SSC CGL - Detailed Guide 2025
Self-Paced Course

Electricity and Magnetism
Reference: Lucent GK, NCERT Class 6–12
Current, Voltage, Resistance & Ohm’s Law
| Concept | Description | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Electric Current (I) | Flow of electric charge per unit time; I = Q / t | Ampere (A) |
| Electric Charge (Q) | Fundamental property of matter | Coulomb (C) |
| Voltage (V) | Electric potential difference between two points | Volt (V) |
| Resistance (R) | Opposition to current flow; depends on material, length, area, & temperature | Ohm (Ω) |
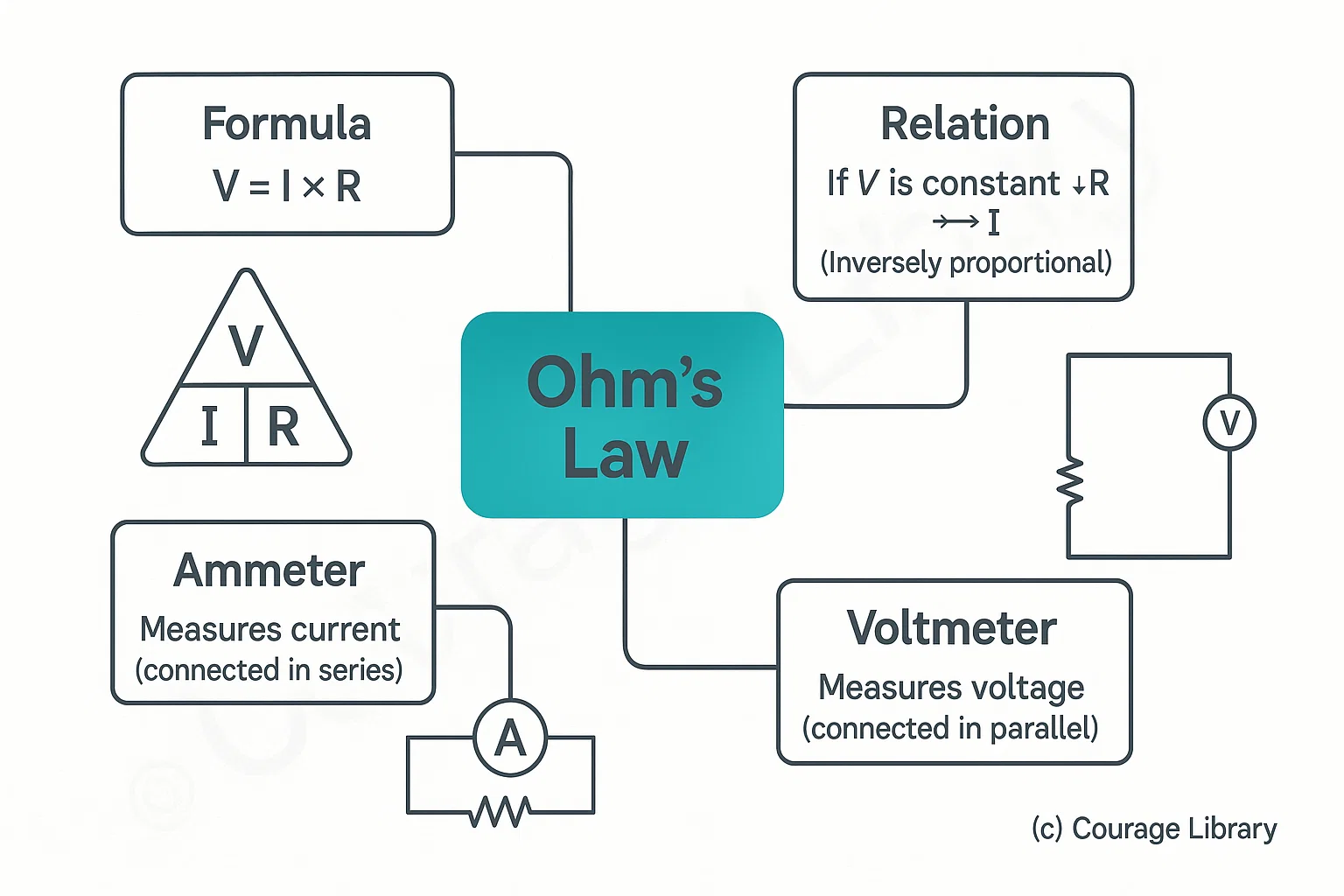
Ohm’s Law:
V = I × R
(V = Voltage, R = Resistance, I = Current)
- If V is constant: ↑R → ↓I (Inversely proportional)
- Ammeter measures current (connected in series)
- Voltmeter measures voltage (connected in parallel)
Series and Parallel Circuits
| Property | Series Circuit | Parallel Circuit |
|---|---|---|
| Current (I) | Same through all components | Divides among branches |
| Voltage (V) | Divides among components | Same across all branches |
| Resistance (R) | R = R₁ + R₂ + R₃… | 1/R = 1/R₁ + 1/R₂ + 1/R₃… |
| Advantage | Easy to connect, less wires | Devices work independently |
| Disadvantage | One fails → all fail | One fails → others still work |
Bulbs in homes are connected in parallel (not series)
Electric Power and Energy
| Concept | Formula | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Power (P) | P = V × I = I²R = V²/R | Watt (W) |
| Energy (E) | E = P × t | Joule (J), kilowatt-hour (kWh) |
| 1 kilowatt-hour | 1 kWh = 1000 W × 3600 s = 3.6 × 10⁶ J | Unit used in electricity bills |
Higher power appliances consume more energy per unit time.
Fuse: safety device that melts when current exceeds limit (prevents fire).
Magnetism and Electromagnetic Induction
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Magnetic Field (B) | Region around magnet where magnetic force acts |
| Magnetic Lines of Force | Direction from North to South pole outside magnet; never intersect |
| Earth’s Magnetism | Earth behaves like a giant bar magnet (magnetic North ≠ geographic North) |
| Electromagnet | Temporary magnet formed by passing current through a coil |
| Right-Hand Thumb Rule | Thumb = current direction, curled fingers = magnetic field |
| Electromagnetic Induction | Inducing current in conductor by changing magnetic field (discovered by Faraday) |
| Fleming’s Right-Hand Rule | Used for generators: → Thumb = motion, → Forefinger = magnetic field, → Middle finger = current direction |
| Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule | Used for motors: → Thumb = force, → Forefinger = field, → Middle = current |
Generator: Converts mechanical energy → electrical energy
Motor: Converts electrical energy → mechanical energy
Developed By Roopasree Challa
Next
Start Your SSC CGL Journey Now!
Join Courage Library to experience disciplined study and expert support.
Be a Couragian!