SSC CGL - Detailed Guide 2025
Self-Paced Course

Tissues
Reference: NCERT Class 10-12, Lucent GK
Tissues
Tissues are groups of similar cells that perform a specific function.
Tissues are broadly classified into:
- Plant Tissues
- Animal Tissues
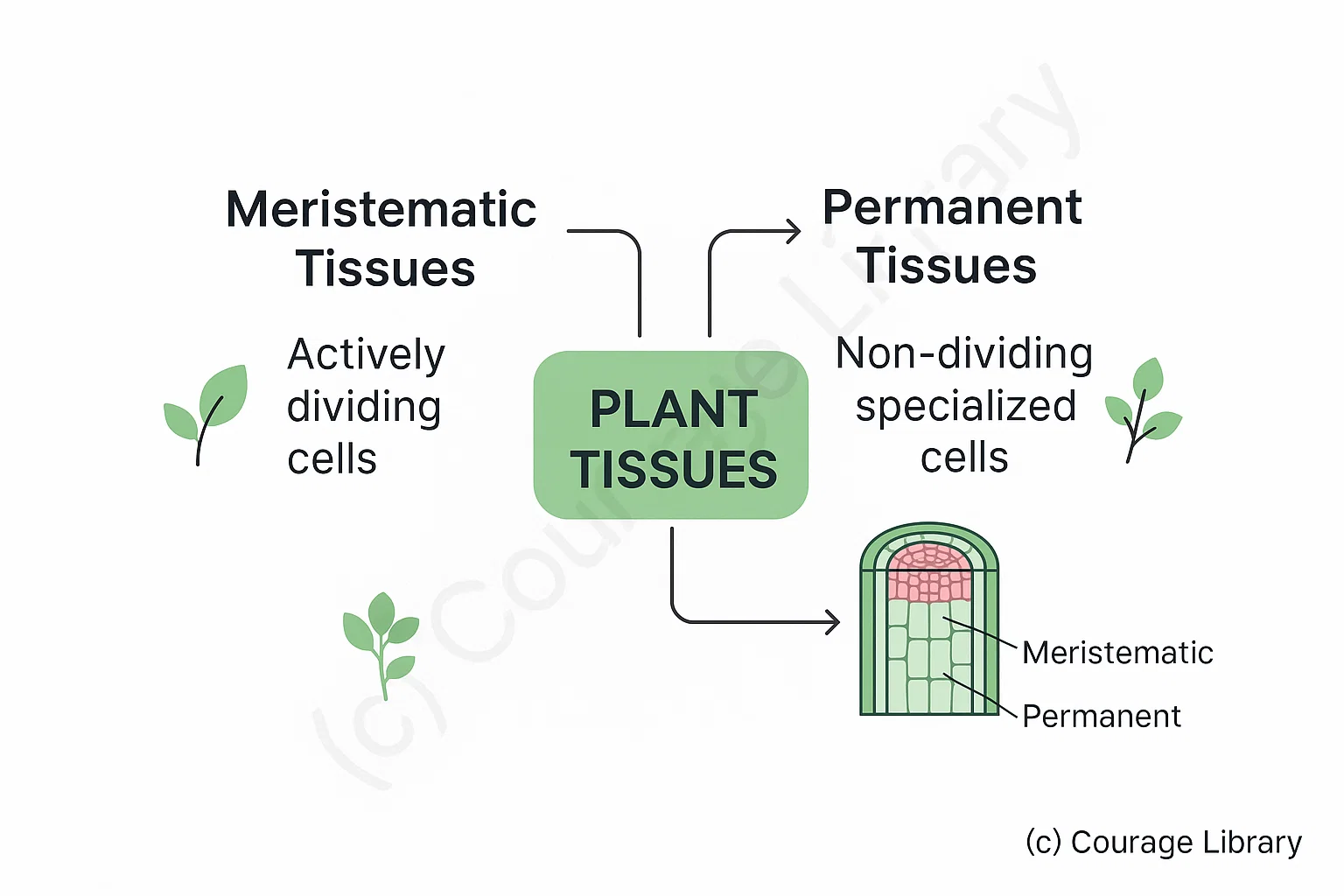
1. Plant Tissues
Plant tissues are classified into:
Meristematic Tissues
Actively dividing cells
Permanent Tissues
Non-dividing specialized cells
Meristematic Tissues
| Type | Location & Features | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Apical Meristem | Tips of roots and shoots | Increases length (primary growth) |
| Intercalary Meristem | At internodes or base of leaves | Increases length of internodes |
| Lateral Meristem | In cambium (side of stems and roots) | Increases thickness (secondary growth) |
Characteristics:
- Cells are small, with dense cytoplasm and large nucleus
- No vacuoles
- Thin cell wall; continuously divide
Permanent Tissues
Differentiated from meristematic cells and do not divide.
