SSC CGL - Detailed Guide 2025
Self-Paced Course

Environmental Chemistry
Reference: Lucent GK, NCERT Class 6–12
Air, Water, and Soil Pollution
Pollution: The undesirable change in the physical, chemical, or biological characteristics of air, water, or soil.
| Type of Pollution | Key Pollutants | Sources | Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Air Pollution | CO, SO₂, NOx, CO₂, Particulate matter | Vehicles, factories, burning fossil fuels | Respiratory diseases, acid rain, smog, global warming |
| Water Pollution | Sewage, heavy metals, detergents, nitrates | Industrial waste, domestic discharge | Waterborne diseases, aquatic death, bioaccumulation |
| Soil Pollution | Pesticides, plastic, heavy metals | Chemical fertilizers, industrial dumping | Loss of fertility, food contamination, disruption of soil microbes |
BOD (Biological Oxygen Demand) is a key indicator of water pollution — higher BOD = higher pollution.
Greenhouse Effect & Ozone Layer
Greenhouse Effect
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Trapping of heat in Earth's atmosphere due to greenhouse gases |
| Major Gases | CO₂, CH₄ (methane), N₂O, CFCs, Water vapor |
| Positive Role | Maintains Earth’s temperature for life |
| Problem | Excess greenhouse gases → Global warming → climate change |
| Effects | Melting glaciers, sea-level rise, desertification, erratic weather |
Measures: Afforestation, renewable energy, reduced emissions
Ozone Layer
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Location | Stratosphere (~10–50 km above Earth) |
| Function | Absorbs harmful UV-B and UV-C rays from Sun |
| Ozone Depletion | Caused by chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), halons |
| Effect | Skin cancer, cataracts, immune suppression, damage to plants/marine life |
| Global Effort | Montreal Protocol (1987) to ban ozone-depleting substances |
Chemical Effects on Environment
| Chemical/Process | Effect on Environment |
|---|---|
| Acid Rain | SO₂ + NOx + Water → H₂SO₄/HNO₃ → Corrosion, soil damage, aquatic harm |
| Pesticides & Fertilizers | Soil and water pollution, biomagnification in food chain |
| E-waste | Toxic metals (Pb, Hg, Cd) → soil and groundwater contamination |
| Plastic Pollution | Non-biodegradable, blocks drainage, harms marine animals |
| Heavy Metals (e.g., Pb) | Neurological disorders, water pollution |
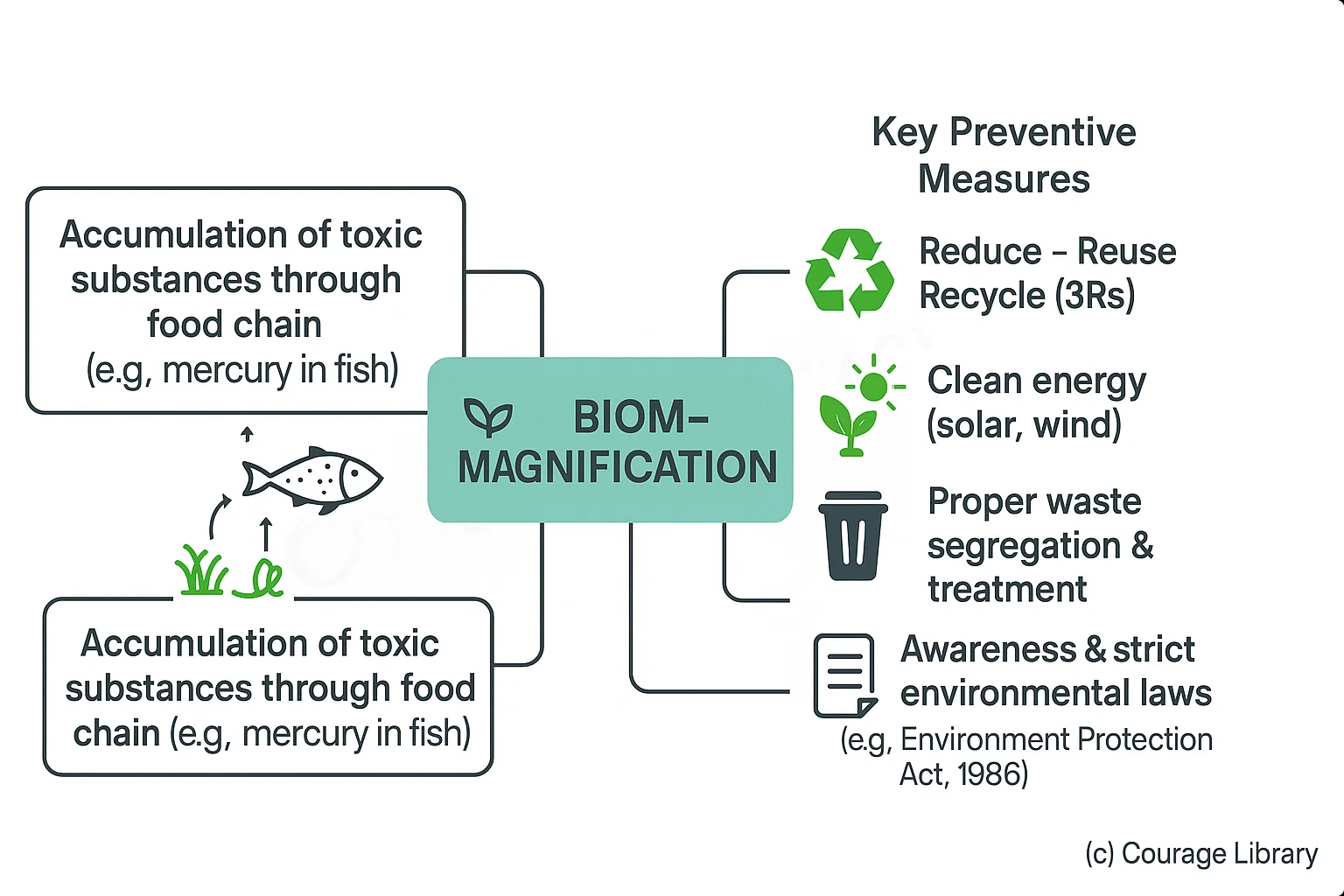
- Biomagnification: Accumulation of toxic substances through food chain (e.g., mercury in fish)
-
Key Preventive Measures:
- Reduce – Reuse – Recycle (3Rs)
- Clean energy (solar, wind)
- Proper waste segregation and treatment
- Awareness and strict environmental laws (e.g., Environment Protection Act, 1986)
Developed By Roopasree Challa
Next
Start Your SSC CGL Journey Now!
Join Courage Library to experience disciplined study and expert support.
Be a Couragian!