SSC CGL - Detailed Guide 2025
Self-Paced Course

Environment and Ecology
Reference: NCERT Class 10-12, Lucent GK
1. Ecosystems and Food Chains
Ecology is the study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their physical environment. The environment includes all biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) factors.
Ecosystem Components
| Components | Examples |
|---|---|
| Biotic | Plants, animals, microbes |
| Abiotic | Air, water, soil, temperature, sunlight |
Types of Ecosystems
- Natural: Forests, oceans, grasslands, deserts
- Artificial: Gardens, aquariums, crop fields
Producers, Consumers, and Decomposers
| Category | Function | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Producers (Autotrophs) | Make food via photosynthesis | Green plants, algae |
| Consumers (Heterotrophs) | Depend on others for food | Animals, humans |
| Decomposers | Break down dead matter | Bacteria, fungi |
Food Chain
- Linear sequence showing who eats whom in an ecosystem
- Starts with producers and ends with top predators
- Example: Grass → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake → Eagle
Trophic Levels:
Each step in a food chain is a trophic level. Energy transfer is only ~10% efficient between levels (10% law).
Food Web and Energy Pyramid
- Food Web: Interconnected food chains in an ecosystem
- Energy Pyramid: Visual representation of energy flow (Producers → Herbivores → Carnivores)
2. Pollution and Conservation
Pollution
Unwanted and harmful changes in the environment due to natural or man-made activities.
| Type of Pollution | Source | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Air Pollution | Vehicles, industries, burning fossil fuels | Respiratory diseases, acid rain, global warming |
| Water Pollution | Sewage, industrial waste, chemicals | Waterborne diseases, aquatic life loss |
| Soil Pollution | Pesticides, plastic, industrial discharge | Loss of fertility, crop contamination |
| Noise Pollution | Traffic, loudspeakers, construction | Hearing loss, stress |
| Thermal Pollution | Hot water from industries into rivers | Affects aquatic life |
