SSC CGL - Detailed Guide 2025
Self-Paced Course

Units and Measurements in Science
Reference: Lucent GK, NCERT Class 6–12
Measurements are essential in all scientific experiments and calculations. Understanding standard units, systems of measurement, and their conversions is crucial for accuracy
Physical Quantities & Units
Physical Quantity: Any property of a material or system that can be quantified (measured).
Quantities are classified into two types:
| Type | Example |
|---|---|
| Fundamental | Length, Mass, Time, Temperature |
| Derived | Speed, Force, Pressure |
Unit: A standard reference used to measure physical quantities.
International System of Units (SI Units)
SI (Système International) is the modern metric system accepted globally for scientific work.
| Physical Quantity | SI Unit | Symbol |
|---|---|---|
| Length | metre | m |
| Mass | kilogram | kg |
| Time | second | s |
| Temperature | kelvin | K |
| Electric Current | ampere | A |
| Luminous Intensity | candela | cd |
| Amount of Substance | mole | mol |
These are called the seven fundamental SI units.
Common Derived Units
Derived from fundamental units using physical laws:
| Quantity | Unit | Symbol | Formula |
|---|---|---|---|
| Area | square metre | m² | length × breadth |
| Volume | cubic metre | m³ | length × breadth × height |
| Speed/Velocity | metre/second | m/s | distance ÷ time |
| Acceleration | meter/second² | m/s² | change in velocity ÷ time |
| Force | newton | N | mass × acceleration (kg·m/s²) |
| Pressure | pascal | Pa | force ÷ area (N/m²) |
| Energy/Work | joule | J | force × distance (N·m) |
| Power | watt | W | energy ÷ time (J/s) |
| Electric Charge | coulomb | C | current × time (A·s) |
| Potential Difference | volt | V | work ÷ charge (J/C) |
Most of these units are derived and standardized in SI.
Important Conversions
| Quantity | Conversion |
|---|---|
| 1 km | 1000 m |
| 1 m | 100 cm |
| 1 cm | 10 mm |
| 1 kg | 1000 g |
| 1 g | 1000 mg |
| 1 L | 1000 mL |
| 1 tonne | 1000 kg |
| 1 hour | 3600 seconds |
| 1 minute | 60 seconds |
| 1 cal (calorie) | 4.184 joules |
| 1 horsepower | 746 watts |
Temperature Conversion:
°C to K → T(K) = °C + 273.15
°F to °C → (°F − 32) × 5⁄9
Instruments Used in Measurement
| Quantity | Instrument |
|---|---|
| Length | Ruler, Vernier caliper, Micrometer screw gauge |
| Mass | Beam balance, Electronic balance |
| Temperature | Thermometer |
| Time | Stopwatch, Clock |
| Electric current | Ammeter |
| Voltage | Voltmeter |
| Pressure | Barometer, Manometer |
| Light intensity | Photometer |
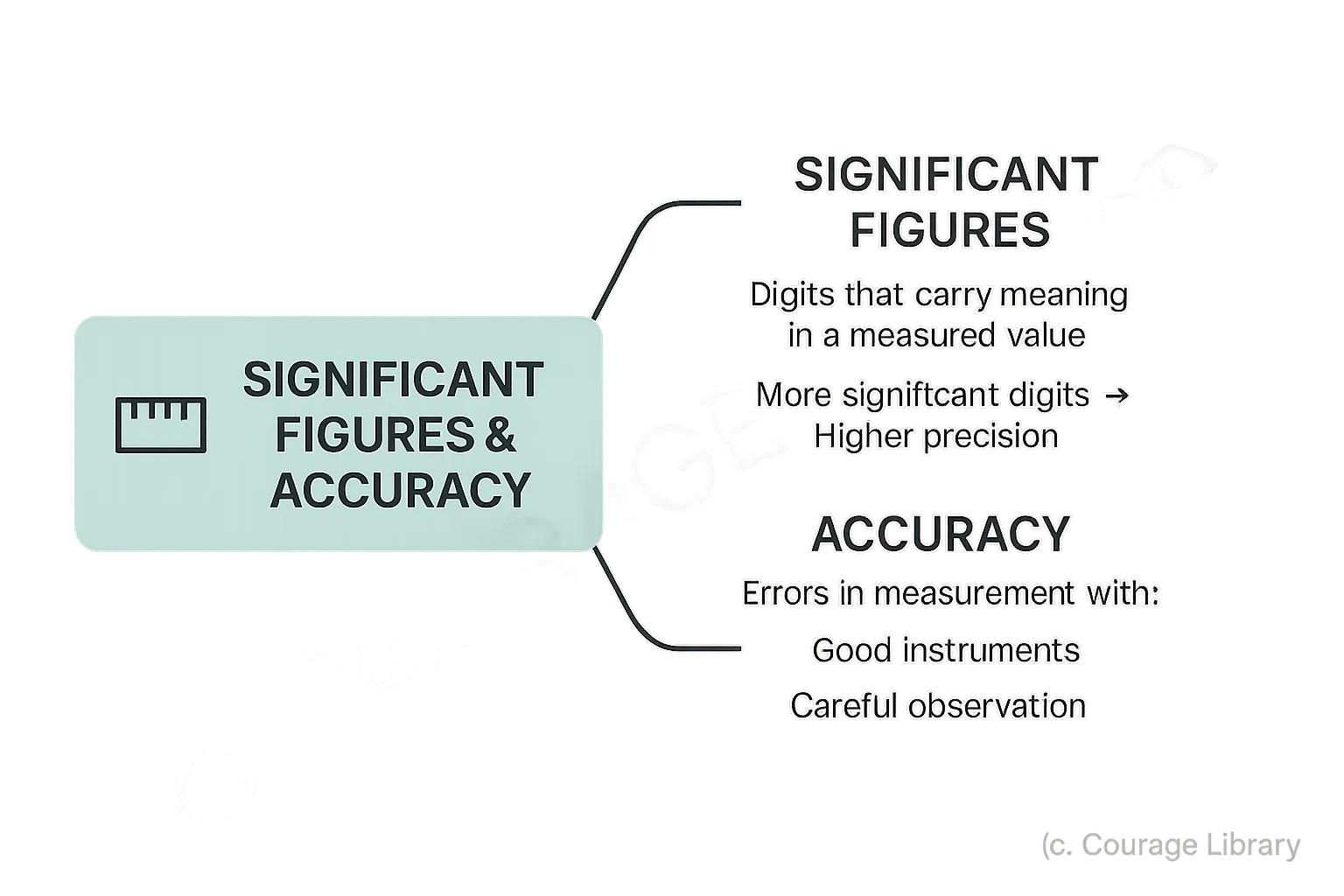
Significant Figures & Accuracy (for conceptual understanding)
- Significant figures represent the digits that carry meaning in a measured value.
- More significant digits imply higher precision.
- Errors in measurement are inevitable; accuracy improves with good instruments and careful observation.
Start Your SSC CGL Journey Now!
Join Courage Library to experience disciplined study and expert support.
Be a Couragian!