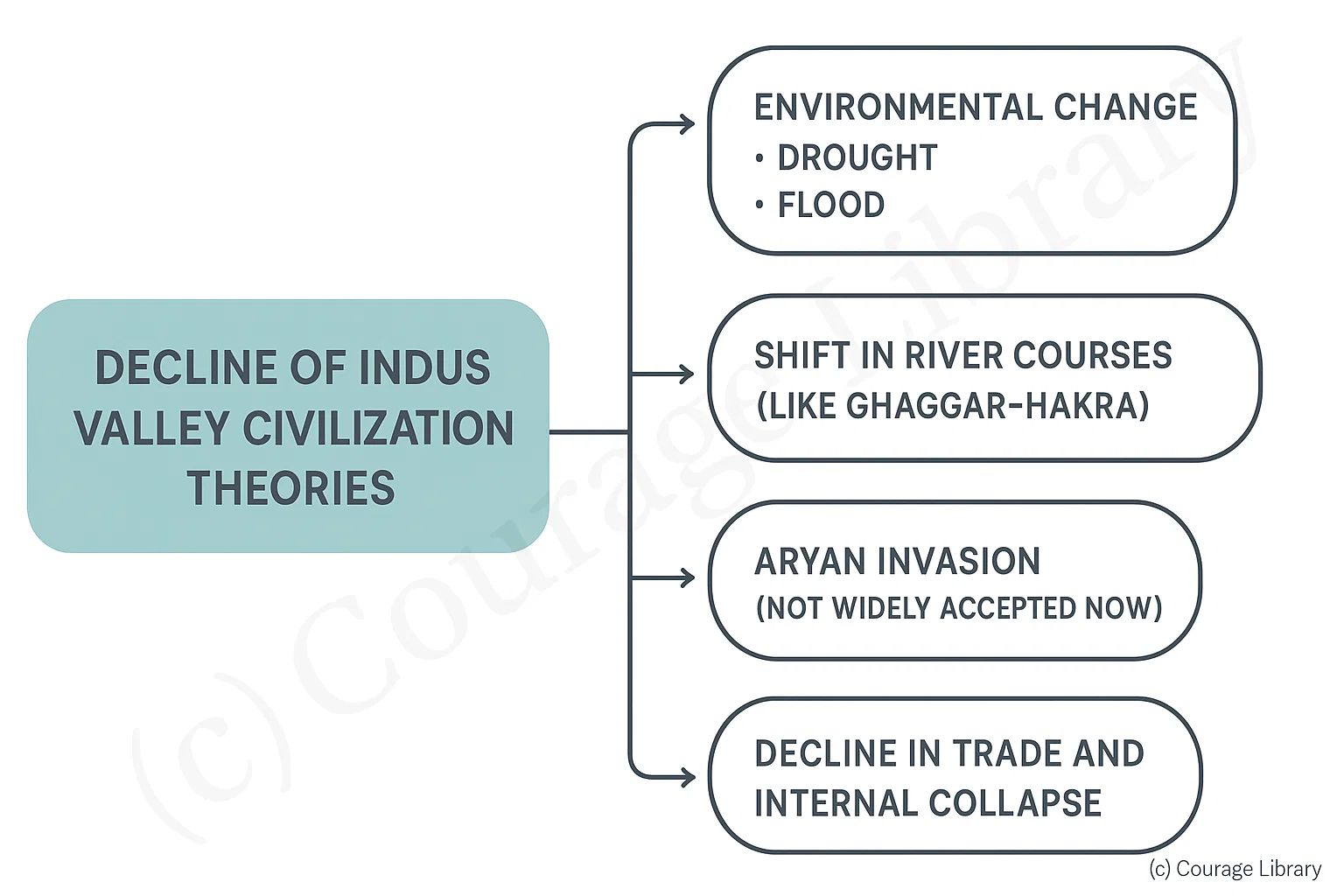
Decline (Theories)
- Environmental change: Drought, flood
- Shift in river courses (like Ghaggar-Hakra)
- Aryan invasion (not widely accepted now)
- Decline in trade and internal collapse
Quick Revision Points
| Topic | Important Point |
|---|---|
| First site discovered | Harappa (1921) by Daya Ram Sahni |
| Excavation of Mohenjodaro | 1922 by R.D. Banerjee |
| Largest site (India) | Rakhigarhi (Haryana) |
| Largest site(overall) | Mohenjodaro (Pakistan) |
| Smallest site | Allahdino (Pakistan) |
| Dockyard | Lothal |
| Great bath | Mohenjodaro |
| Fire altars | Kalibangan and Lothal |
| Ploughed field evidence | Kalibangan |
| Bead factory | Chanhudaro |
Developed By Roopasree Challa
Next
Start Your SSC CGL Journey Now!
Join Courage Library to experience disciplined study and expert support.
Be a Couragian!