SSC CGL - Detailed Guide 2025
Self-Paced Course

Plant Physiology
Reference: Lucent GK, NCERT Class 6–12
Plant physiology deals with the functions and processes in plants that help them survive, grow, and reproduce.
Photosynthesis
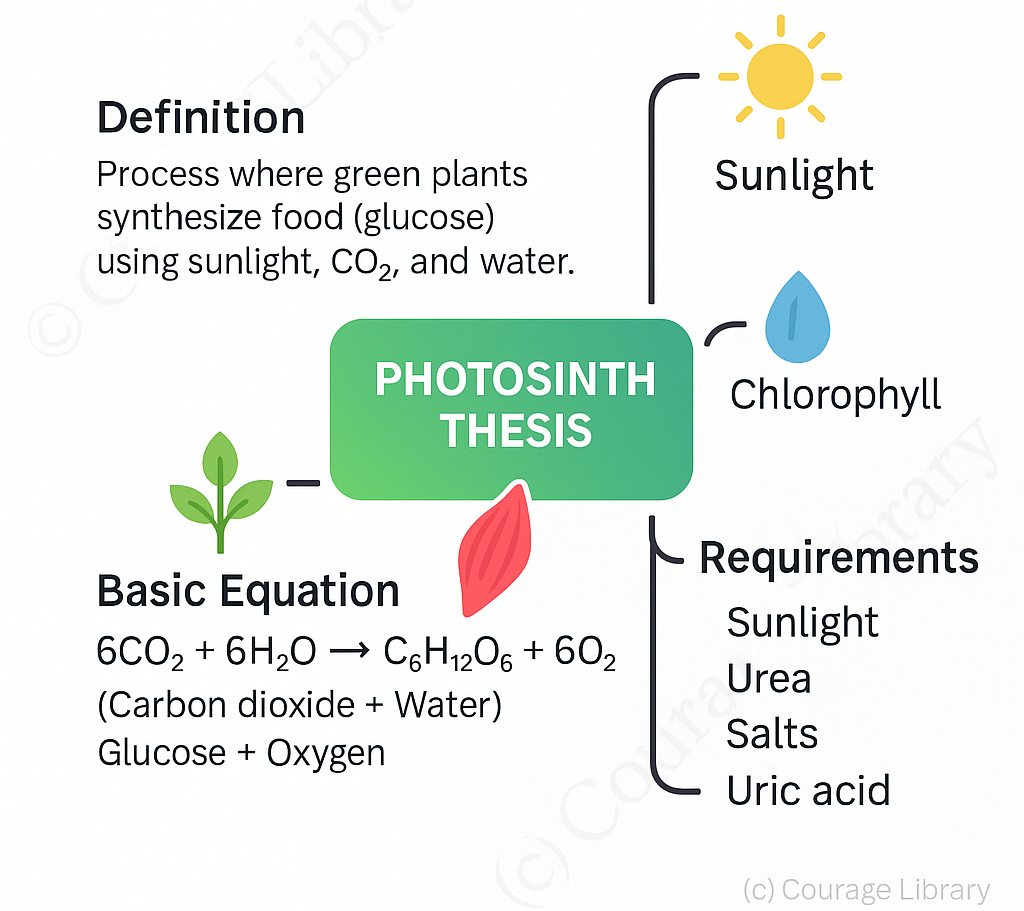
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants synthesize food (glucose) using sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water.
