SSC CGL - Detailed Guide 2025
Self-Paced Course

Periodic Table
Reference: NCERT Class 10-12, Lucent GK
1. Mendeleev and Modern Periodic Table
Mendeleev's Periodic Table (1869)
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Basis | Arranged elements in order of increasing atomic mass |
| Periodic Law | "Properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic masses." |
| Success | Left gaps for undiscovered elements like Gallium, Scandium |
| Limitation | Anomalous positions (e.g., Co & Ni), isotopes not explained |
Modern Periodic Table (Henry Moseley, 1913)
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Basis | Arranged elements by increasing atomic number (Z) |
| Periodic Law | "Properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic number." |
| Advantage | Corrects Mendeleev's issues, accommodates isotopes |
| Total Elements | 118 elements (till Og, Z = 118) |
| Structure | 7 Periods (horizontal) & 18 Groups (vertical) |
Note: Modern periodic table is based on the electron configuration of elements.
2. Groups and Periods
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Groups (Vertical columns) | 18 groups: Elements in a group have same valence electrons, hence similar chemical properties |
| Periods (Horizontal rows) | 7 periods: Number of shells increases as you move down a period |
Group 1: Alkali metals (Li, Na, K...)
Group 17: Halogens (F, Cl, Br...)
Group 18: Noble gases (He, Ne, Ar...) — inert, stable
Modern Periodic Table
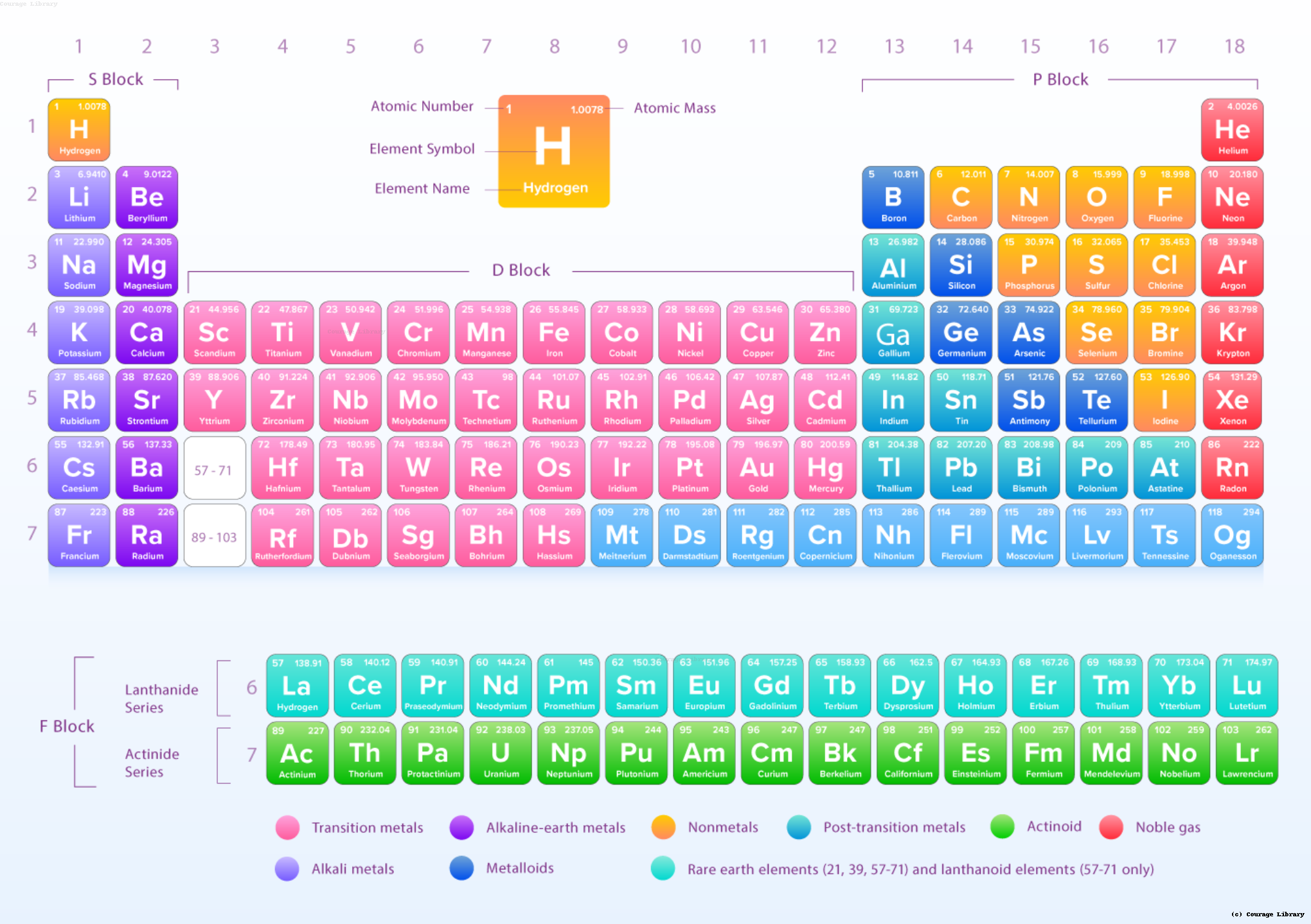
Color-coded periodic table showing groups and periods
3. Important Trends in the Periodic Table
| Trend | Across a Period (Left → Right) | Down a Group (Top → Bottom) | Reason |
|---|---|---|---|
| Atomic Size | Decreases | Increases | ↑ Nuclear charge pulls electrons inward across a period; ↑ shells down a group |
| Ionization Energy | Increases | Decreases | More energy needed to remove electron (tight hold) across; looser down the group |
| Electron Affinity | Increases (with exceptions) | Decreases | Attraction for electrons stronger across; weaker down |
| Electro - Negativity | Increases | Decreases | Greater tendency to attract shared electrons across |
Metals → On the left & center; form cations (lose electrons)
Non-metals → On the right; form anions (gain electrons)