A. Simple Permanent Tissues — made of one type of cell
| Type | Features | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Parenchyma | Living, thin-walled, unspecialized, large vacuoles | Storage, photosynthesis (if chloroplast present) |
| Collenchyma | Living, thick at corners (cellulose/pectin) | Flexibility & mechanical support |
| Sclerenchyma | Dead, thick-walled (lignin), narrow lumen | Mechanical support & strength |
B. Complex Permanent Tissues — made of different types of cells
| Tissue | Components | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Xylem | Tracheids, Vessels, Xylem parenchyma, Fibres | Transport of water & minerals |
| Phloem | Sieve tubes, Companion cells, Phloem parenchyma, Fibres | Transport of food (photosynthates) |
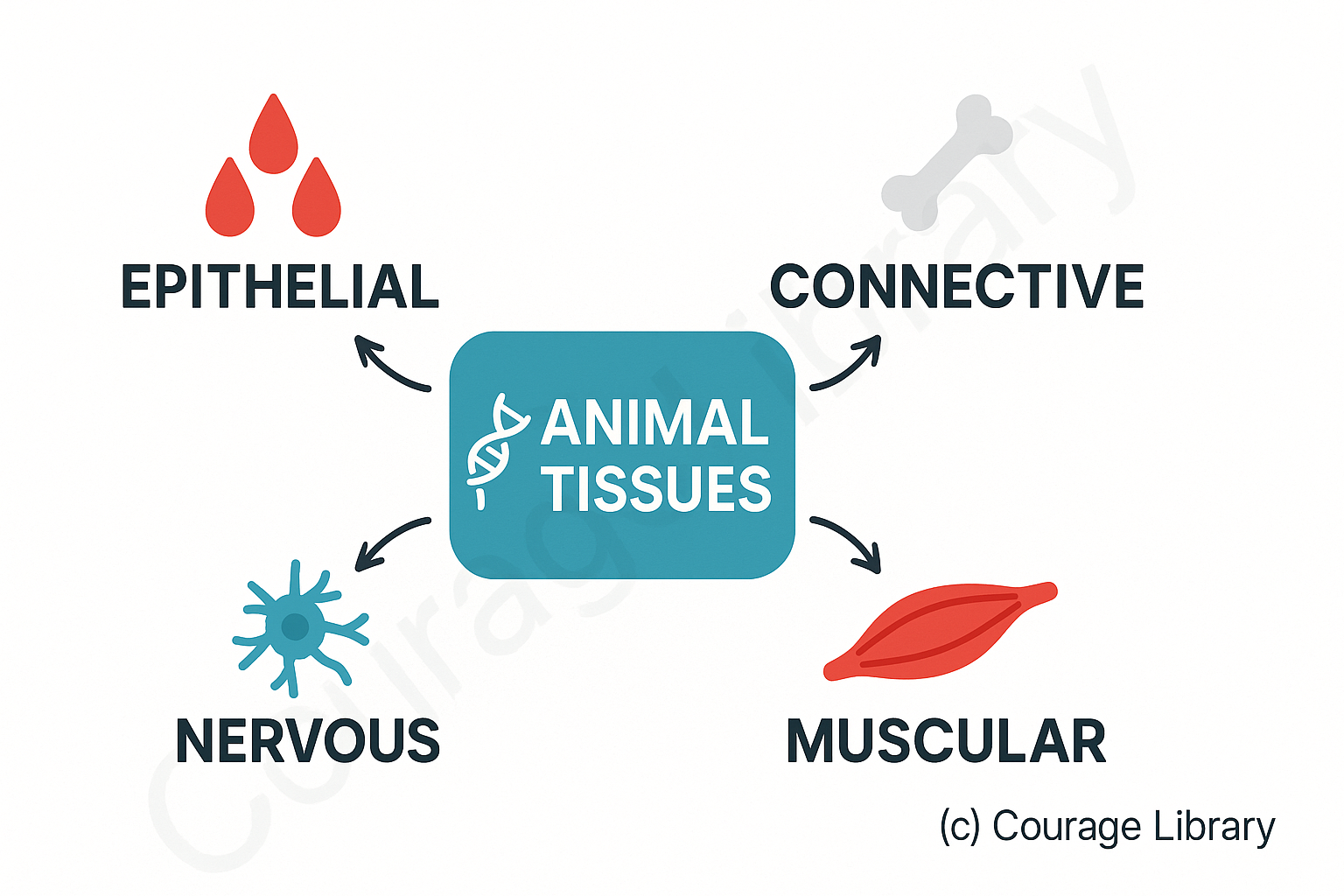
2. Animal Tissues
Animal tissues are categorized into:
Epithelial
Connective
Muscular
Nervous
Epithelial Tissue
Covers body surfaces, lines cavities and organs.
| Type | Structure | Function | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Squamous | Flat and thin cells | Diffusion, filtration | Lining of blood vessels, alveoli |
| Cuboidal | Cube-shaped | Secretion, absorption | Glands, kidney tubules |
| Columnar | Tall, column-like | Absorption, secretion | Intestine lining |
| Ciliated Columnar | Columnar with cilia | Movement of substances | Respiratory tract |
| Stratified | Layers of cells | Protection from mechanical stress | Skin |
Connective Tissue
Connects, supports, and binds tissues and organs.
| Type | Features & Components | Function | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Areolar Tissue | Loose, fibrous tissue with collagen & elastin | Binds skin to muscles | Beneath skin |
| Adipose Tissue | Stores fat; large vacuolated cells | Insulation, energy storage | Below skin, around organs |