Basic Equation:
6CO₂ + 6H₂O ⟶ C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂
(Carbon dioxide + Water ⟶ Glucose + Oxygen), In the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll
Key Components:
| Component | Role |
|---|---|
| Chlorophyll | Pigment in chloroplasts; traps solar energy |
| Sunlight | Provides energy for the process |
| CO₂ | Taken in from the air through stomata |
| H₂O | Absorbed by roots from the soil |
Occurs mainly in mesophyll cells of leaves
By-product oxygen is released into the atmosphere
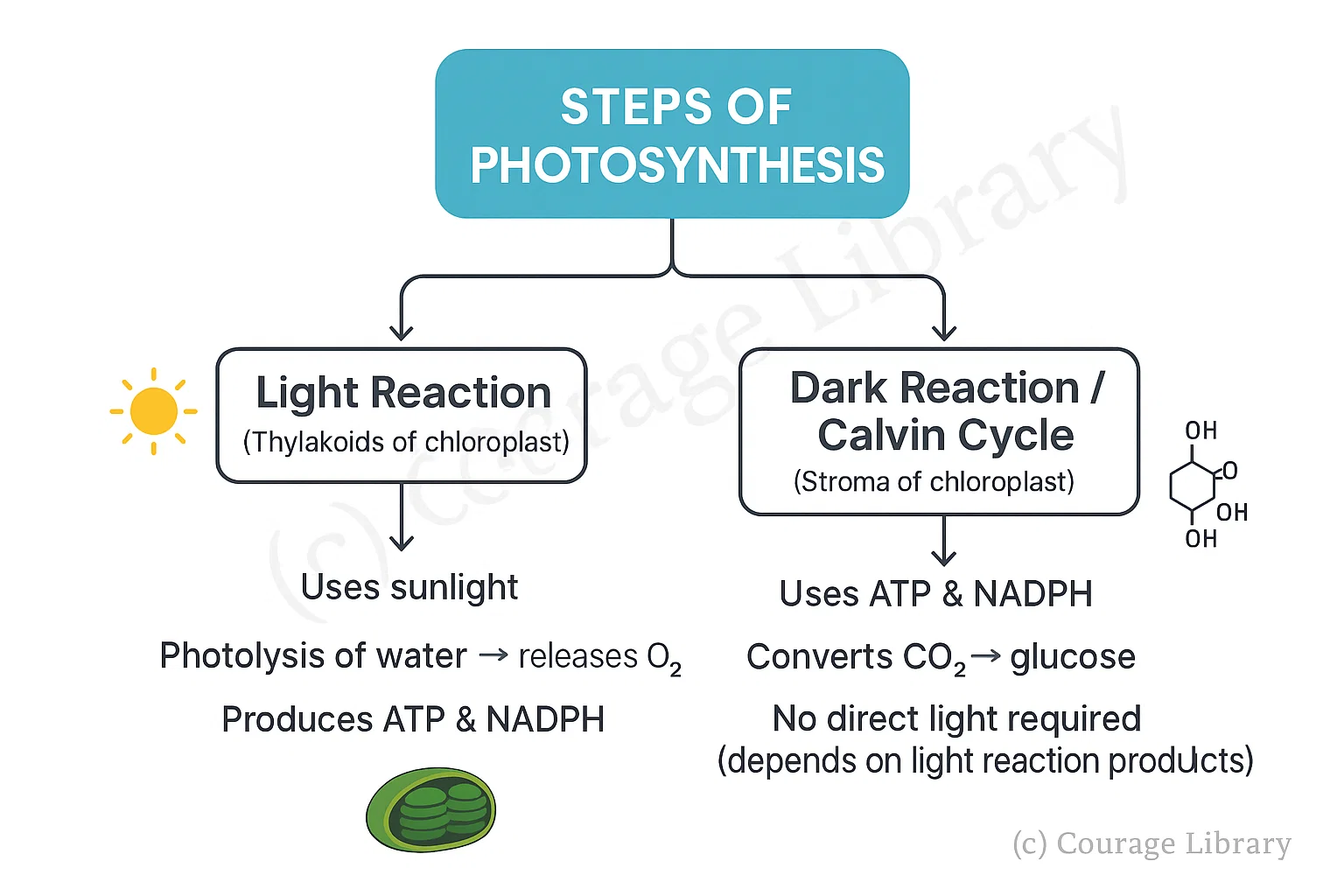
Steps of Photosynthesis:
-
Light Reaction (occurs in thylakoids of chloroplast)
- Uses sunlight
- Splits water (photolysis) → releases O₂
- Produces ATP and NADPH
-
Dark Reaction / Calvin Cycle (occurs in stroma)
