SSC CGL - Detailed Guide 2025
Self-Paced Course

Circulatory and Excretory Systems
Reference: NCERT Class 10-12, Lucent GK
1. Circulatory System
The circulatory system is responsible for the transport of oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and waste products throughout the body.
A. Heart
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Type | Muscular organ, about the size of a fist |
| Location | In the thoracic cavity, slightly left of center |
| Chambers | 4 chambers: 2 atria (upper), 2 ventricles (lower) |
| Valves | Prevent backflow (e.g. tricuspid, bicuspid/mitral, pulmonary, aortic) |
| Beats per minute | Average: 72 bpm |
| Double Circulation | Blood passes twice through the heart in one complete cycle (systemic + pulmonary) |
Path of Blood Flow:
- Deoxygenated blood: Body → Right Atrium → Right Ventricle → Lungs
- Oxygenated blood: Lungs → Left Atrium → Left Ventricle → Body
B. Blood
| Component | Description | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Plasma | Yellow fluid (55% of blood); contains proteins, hormones | Transports nutrients, hormones |
| RBCs (Erythrocytes) | Contain hemoglobin; biconcave; no nucleus | Carry oxygen |
| WBCs (Leukocytes) | Nucleated; various types (lymphocytes, neutrophils, etc.) | Fight infection (immune defense) |
| Platelets | Cell fragments, help in blood clotting | Prevent bleeding |
Blood Groups:
| Group | Antigen on RBC | Antibody in Plasma | Can Receive From |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | A | Anti-B | A, O |
| B | B | Anti-A | B, O |
| AB (Universal Recipient) | A & B | None | A, B, AB, O |
| O (Universal Donor) | None | Anti-A, Anti-B | O |
| Rh Factor | Rh+ or Rh- | Determines + or - | Rh- can donate to Rh+, not vice versa |
C. Blood Vessels
| Type | Structure & Function | Direction of Blood Flow |
|---|---|---|
| Arteries | Thick-walled, elastic; carry oxygenated blood (except pulmonary artery) | Heart → Body |
| Veins | Thin-walled, valves present; carry deoxygenated blood (except pulmonary vein) | Body → Heart |
| Capillaries | One-cell thick; site of exchange between blood and tissues | Connect arteries to veins |
