SSC CGL - Detailed Guide 2025
Self-Paced Course

Light and Optics
Reference: NCERT Class 10-12, Lucent GK
1. Reflection, Refraction, and Dispersion
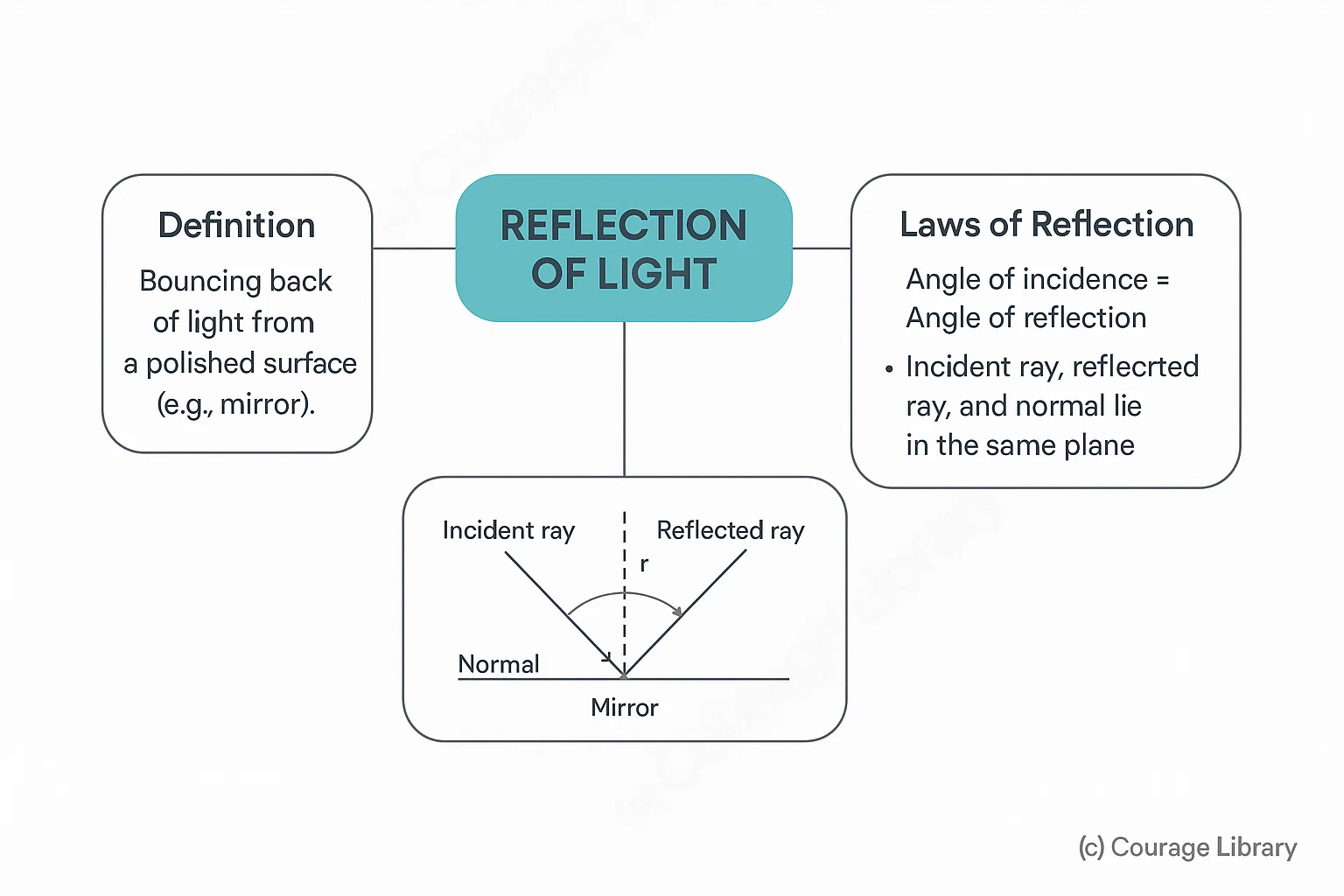
A. Reflection of Light
- Bouncing back of light from a polished surface (e.g. mirror).
- Laws of Reflection:
- Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection
- Incident ray, reflected ray, and normal lie in the same plane
| Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Regular Reflection | From smooth surface, forms clear image | Plane mirror |
| Diffused Reflection | From rough surface, forms no image | Wall, paper surface |
Plane mirror: Image is virtual, erect, laterally inverted, same size
B. Refraction of Light
- Bending of light when it passes from one medium to another (due to change in speed)
| Quantity | Formula | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Refractive Index (n) | n = Speed of light in vacuum / Speed in medium | n > 1 for denser medium |
- Light bends:
- Towards normal: from rarer to denser medium (e.g., air → glass)
- Away from normal: denser to rarer medium (glass → air)
- Critical Angle: Angle of incidence for which angle of refraction = 90°
- Total Internal Reflection (TIR): Occurs when incidence > critical angle (used in optical fibers, diamond sparkle)
C. Dispersion of Light
- Splitting of white light into its constituent colors (VIBGYOR) when passed through a prism
- Violet refracts the most; Red the least
2. Lenses and Mirrors
Mirror Formula
1/f = 1/v + 1/u
(Where f = focal length, v = image distance, u = object distance)
Lens Formula
1/f = 1/v - 1/u
(Where f = focal length, v = image distance, u = object distance)
Sign Convention: All distances measured from pole (mirror) or optical center (lens); left side negative, right side positive.