Key Pollutants
- CO₂, SO₂, NOx, CFCs (chlorofluorocarbons), heavy metals, plastics
Conservation
Efforts to protect natural resources and maintain ecological balance.
| Type | Examples |
|---|---|
| Wildlife Conservation | National parks, wildlife sanctuaries |
| Forest Conservation | Afforestation, preventing deforestation |
| Water Conservation | Rainwater harvesting, drip irrigation |
| Air Conservation | Reducing vehicle emissions, clean energy |
Important Acts in India
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972
- Forest Conservation Act, 1980
- Environment Protection Act, 1986
International Initiatives
- Kyoto Protocol: Reduce greenhouse gases
- Paris Agreement: Climate change mitigation
- Montreal Protocol: Ban on ozone-depleting substances
3. Biodiversity and Sustainable Development
Biodiversity
The variety of living organisms in a given area.
| Level | Description |
|---|---|
| Genetic Diversity | Variety within species (e.g., dog breeds) |
| Species Diversity | Variety of species in an area |
| Ecosystem Diversity | Variety of ecosystems (e.g., deserts, forests, wetlands) |
India is one of the 17 megadiverse countries.
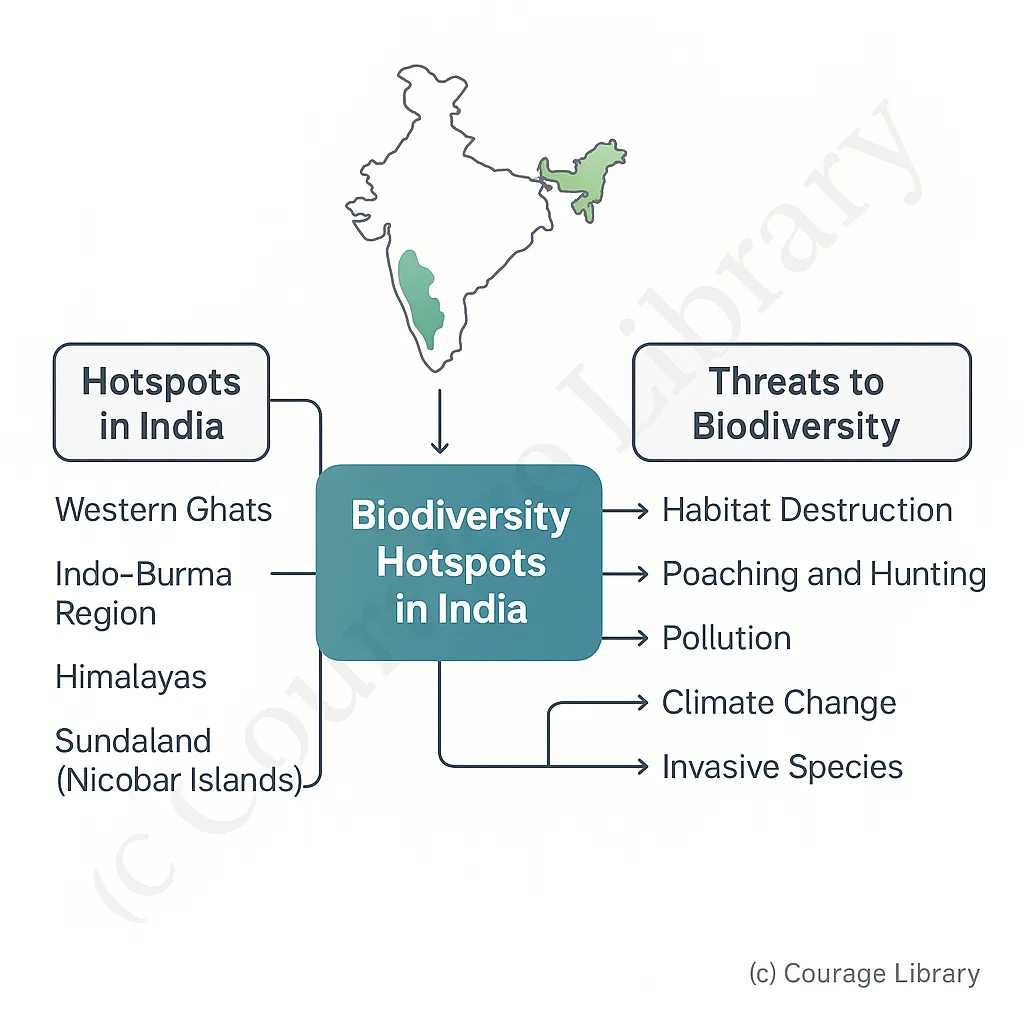
Biodiversity Hotspots in India
- Western Ghats
- Indo-Burma region
- Himalayas
- Sundaland (Nicobar Islands)
Threats to Biodiversity
- Habitat destruction
- Poaching and hunting
- Pollution
- Climate change
- Invasive species
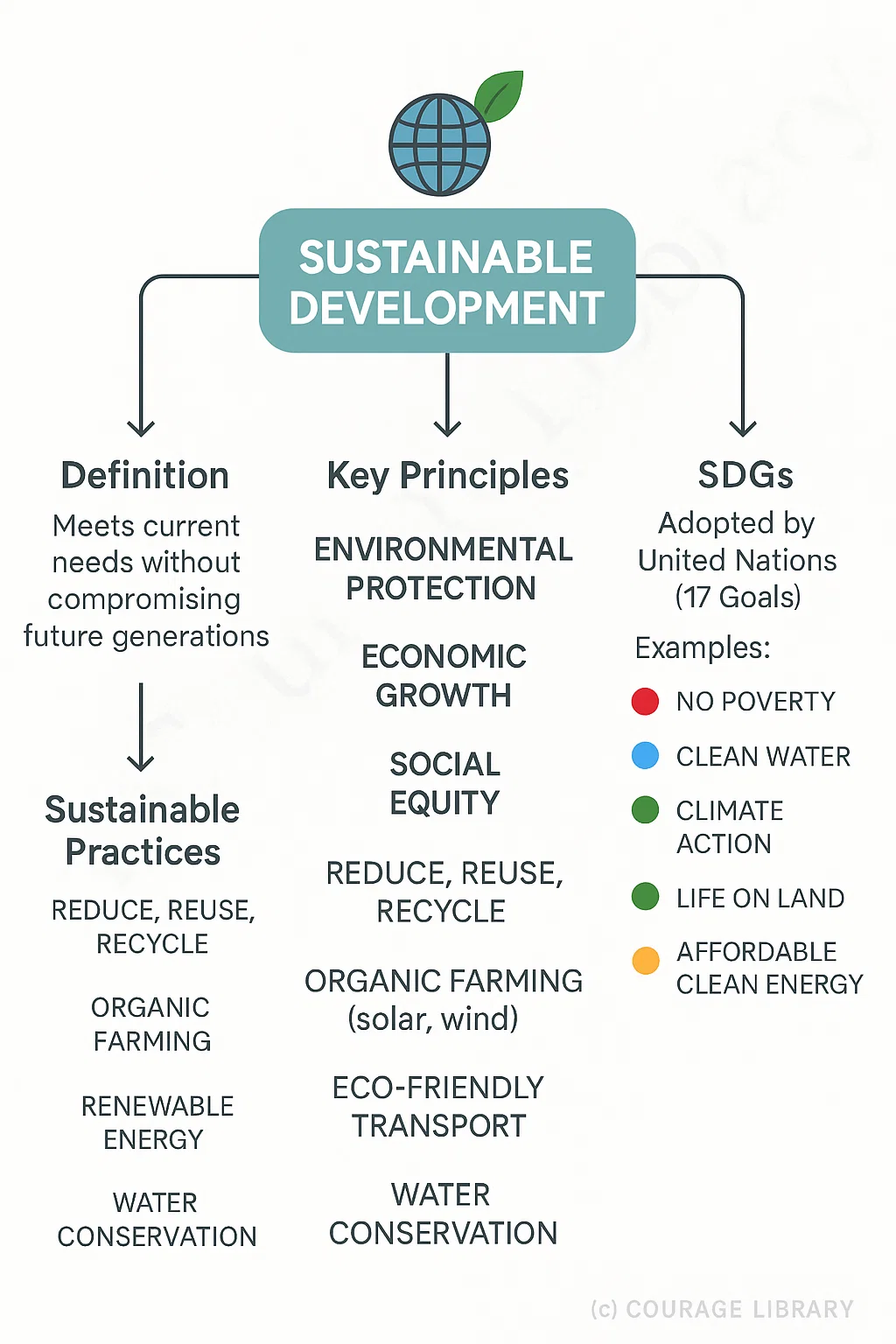
Sustainable Development
Development that meets current needs without compromising future generations.
Key principles:
- Environmental protection
- Economic growth
- Social equity
Sustainable Practices
- Reduce, Reuse, Recycle (3Rs)
- Organic farming
- Renewable energy (solar, wind)
- Eco-friendly transport
- Water conservation
SDGs (Sustainable Development Goals)
- Adopted by the United Nations (17 goals)
- Examples: No poverty, clean water, climate action, life on land, affordable clean energy
Master Biology Concepts with Us!
Join Courage Library for comprehensive study materials and expert guidance.
Be a Couragian!