2. Excretory System
The excretory system removes nitrogenous wastes (mainly urea), excess salts, and water from the body.
A. Excretory Organs
| Organ | Function |
|---|---|
| Kidneys | Filter blood to form urine |
| Ureters | Transport urine from kidneys to urinary bladder |
| Urinary Bladder | Stores urine |
| Urethra | Removes urine from body |
| Skin (accessory) | Removes salts, water through sweat |
| Lungs (accessory) | Remove CO₂ and water vapor |
| Liver (accessory) | Converts ammonia to urea |
B. Kidney: Structure & Function
- Bean-shaped, 2 in number
- Located in the abdominal cavity (retroperitoneal)
- Each kidney contains ~1 million nephrons
- Blood enters via renal artery, filtered blood exits via renal vein
C. Nephron: The Functional Unit
| Part | Function |
|---|---|
| Bowman's Capsule | Cup-like structure that encloses glomerulus; filtration of blood |
| Glomerulus | Network of capillaries; filters small molecules from blood |
| Proximal Tubule | Reabsorption of water, glucose, ions |
| Loop of Henle | Creates concentration gradient in medulla |
| Distal Tubule | Secretion of ions and drugs |
| Collecting Duct | Collects urine and sends to ureter |
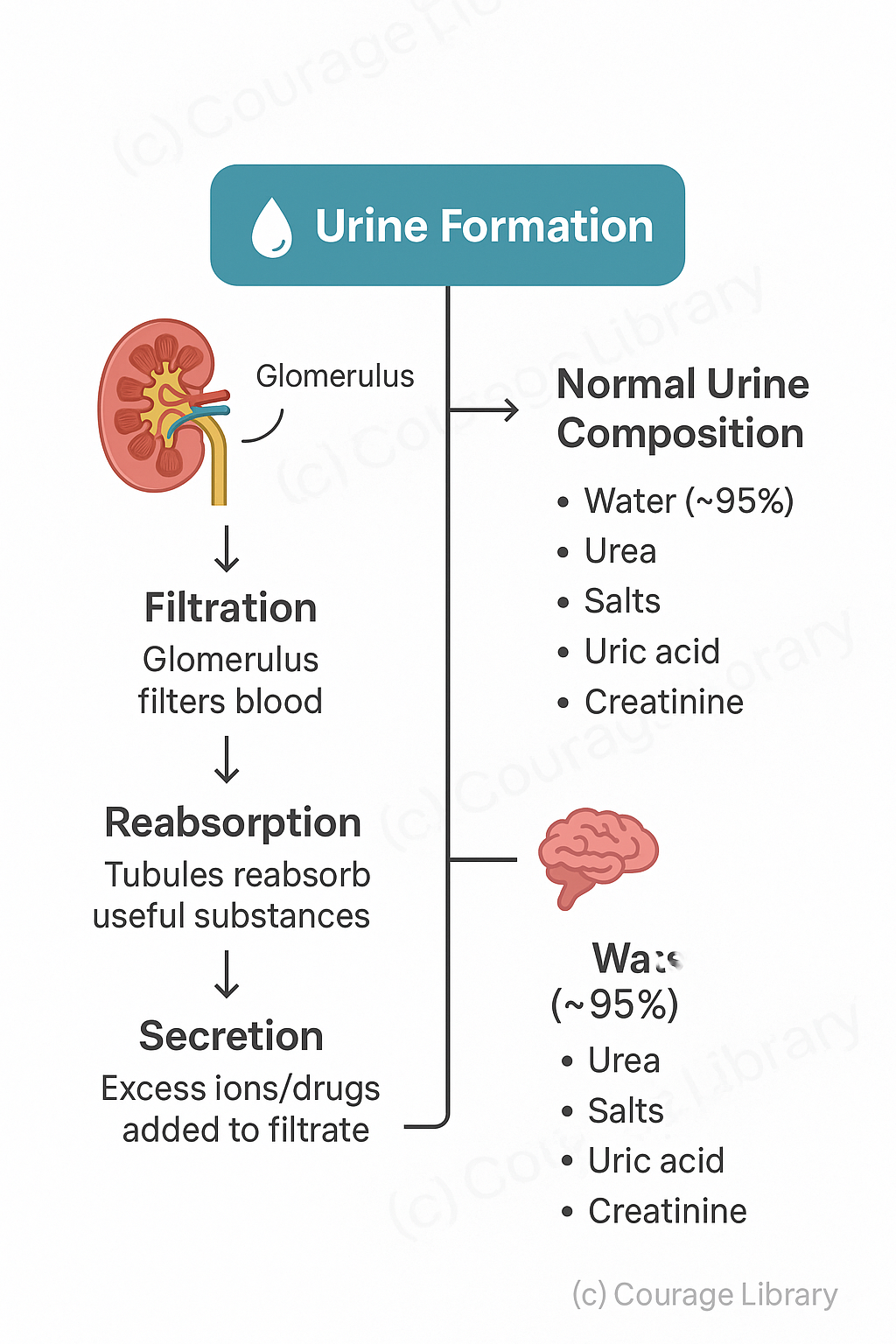
Urine Formation Steps:
- Filtration – in glomerulus (filters blood)
- Reabsorption - in tubules (useful substances reabsorbed)
- Secretion - excess ions/drugs added to filtrate
- Excretion - urine formed & passed to bladder
Normal Urine Composition:
- Water (~95%)
- Urea
- Salts
- Uric acid
- Creatinine
Quick Facts
- • The heart pumps about 70 ml of blood per beat (5 liters/minute)
- • Hemoglobin gives blood its red color and can carry 4 oxygen molecules
- • Kidneys filter 180 liters of blood daily but produce only 1-2 liters of urine
- • Dialysis is an artificial process that performs kidney functions when kidneys fail
- • The pulmonary artery is the only artery that carries deoxygenated blood
Developed By Satyam Kumar
Next
Master Biology Concepts with Us!
Join Courage Library for comprehensive study materials and expert guidance.
Be a Couragian!