- Uses ATP & NADPH to convert CO₂ → glucose
- Does not require direct light, but depends on products of light reaction
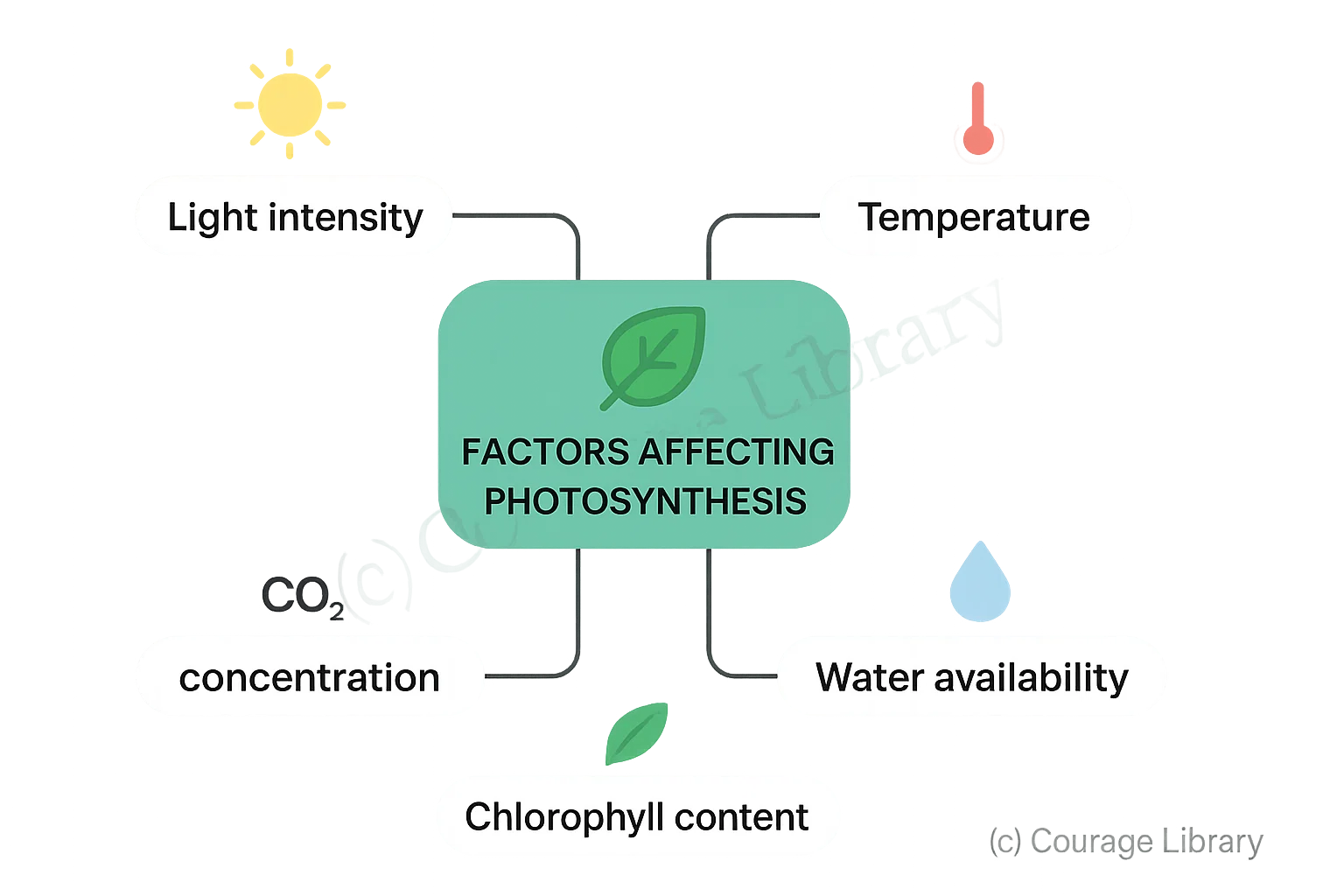
Factors Affecting Photosynthesis:
- Light intensity
- CO₂ concentration
- Temperature
- Chlorophyll content
- Water availability
Transpiration
Transpiration is the loss of water in the form of water vapor from aerial parts of a plant (mainly leaves).
Types of Transpiration
| Type | Through Which Part |
|---|---|
| Stomatal Transpiration | Stomata (major portion) |
| Cuticular Transpiration | Cuticle (waxy leaf covering) |
| Lenticular Transpiration | Lenticels (small openings on stem) |
Stomata open during the day (for gas exchange) and close at night.
Transpiration pull helps in ascent of sap (movement of water upward.
