SSC CGL - Detailed Guide 2025
Self-Paced Course

SI-Units-and-Their-Applications
Reference: Lucent GK, NCERT Class 6–12
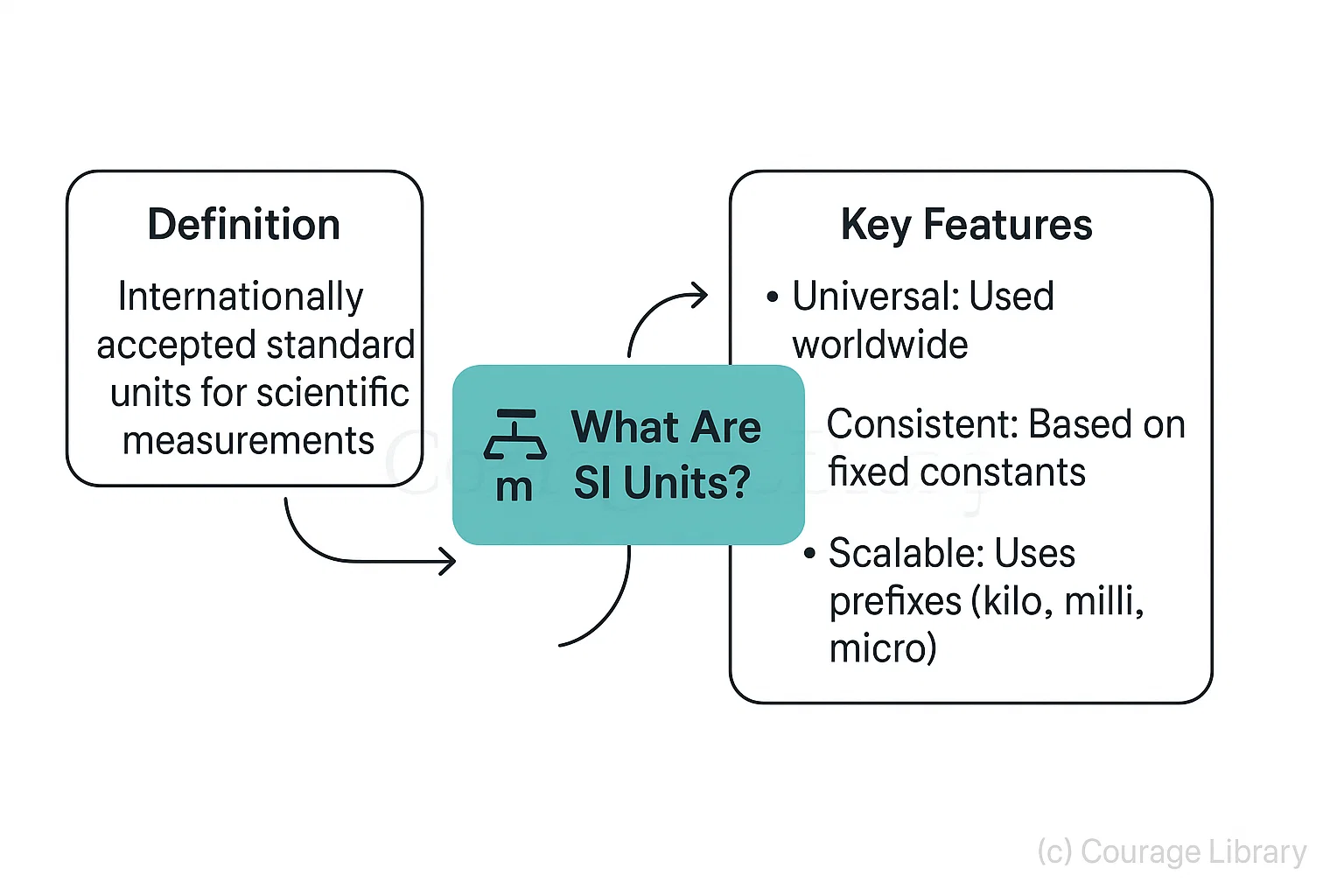
1. What Are SI Units?
SI units are internationally accepted standard units used for scientific measurements.
They are designed to be:
- Universal (used worldwide)
- Consistent (based on fixed constants)
- Scalable (with standard prefixes like kilo, milli, micro)
All measurements in science, engineering, and most standardized systems use SI units for clarity and precision.
2. The Seven Fundamental SI Units
| Physical Quantity | SI Unit | Symbol | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Length | metre | m | Distance between two points |
| Mass | kilogram | kg | Amount of matter |
| Time | second | s | Duration of an event |
| Electric Current | ampere | A | Flow of electric charge |
| Temperature | kelvin | K | Measure of thermal energy |
| Amount of Substance | mole | mol | Quantity of particles (atoms/molecules) |
| Luminous Intensity | candela | cd | Brightness of light source |
3. Common Derived SI Units
These are combinations of fundamental units based on physical laws.
| Quantity | Unit (Name) | Symbol | Derived from |
|---|---|---|---|
| Area | square metre | m² | m × m |
| Volume | cubic metre | m³ | m × m × m |
| Speed / Velocity | metre/second | m/s | m ÷ s |
| Acceleration | m/s² | m/s² | velocity ÷ time |
| Force | newton | N | kg·m/s² |
| Work / Energy | joule | J | N·m or kg·m²/s² |
| Power | watt | W | J/s or kg·m²/s³ |
| Pressure | pascal | Pa | N/m² or kg/m·s² |
| Frequency | hertz | Hz | cycles per second |
| Electric Charge | coulomb | C | A·s |
| Voltage | volt | V | J/C |
| Resistance | ohm | Ω | V/A |
| Capacitance | farad | F | C/V |
| Magnetic Field | tesla | T | Wb/m² |
These units form the basis of calculations in physics and chemistry.
4. Prefixes Used with SI Units
To express very large or very small values, prefixes are added to base units:
| Prefix | Symbol | Factor | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| giga | G | 10⁹ | 1 GW = 10⁹ watts |
| mega | M | 10⁶ | 1 MW = 10⁶ watts |
| kilo | k | 10³ | 1 km = 1000 m |
| deci | d | 10⁻¹ | 1 dL = 0.1 L |
| centi | c | 10⁻² | 1 cm = 0.01 m |
| milli | m | 10⁻³ | 1 mg = 0.001 g |
| micro | μ | 10⁻⁶ | 1 μm = 0.000001 m |
| nano | n | 10⁻⁹ | 1 ns = 0.000000001 s |
5. Applications of SI Units
In Science & Engineering:
- Physics uses SI for precise calculations (e.g., motion, force, electricity)
- Chemistry uses moles, joules, and kelvin for reaction calculations and energy
- Biology uses metres, grams, litres, etc., in lab work and medical measurements
In Daily Life:
| Field | SI Unit Application |
|---|---|
| Health | kg (body mass), mL (medicines), °C → K |
| Transport | m/s, km/h (speed), m (distance) |
| Construction | m² (area), m³ (volume) |
| Electricity Bill | kWh (kilowatt-hour, = 3.6 × 10⁶ J) |
| Food Labels | kJ (energy), g (nutrition facts) |
Accuracy in SI-based units ensures uniformity across industries and countries.
6. Advantages of SI Units
- Universal acceptance
- Easy to convert using powers of 10
- Reduces confusion in international trade, science, and education
- Legally enforced in most countries (including India)
Start Your SSC CGL Journey Now!
Join Courage Library to experience disciplined study and expert support.
Be a Couragian!