| Tendons | Dense fibrous connective tissue | Connects muscle to bone | Joints |
| Ligaments | Elastic tissue | Connects bone to bone | Joints |
| Cartilage | Semi-rigid, flexible | Support with flexibility | Ear, nose, trachea |
| Bone | Hard matrix of calcium and phosphorus | Support, protection, blood cell production | Skeleton |
| Blood | Liquid connective tissue (plasma, RBCs, WBCs, platelets) | Transport of substances | Throughout body |
| Lymph | Fluid connective tissue | Immune response, transport | Lymphatic system |
Muscular Tissue
Responsible for movement. Contains contractile proteins (actin & myosin).
| Type | Control | Striations | Nucleus | Function | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Skeletal | Voluntary | Present | Multinucleated | Moves skeleton | Limbs, face, trunk |
| Smooth | Involuntary | Absent | Uninucleated | Movement of internal organs | Stomach, intestine |
| Cardiac | Involuntary | Present | Uninucleated | Rhythmic contraction | Heart |
Nervous Tissue
- Made up of neurons and neuroglial cells
- Specialized for transmission of nerve impulses
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Neuron | Basic unit; has cell body, axon, dendrites |
| Neuroglia | Supports and nourishes neurons |
Function: Coordination, response to stimuli, and communication between body parts.
3. Quick Facts
- • Parenchyma is the most common and versatile plant tissue
- • Cardiac muscle never fatigues under normal conditions
- • Neurons are the longest cells in the human body (some over 1m long)
- • Xylem transports water upwards, while phloem transports food bidirectionally
- • Epithelial tissues are avascular (no blood vessels)
Developed By Satyam Kumar
Next
Master Biology Concepts with Us!
Join Courage Library for comprehensive study materials and expert guidance.
Be a Couragian!