Metalloids → Stair-step line (B, Si, As, etc.); show mixed properties
4. Blocks of the Periodic Table
| Block | Groups | Elements |
|---|---|---|
| s-block | 1–2 | Alkali & Alkaline Earth metals |
| p-block | 13–18 | Contains all types – metals, nonmetals, metalloids |
| d-block | 3–12 | Transition metals (form colored compounds) |
| f-block | Bottom row | Lanthanides and Actinides (inner-transition elements) |
5. Diagonal Relationship
Li and Mg, Be and Al show similar properties despite being in different groups.
Reason: Due to similar size and charge density.
6. Exceptions in Trends
| Property | Exception |
|---|---|
| Ionization Energy (IE) | Be > B and N > O |
| Electron Affinity (EA) | Noble gases (EA ≈ 0), Nitrogen has low EA due to half-filled p-orbitals |
| Electronegativity (EN) | Noble gases are not assigned EN due to inert nature |
SSC might ask: "Why is nitrogen's electron affinity less than
carbon's?"
Answer: Due to nitrogen's stable half-filled p-orbital configuration.
7. Important Extremes in Periodic Table
| Property | Element |
|---|---|
| Most electronegative | Fluorine (F) |
| Most electropositive | Cesium (Cs) / Francium (Fr) |
| Smallest atom | Helium (He) |
| Largest atom | Francium (Fr) |
| Highest Ionization Energy | Helium (He) |
| Most metallic | Francium (Fr) |
| Most reactive non-metal | Fluorine (F) |
| Most reactive metal | Francium (Fr) |
Fast Recall for MCQs
- • 118 known elements
- • Transition metals form complex compounds and show variable oxidation states
- • Noble gases have zero valency
- • Period 6 contains Lanthanides (14 elements)
- • Atomic number = number of protons = number of electrons (in neutral atom)
- • Group 1 elements are called alkali metals (except Hydrogen)
- • Group 2 elements are called alkaline earth metals
Quick Facts
- • Hydrogen is unique — it can be placed in both Group 1 and Group 17
- • Lanthanides and Actinides are placed separately below the main table
- • Francium (Fr) is the most reactive metal, while Fluorine (F) is the most reactive non-metal
- • Period 1 has only 2 elements (H and He), while Period 6 has 32 elements
- • Dmitri Mendeleev predicted properties of undiscovered elements with remarkable accuracy
Master Chemistry Concepts with Us!
Join Courage Library for comprehensive study materials and expert guidance.
Be a Couragian!