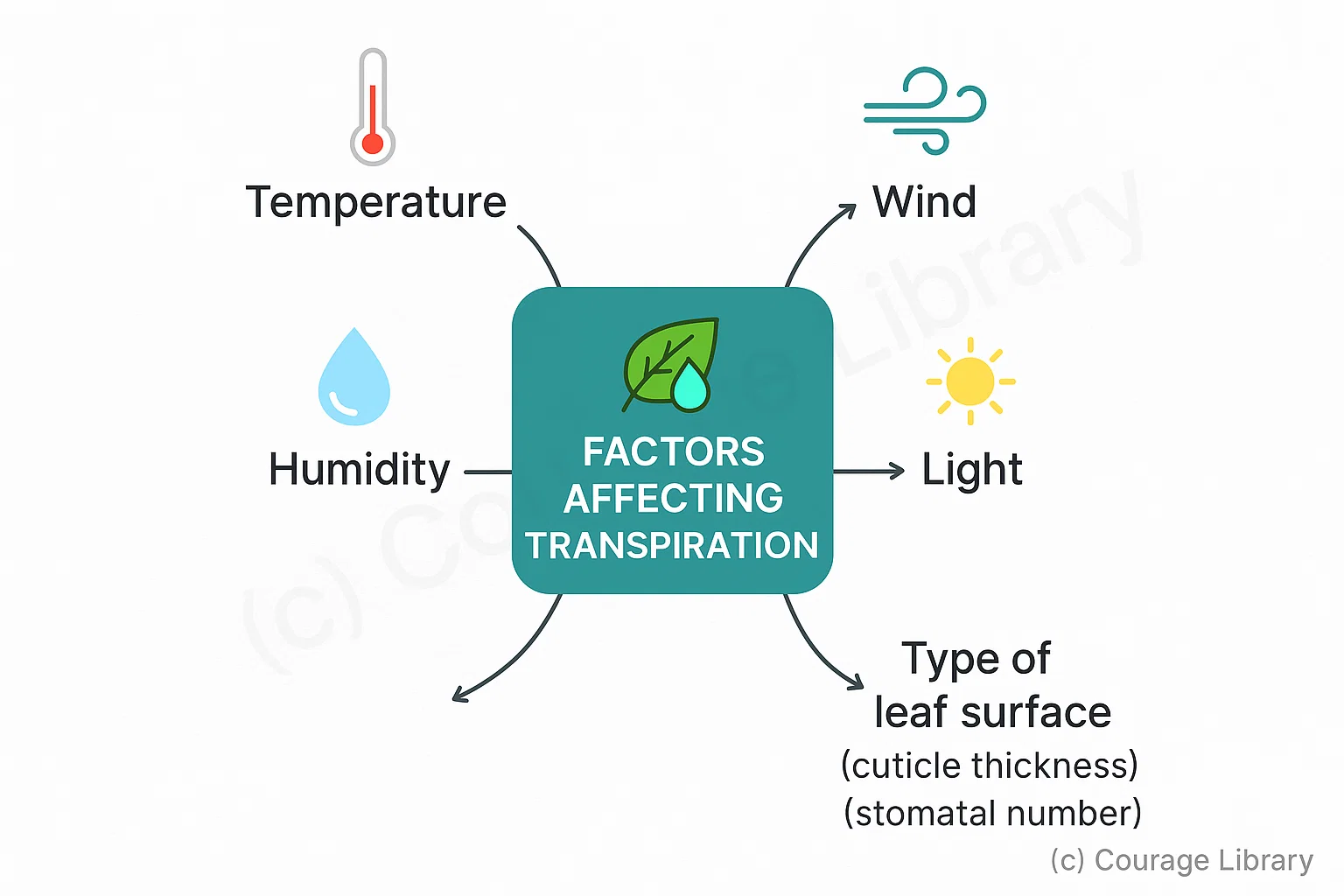
Factors Affecting Transpiration:
- Temperature
- Humidity
- Wind
- Light
- Type of leaf surface (cuticle thickness, stomatal number)
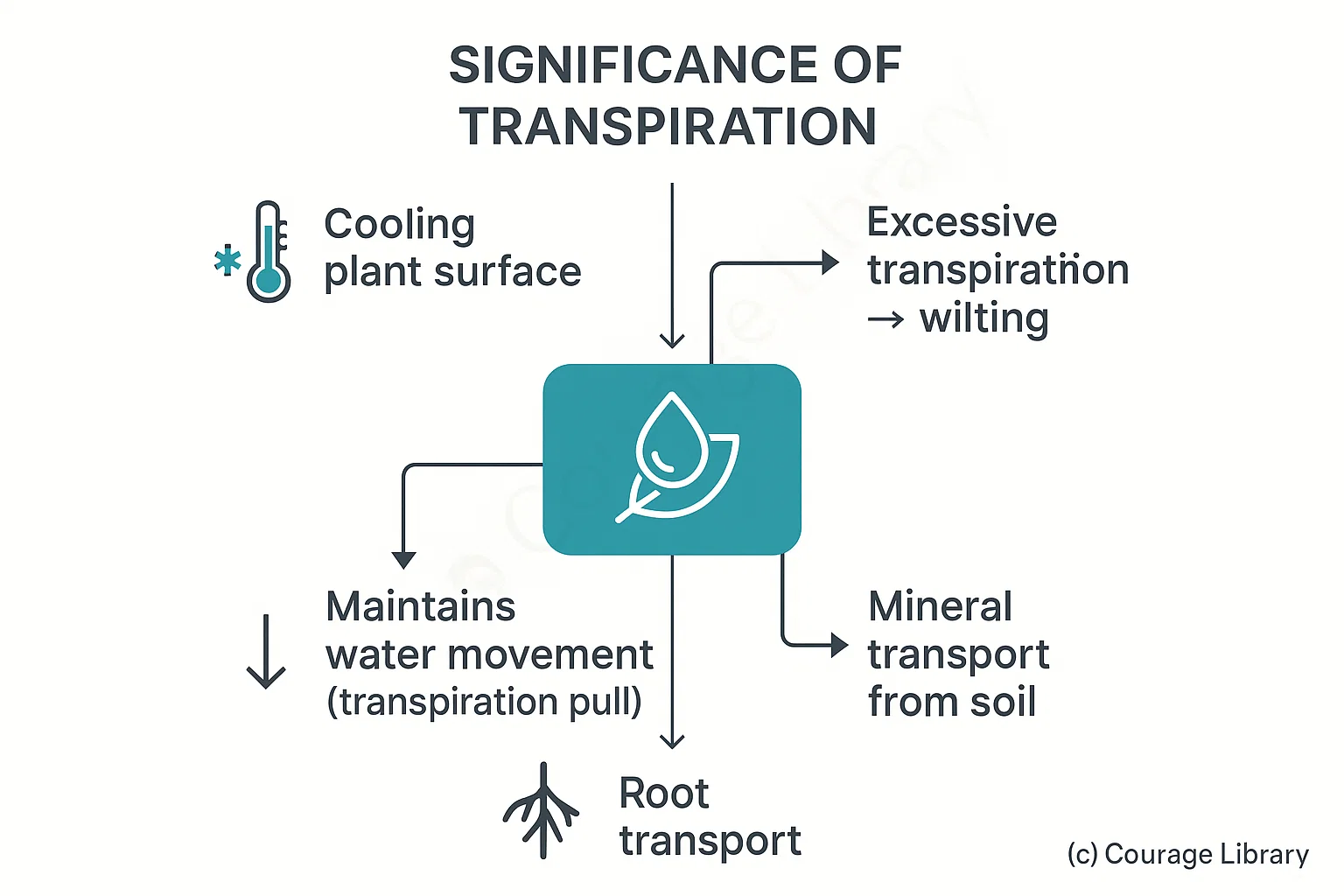
Significance of Transpiration:
- Helps in cooling plant surface
- Maintains water movement (transpiration pull)
- Helps in mineral transport from soil
- Excessive transpiration causes wilting
Reproduction in Plants
Plants reproduce by various methods: asexual and sexual.
Asexual Reproduction
Method
Description
Example
Vegetative
Propagation
New plants grow from roots,
stems, leaves
Potato (tuber), Onion
(bulb),
Money plant (stem cutting)
Budding
Outgrowth forms new
individual
Yeast
Fragmentation
Body breaks into fragments
Spirogyra
Spore
Formation
Spores develop into new
plants
Fungi, Ferns
Advantages: Fast, identical offspring.
Disadvantages: No genetic variation.
| Method | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Vegetative Propagation | New plants grow from roots, stems, leaves | Potato (tuber), Onion (bulb), Money plant (stem cutting) |
| Budding | Outgrowth forms new individual | Yeast |
| Fragmentation | Body breaks into fragments | Spirogyra |
| Spore Formation | Spores develop into new plants | Fungi, Ferns |
Advantages: Fast, identical offspring.
Disadvantages: No genetic variation.