3. Human Eye and Vision Defects
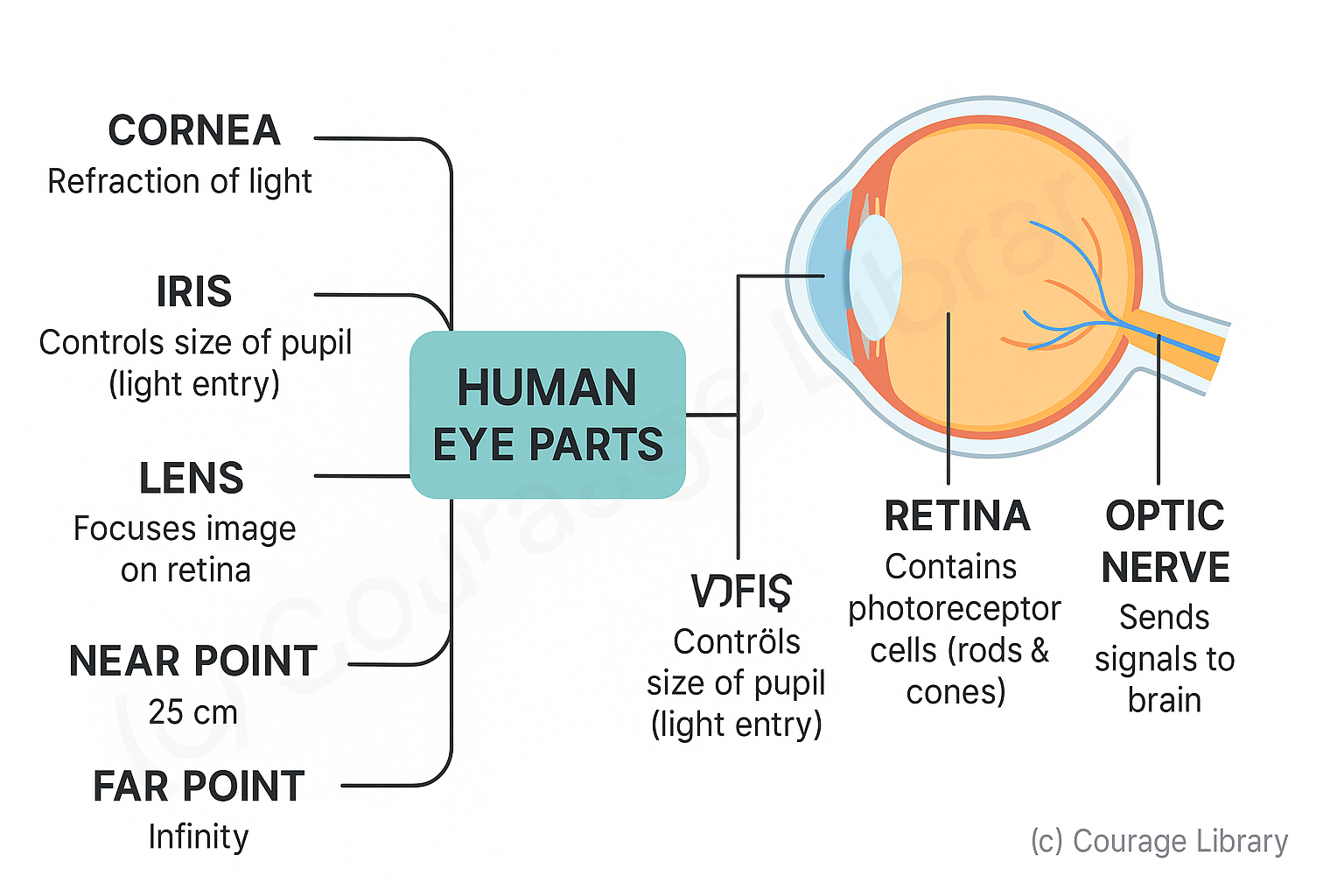
Human Eye Parts:
- Cornea: Refraction of light
- Iris: Controls size of pupil (light entry)
- Lens: Focuses image on retina
- Retina: Contains photoreceptor cells (rods & cones)
- Optic nerve: Sends signals to brain
Near point of human eye = 25 cm
Far point = Infinity
Common Vision Defects
| Defect | Cause | Correction |
|---|---|---|
| Myopia (Nearsightedness) | Eye too long or lens too curved | Concave lens |
| Hypermetropia (Farsightedness) | Eye too short or lens too flat | Convex lens |
| Presbyopia | Aging - loss of accommodation power | Bifocal lenses |
| Astigmatism | Irregular curvature of cornea/lens | Cylindrical lens |
| Cataract | Lens becomes opaque (clouding) | Surgery & artificial lens |
Master Physics Concepts with Us!
Join Courage Library for comprehensive study materials and expert guidance.
Be a Couragian!