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
| Flower Part | Role |
|---|---|
| Stamen | Male reproductive part (Anther + Filament) |
| Carpel/Pistil | Female reproductive part (Ovary + Style + Stigma) |
| Pollination | Transfer of pollen from anther to stigma |
| Fertilization | Fusion of male and female gametes in ovary |
| Ovary | Develops into fruit |
| Ovule | Develops into seed |
Types of Pollination
| Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Self-Pollination | Pollen from same flower or same plant | Pea, Wheat |
| Cross-Pollination | Pollen from different plant | Apple, Mustard |
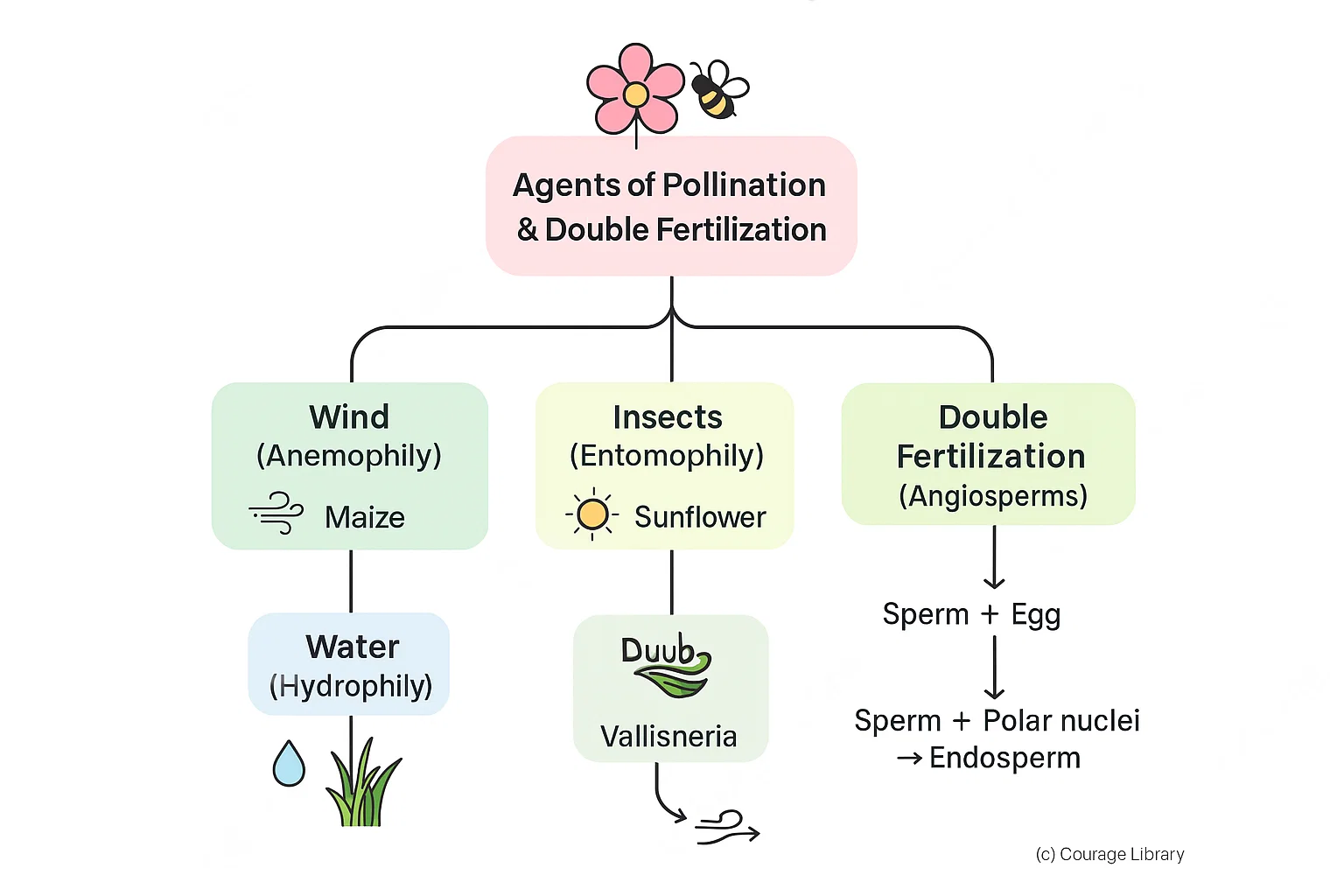
Agents of Pollination
- Wind (Anemophily): Maize
- Insects (Entomophily): Sunflower
- Water (Hydrophily): Vallisneria
Double fertilization is unique to angiosperms (one sperm fertilizes egg → zygote, other fuses with two polar nuclei → endosperm)
Start Your SSC CGL Journey Now!
Join Courage Library to experience disciplined study and expert support.
Be a Couragian!